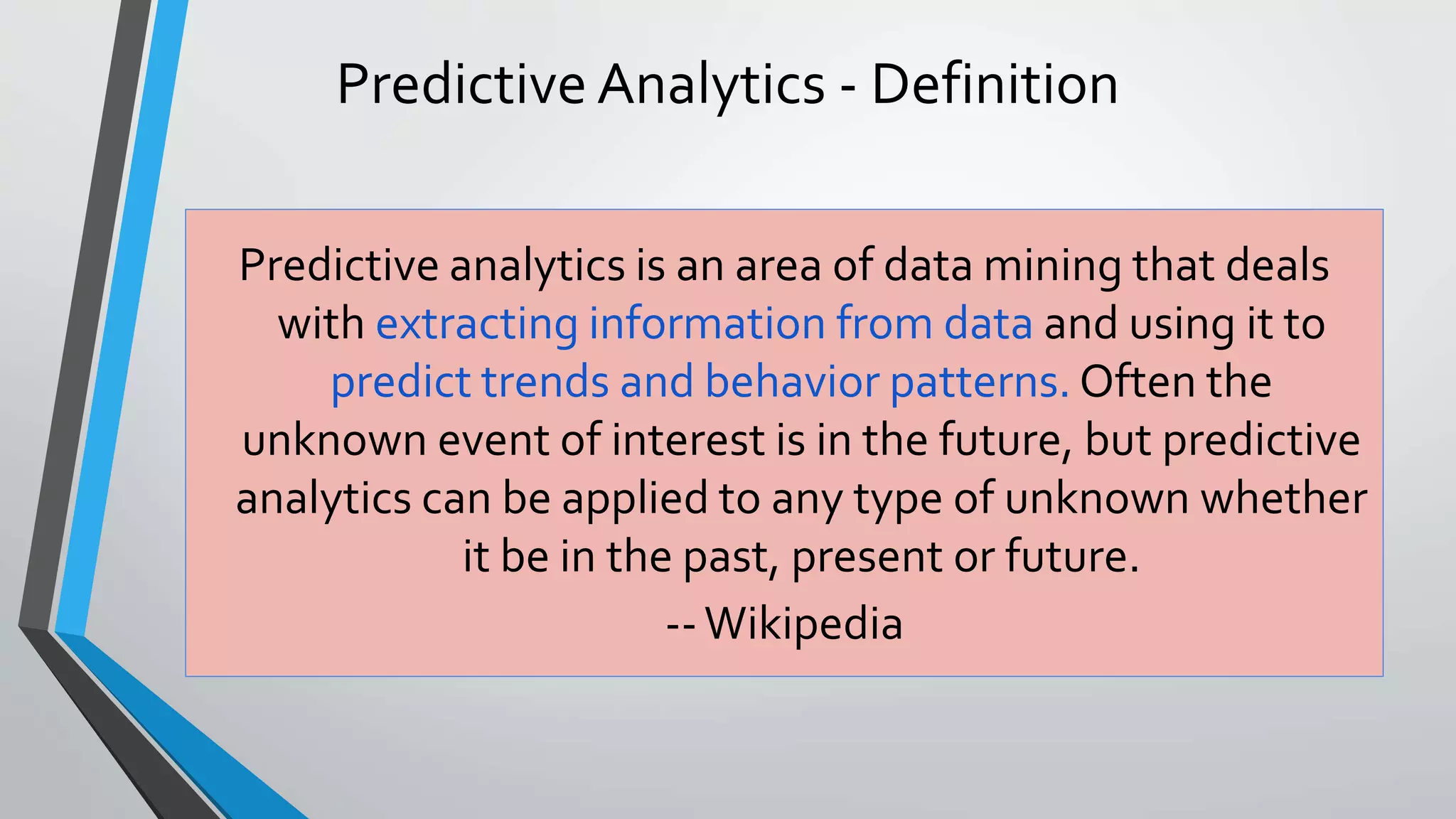
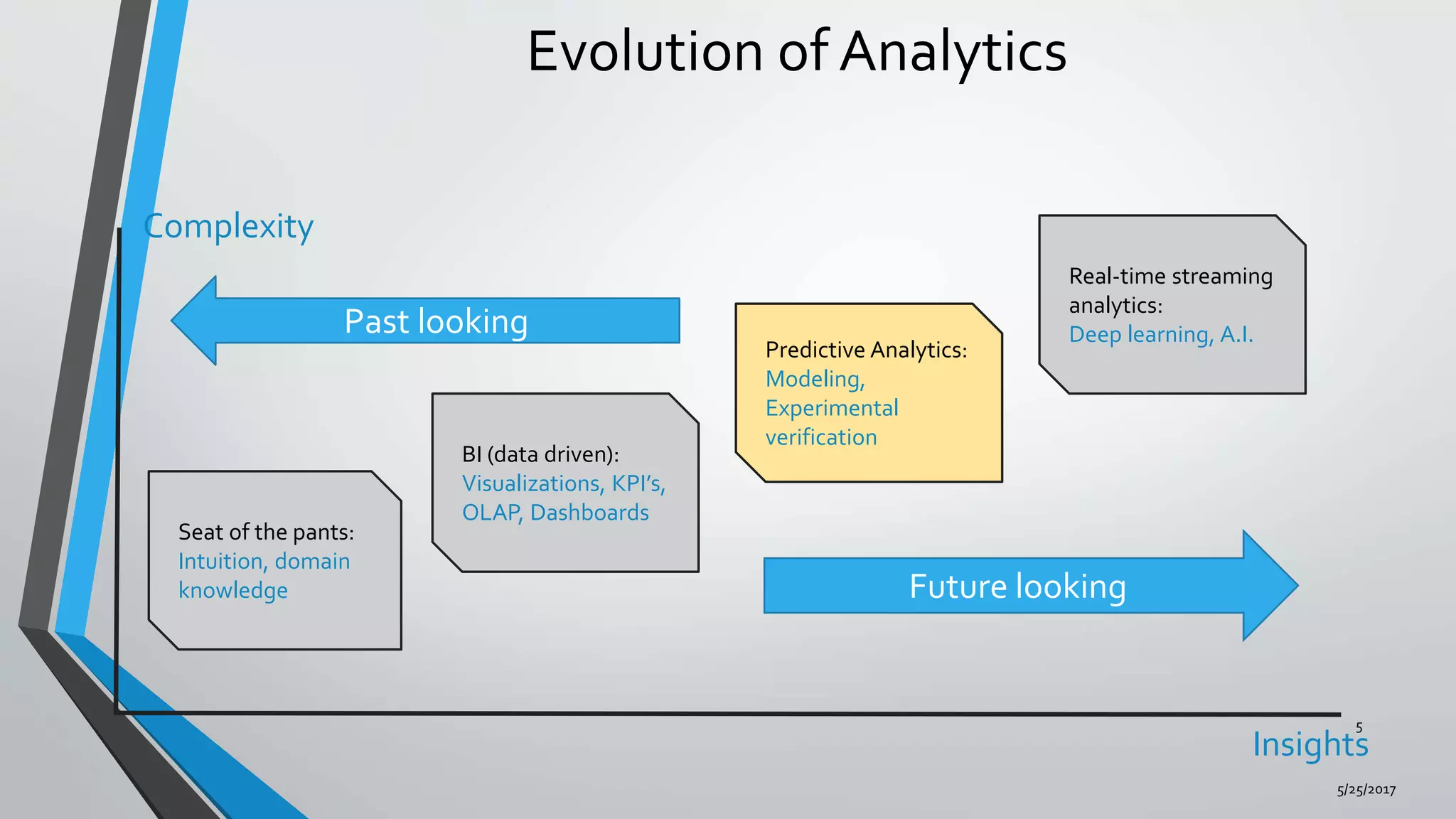
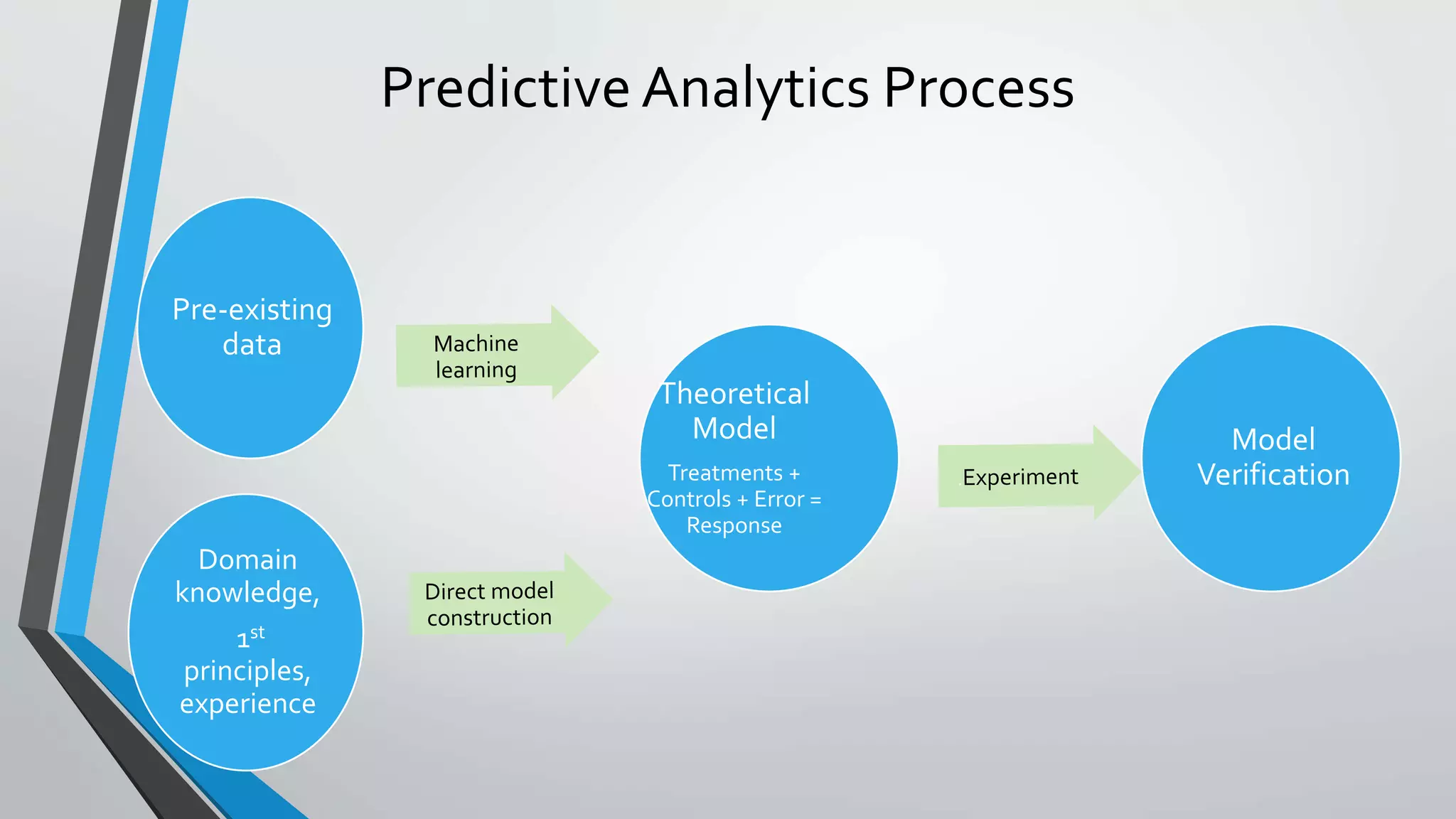
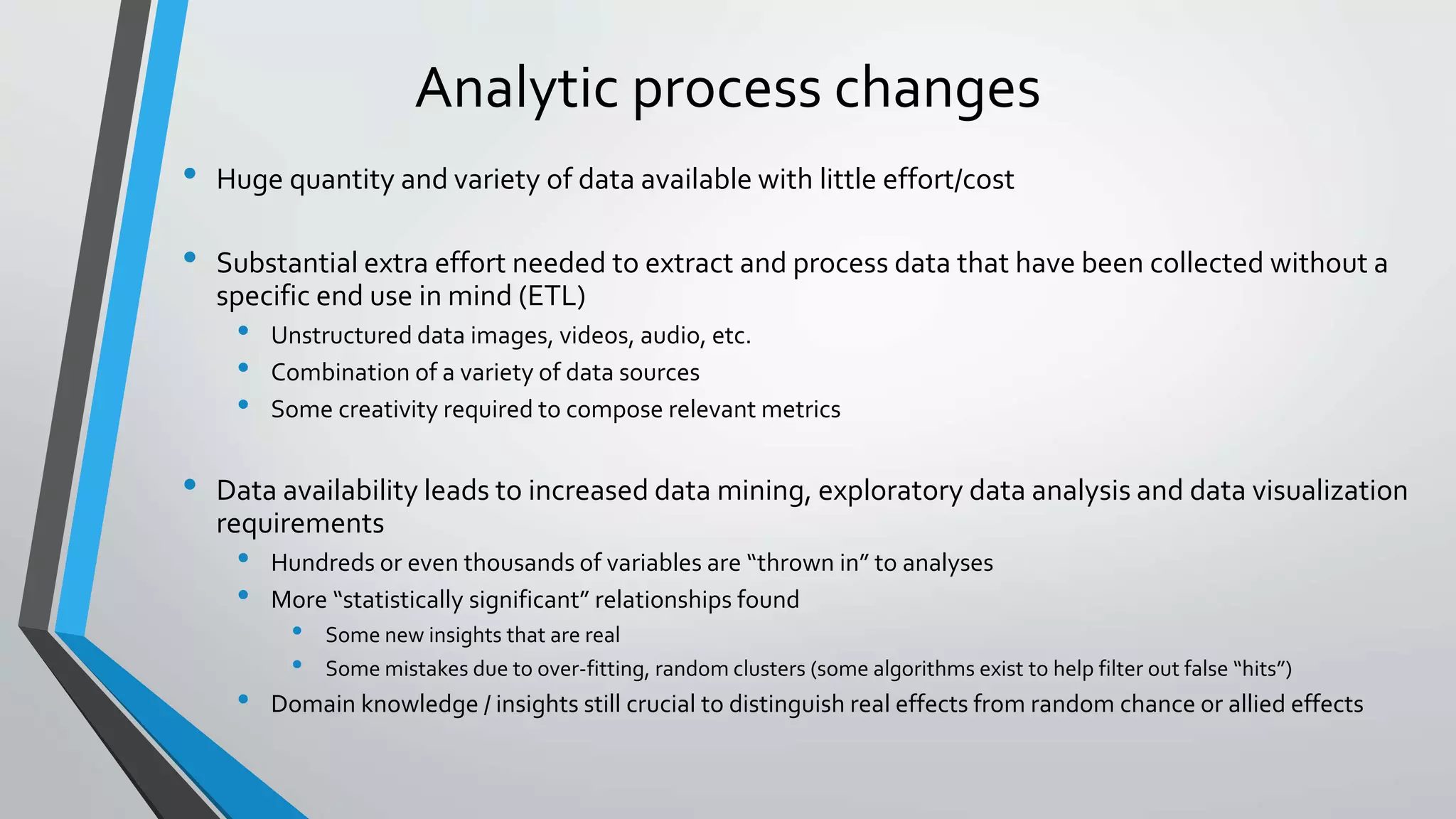
