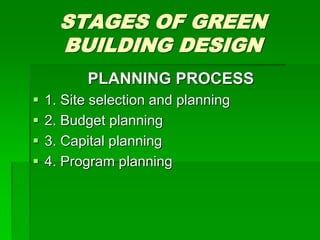
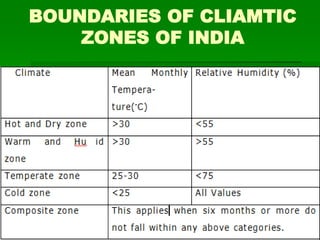
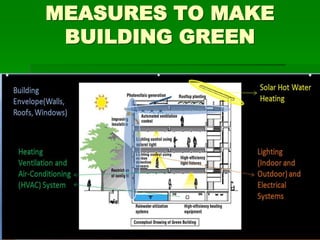
The document discusses the concept of green buildings, emphasizing their role in increasing efficiency in energy, water, and materials usage while protecting human health and the environment. It highlights various strategies for designing and constructing green buildings, including site selection, energy efficiency, and sustainable materials, along with the economic, environmental, and social benefits they provide. The conclusion stresses the importance of integrating sustainable practices in building projects to address issues like water scarcity, energy crises, and climate change.