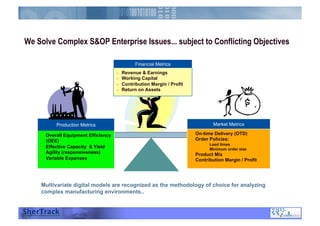
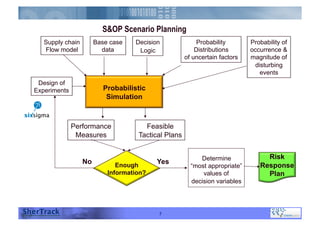
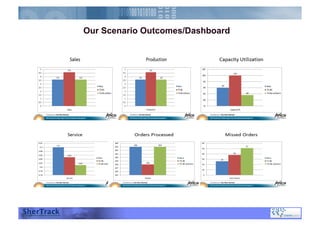
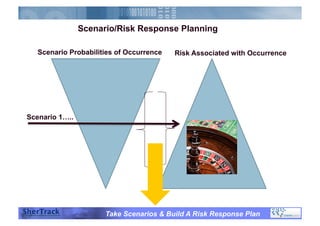
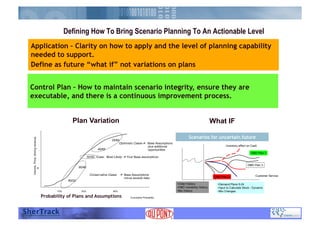
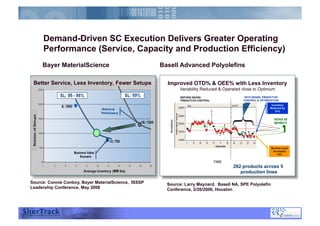
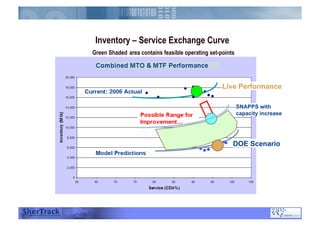
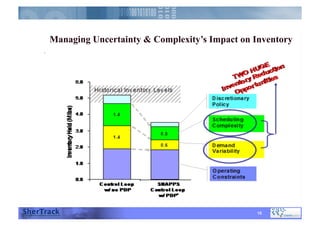
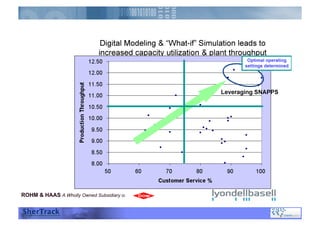
This document discusses how companies can improve their sales and operations planning (S&OP) processes through predictive analytics, scenario planning, and risk management. It recommends that companies use digital modeling, simulation, and probabilistic predictive analytics to evaluate different scenarios and supply chain designs without experimenting on live operations. Incorporating risk management into S&OP allows companies to develop response plans for uncertain events and improve long-term sustainability and competitive advantage.