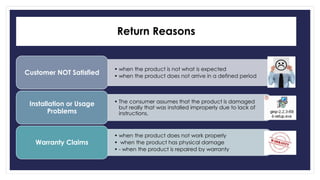
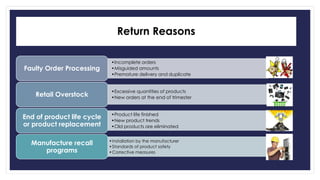
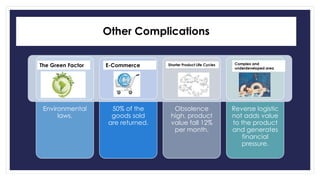
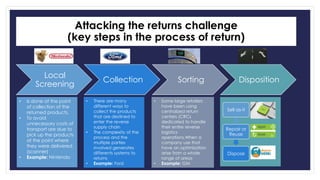
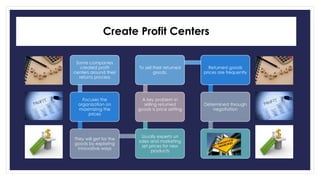
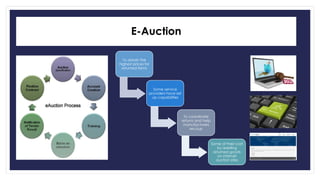
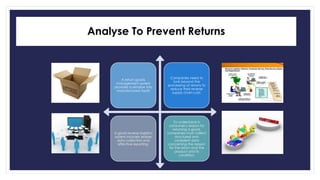
Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from the point of consumption back to the point of origin for recapturing value or proper disposal. It includes processing returned merchandise for reasons such as damage, product obsolescence, warranty claims, faulty orders, or end of product life cycles. Successful reverse logistics requires collecting return information, segmenting forward and reverse supply chains, implementing information technology, analyzing return reasons to prevent future returns, and potentially outsourcing return processing.