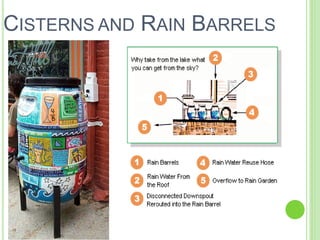
The document discusses green infrastructure, defined as an interconnected network of green spaces that includes natural areas, conservation lands, and protected open spaces, which are managed for their ecological value and human benefits. It highlights various components such as storm water green streets, green roofs, rain gardens, and subsurface detention systems, emphasizing their role in managing storm water and providing ecological advantages. The benefits of implementing green infrastructure include reduced storm water runoff, enhanced groundwater recharge, improved air quality, and increased land values.