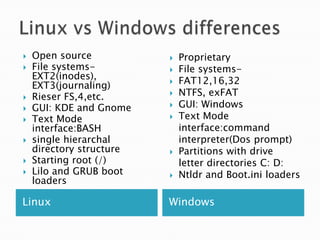
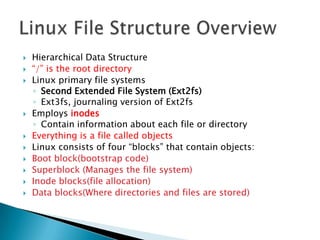
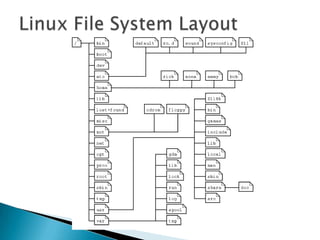
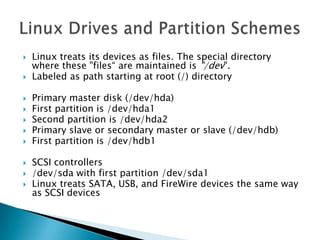
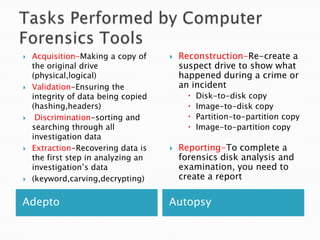
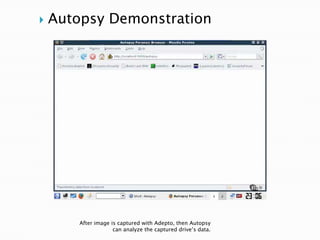
Linux is a freely distributed open source operating system similar to Unix. It was developed by Linus Torvalds and has become widely used by companies, academics, and individuals due to its free source code and ability to scale across systems. Helix is a Linux distribution tailored for computer forensics that contains tools like Adepto for acquiring forensic images and Autopsy for analyzing the images to extract evidence from investigations.