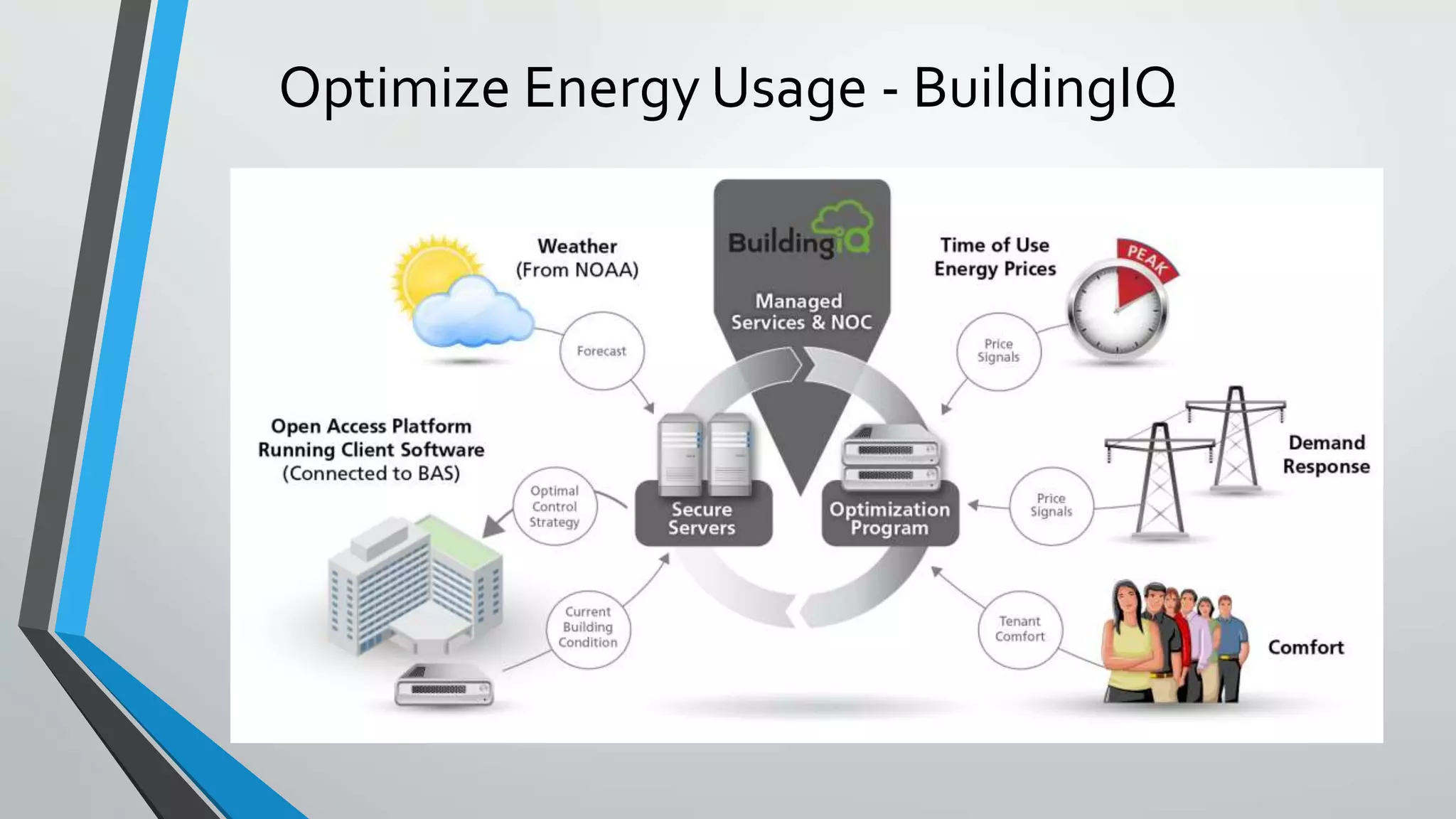
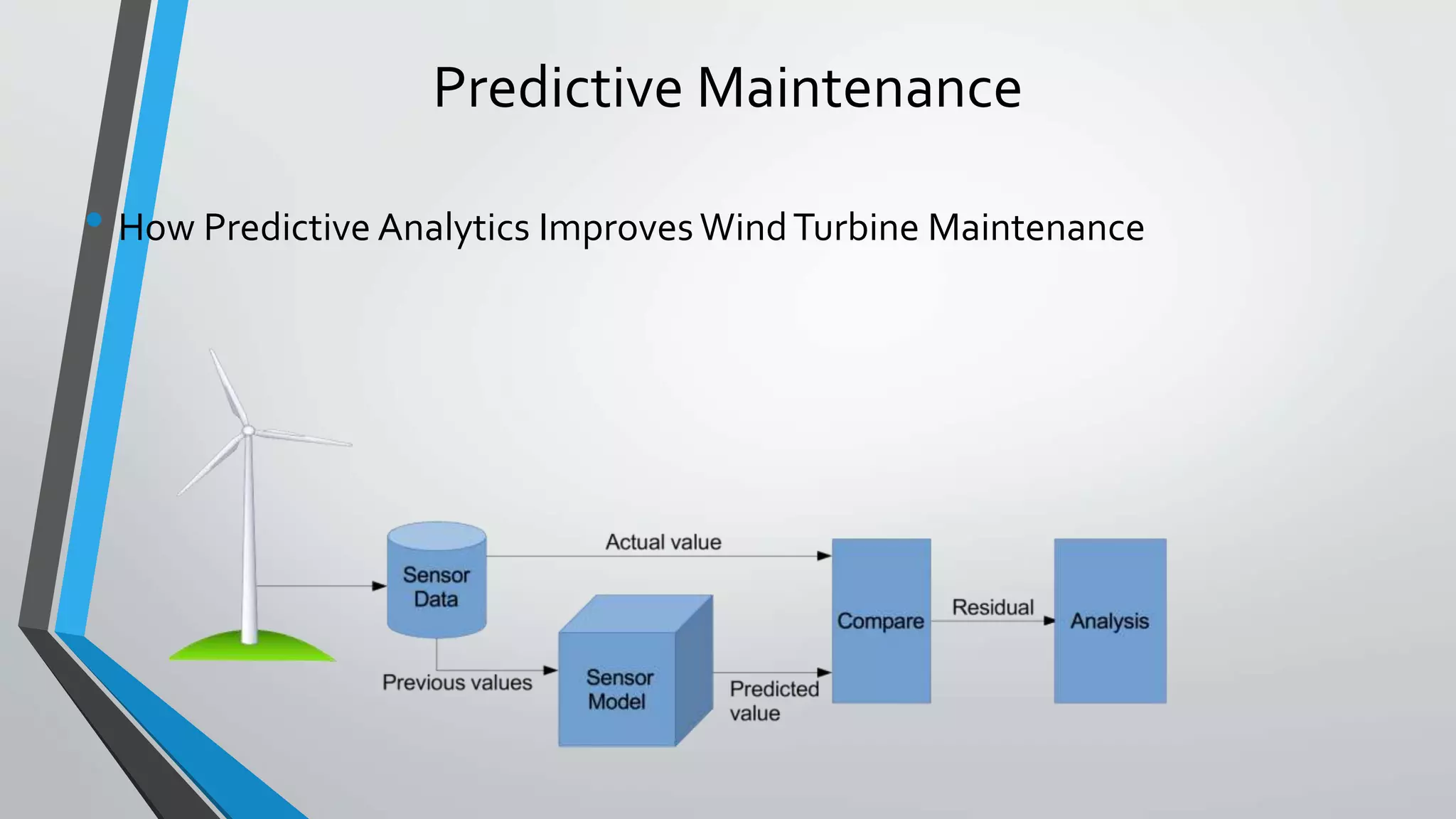
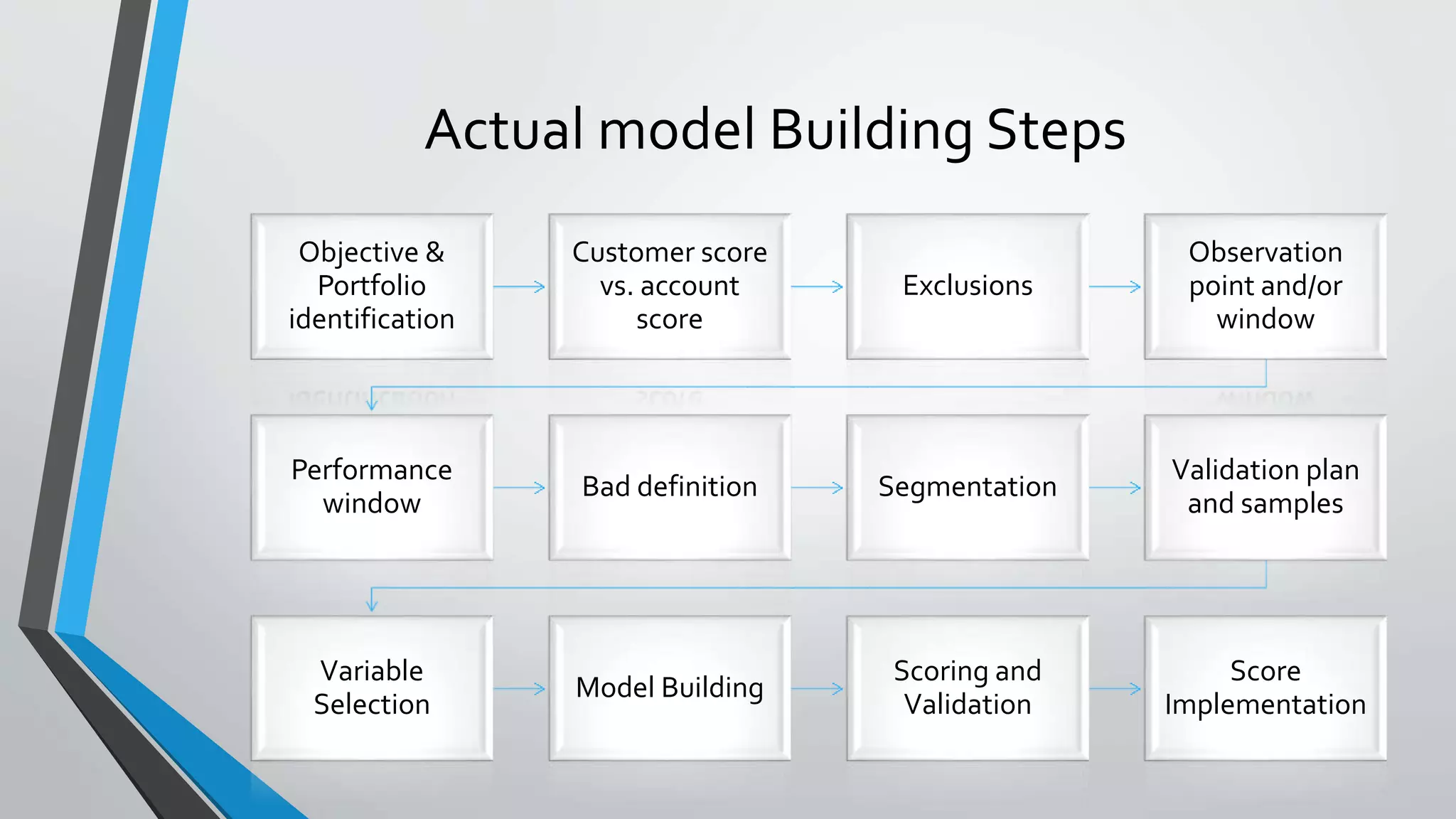
