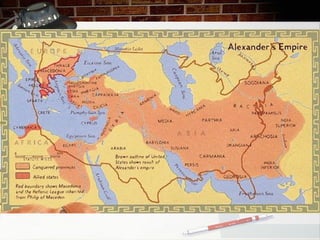
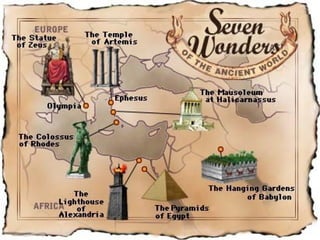
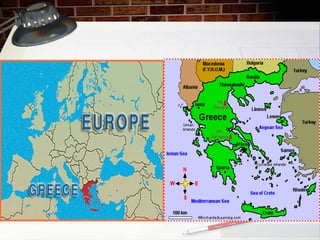
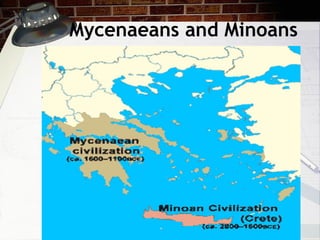
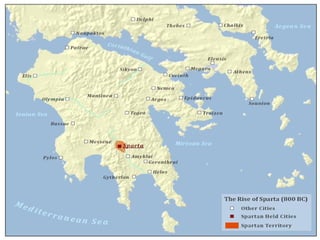
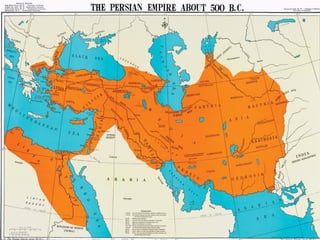
This document provides an overview of ancient Greece from 2000 BC to 300 BC. It discusses the rise and fall of the Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations, followed by a Greek Dark Age. The development of city-states and different forms of government are examined. Key events like the Trojan War, Persian Wars, and battles of Marathon, Thermopylae and Salamis are summarized. The roles of important figures like Homer and Spartan culture are also highlighted. Geography played a large role in shaping Greek civilization and limiting its population size.