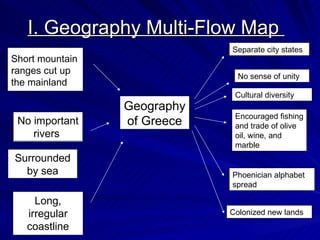
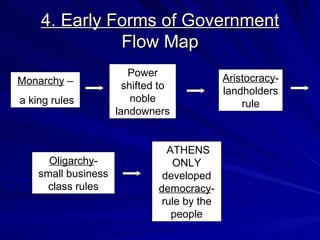
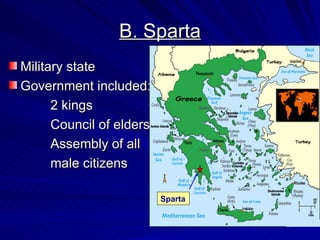
The document provides an overview of Greek history from 1750 BCE to 133 BCE. It describes Greece's geography of mountain ranges and coastlines that divided it into separate city-states. Early Greek civilizations like the Minoans and Mycenaeans dominated trade in the Aegean Sea. Homer wrote the epic poems The Iliad and The Odyssey. Warfare changed with the use of iron and the phalanx formation. Athens developed as the first democracy while Sparta was a strict military state. The Persian Wars and Peloponnesian War were two major conflicts between Greek city-states and outside forces.