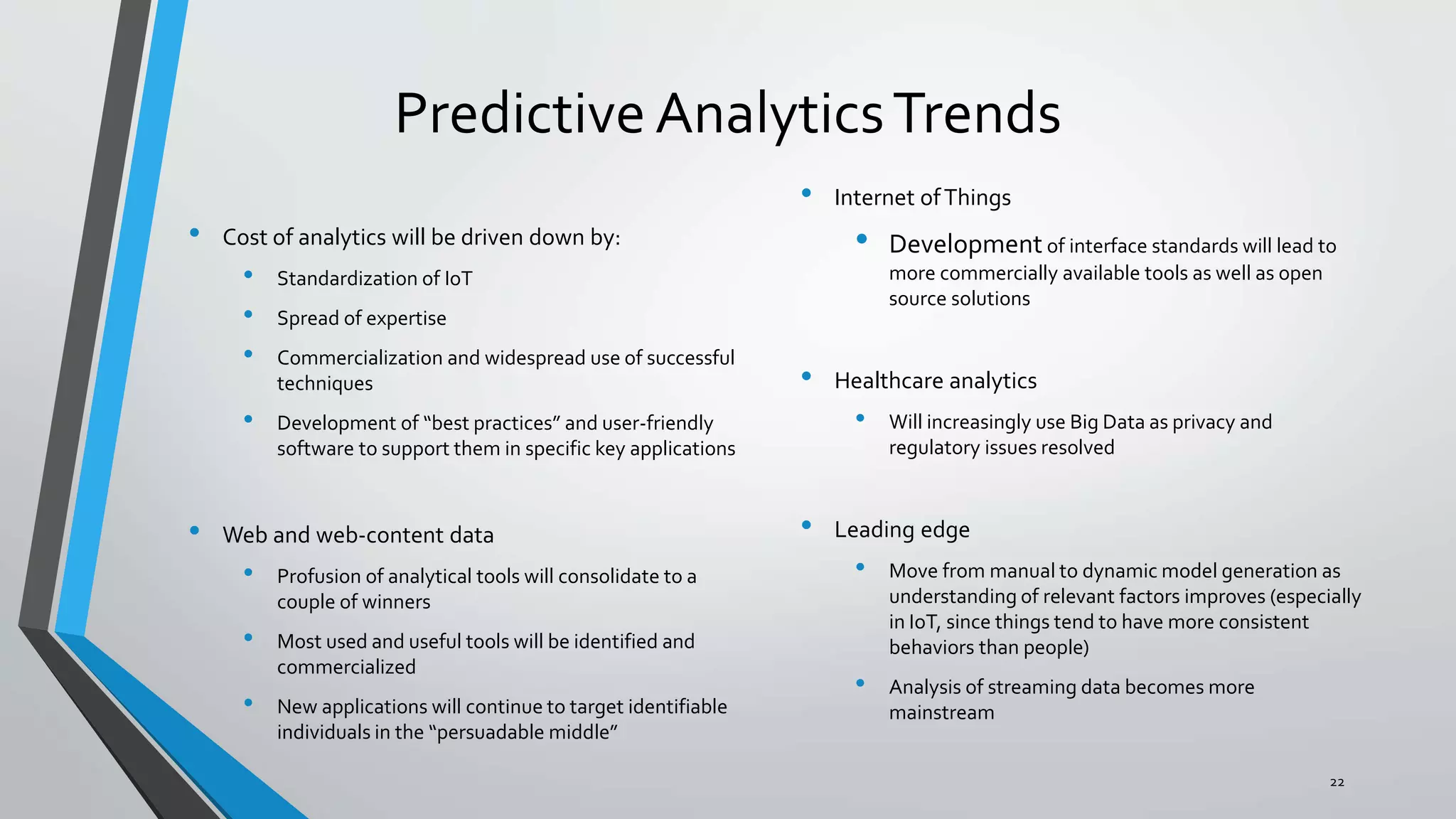
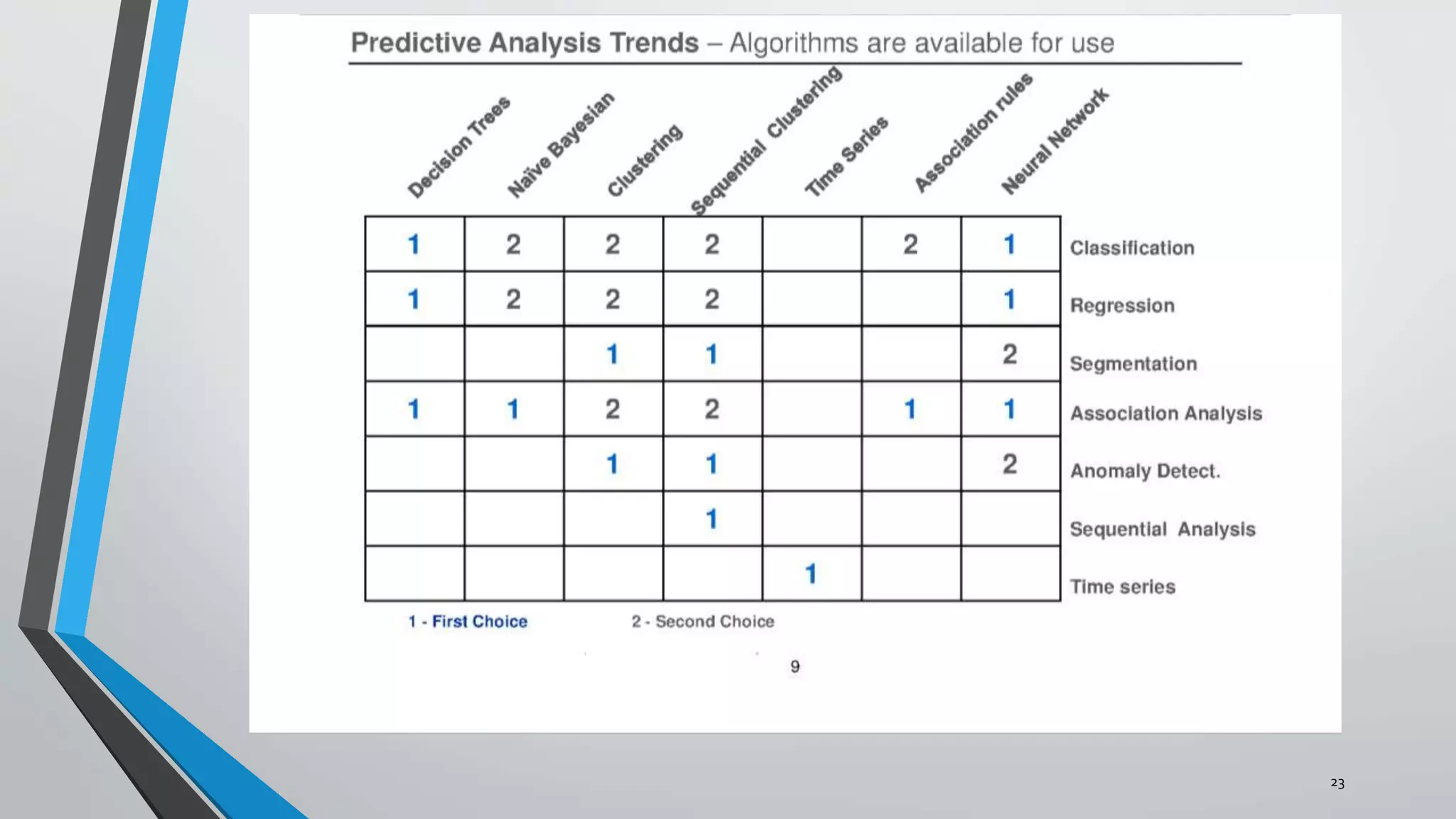
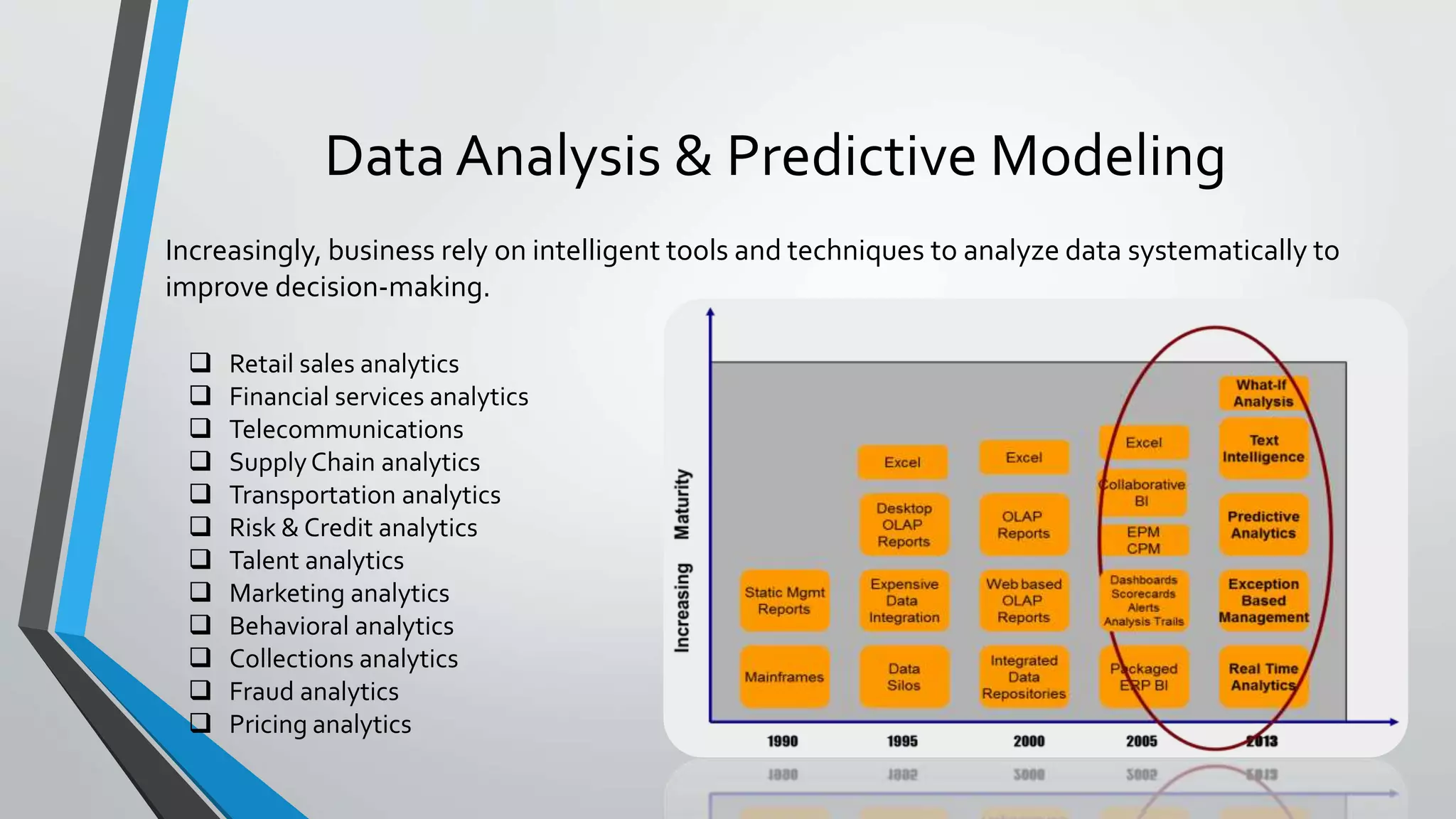
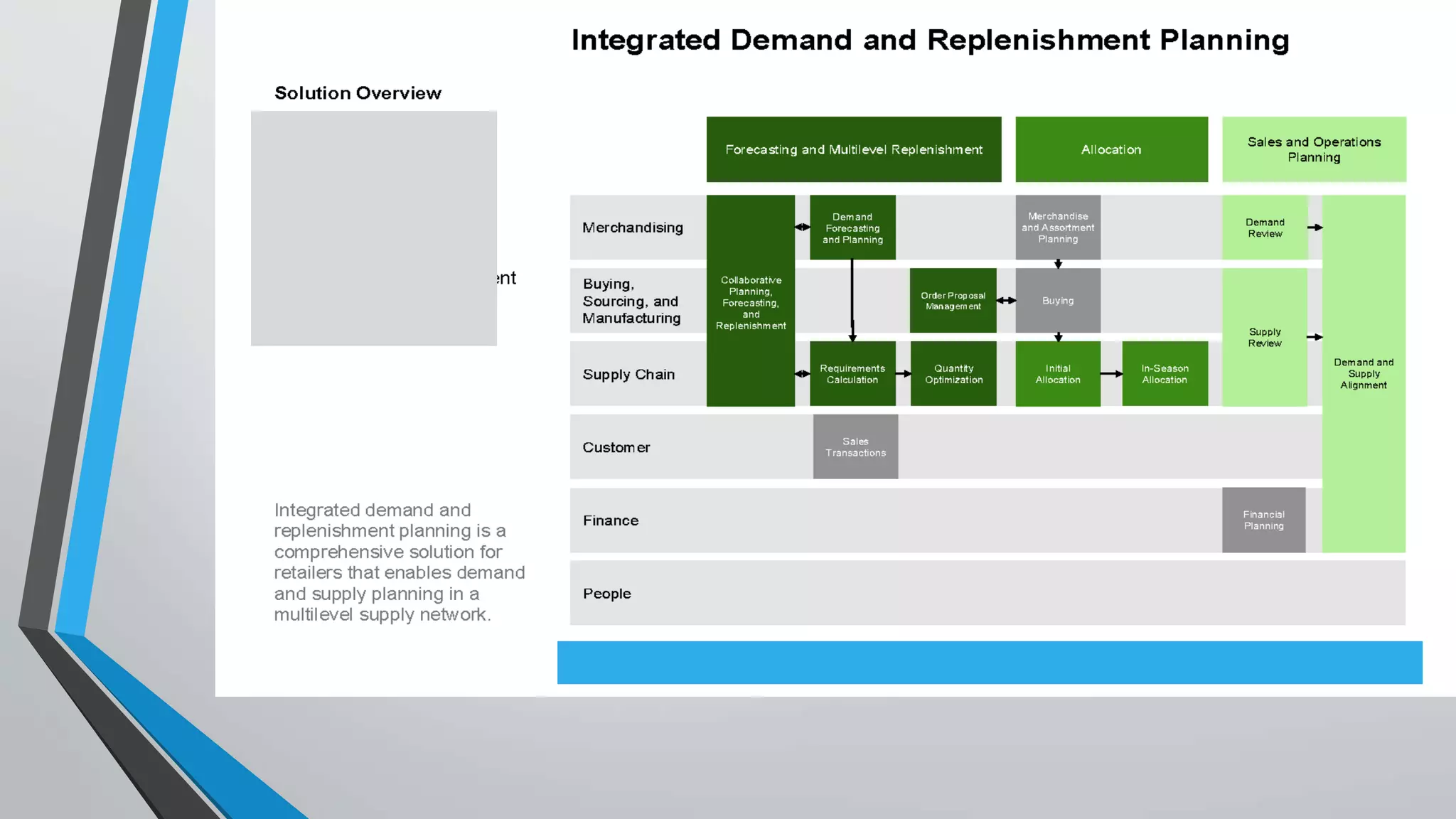
