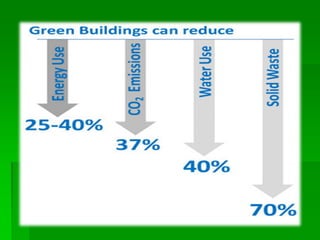
The document discusses green buildings and their benefits. It defines green buildings as structures that are environmentally responsible and efficient in their energy, water, and materials use over the lifetime of the building. Green buildings can help reduce environmental impacts, protect health, and lower costs. They incorporate sustainable materials and efficient systems to lessen pollution and resource usage. The document outlines some key characteristics of green buildings and sustainable materials. It also describes various benefits of green buildings, such as environmental, economic, and social advantages.