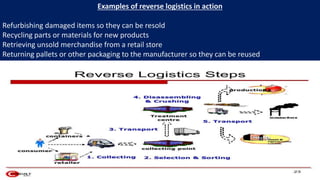
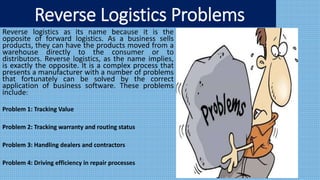
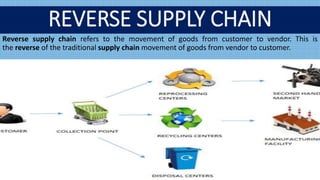
Reverse logistics involves the set of activities conducted after a product sale to recapture value and end the product's lifecycle. This typically includes returning products to manufacturers for refurbishing, recycling, or other purposes. Common examples are refurbishing damaged items, recycling materials, and returning unsold merchandise. Products are returned for reasons like customer dissatisfaction, defects, obsolescence, or overstock. Managing returns effectively requires strategies like optimizing return processes with data. Benefits of effective reverse logistics include improved customer service, sustainability, and cost reductions.