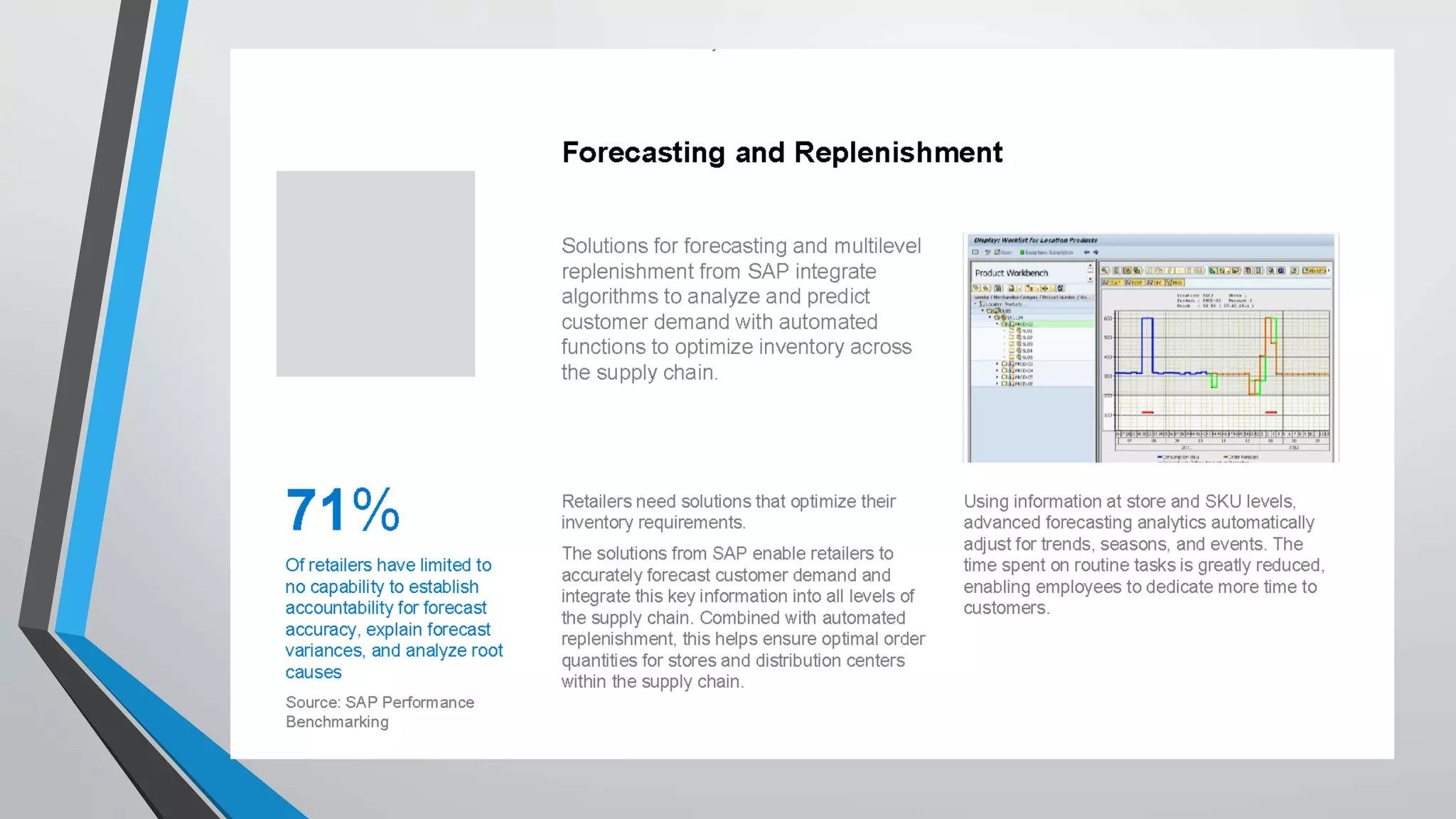
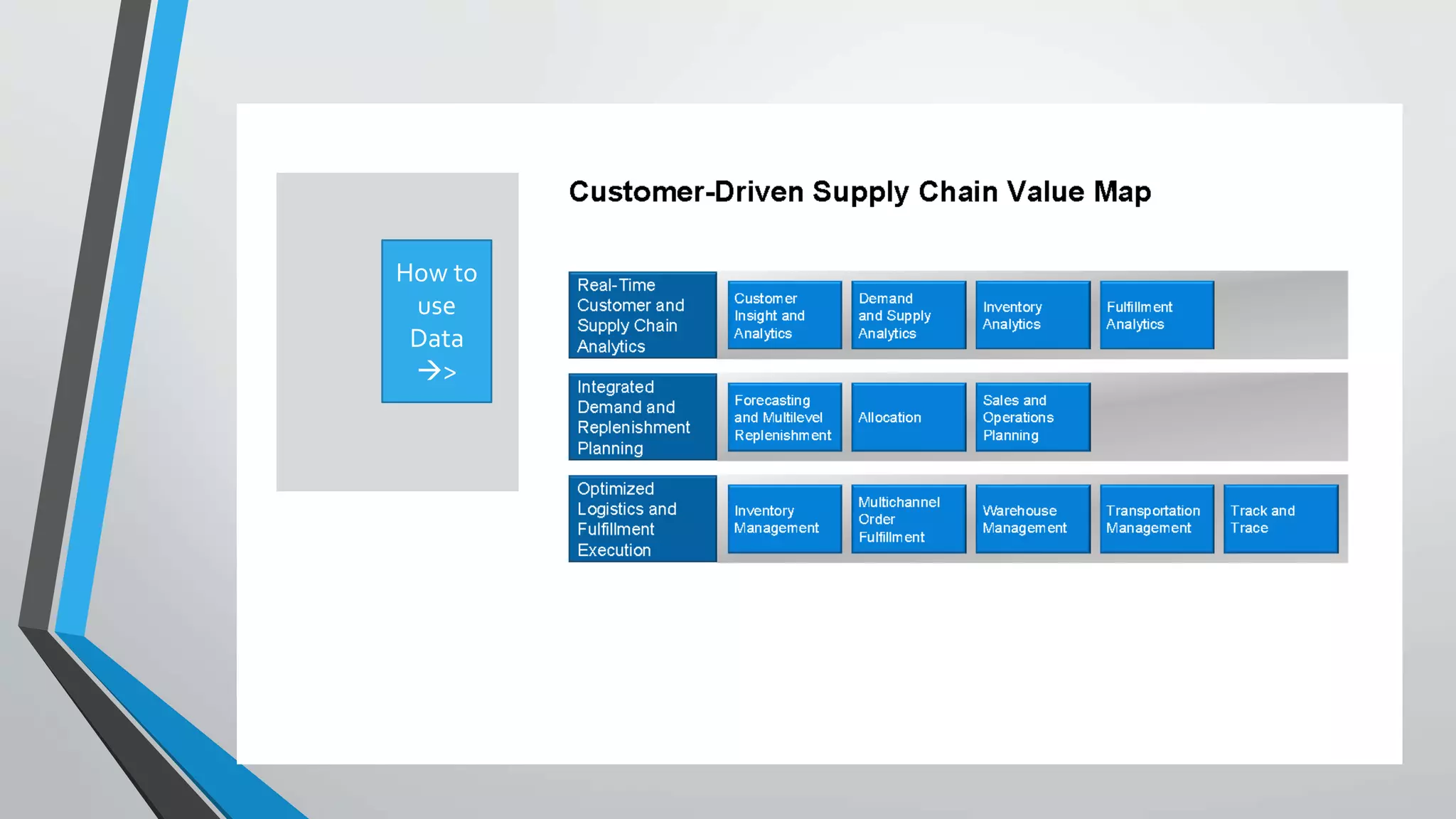
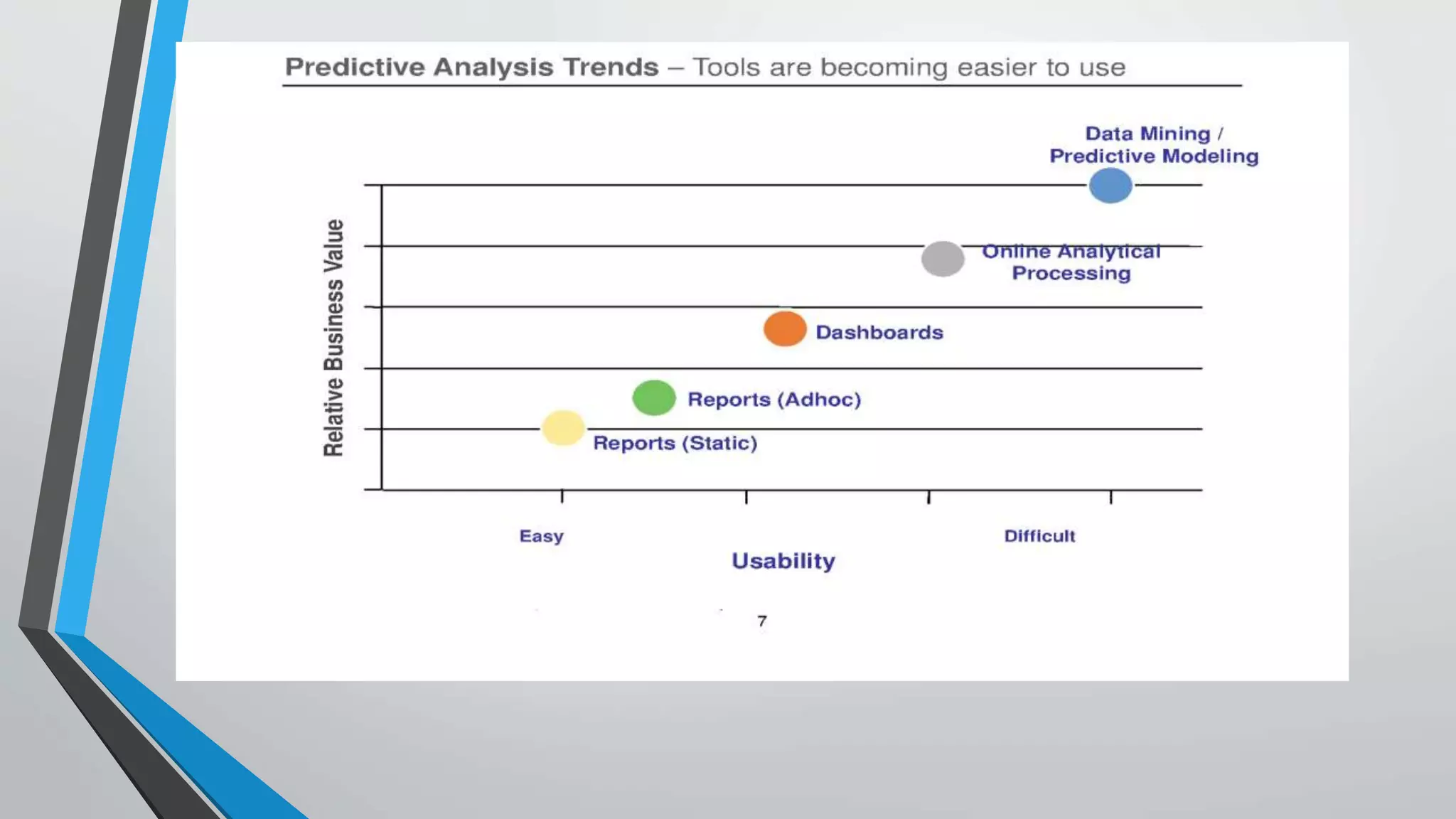
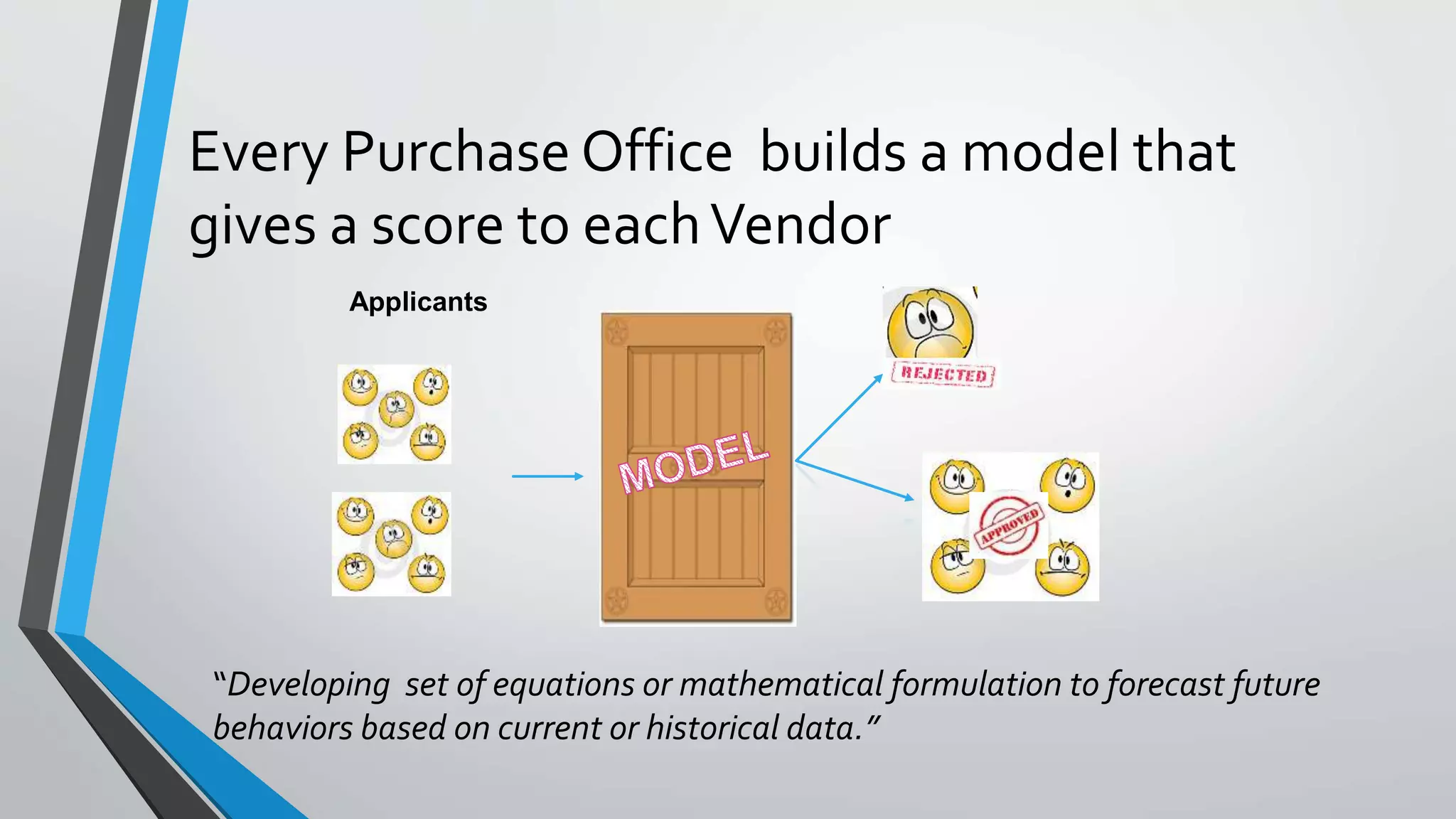
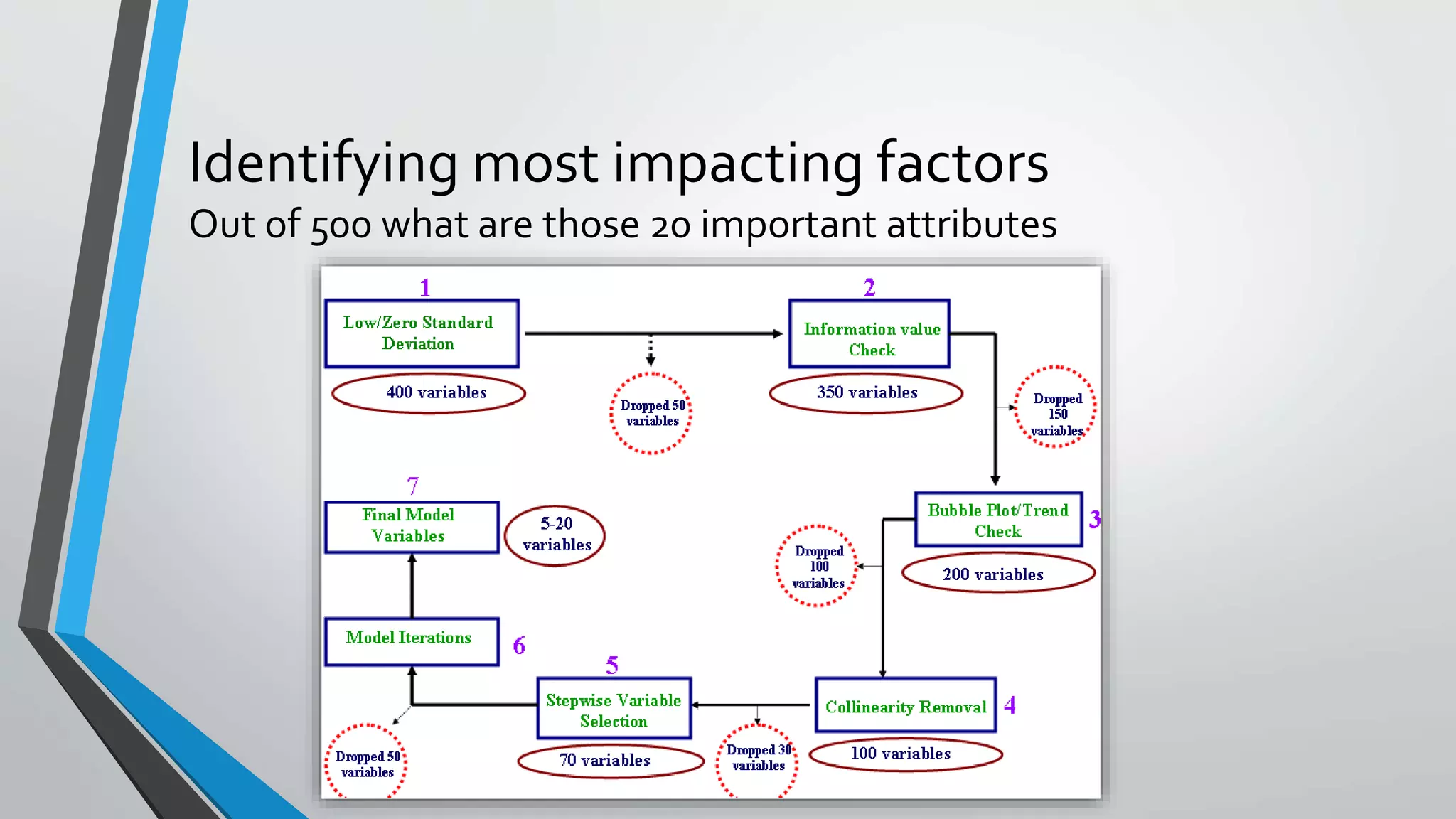
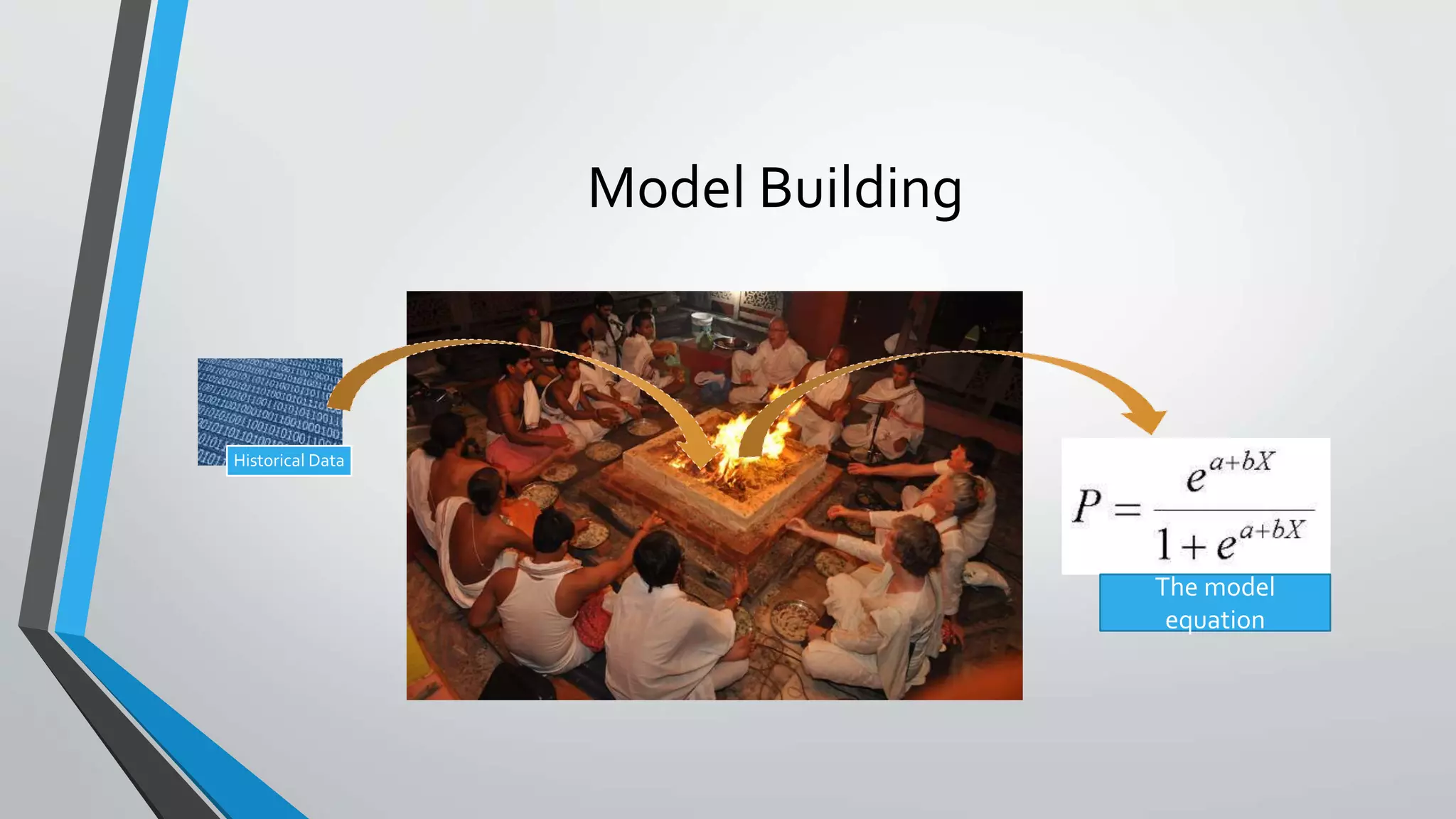
Predictive analytics can help reduce volatility and improve decision making in procurement processes. It allows understanding of future costs, demand, and supply to overcome challenges. Predictive models analyze past data and behaviors to forecast trends and outcomes. As data sources like IoT sensors expand, predictive analytics is increasingly used for applications like manufacturing process improvement, predictive maintenance of equipment, and optimizing building energy usage.