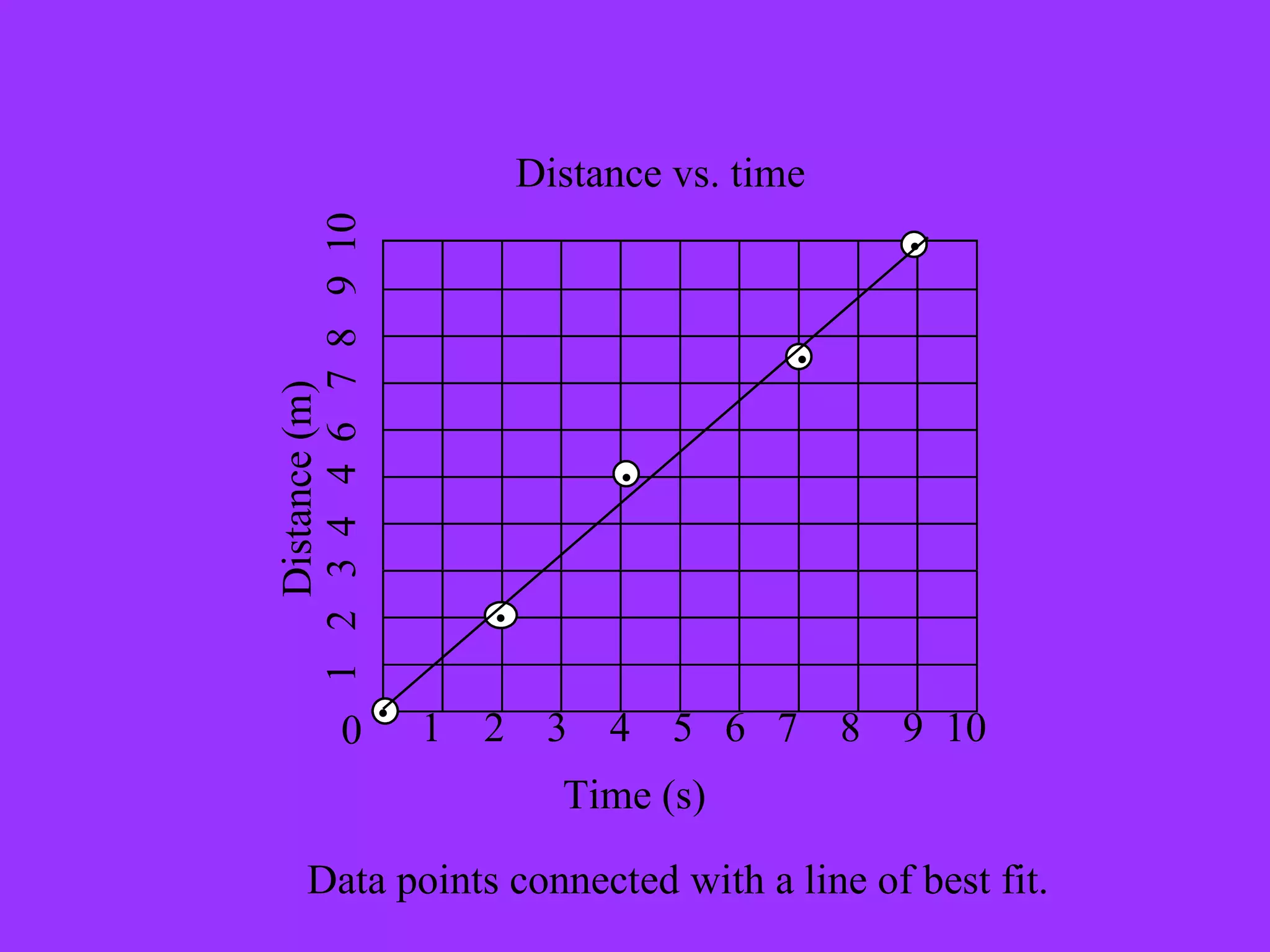
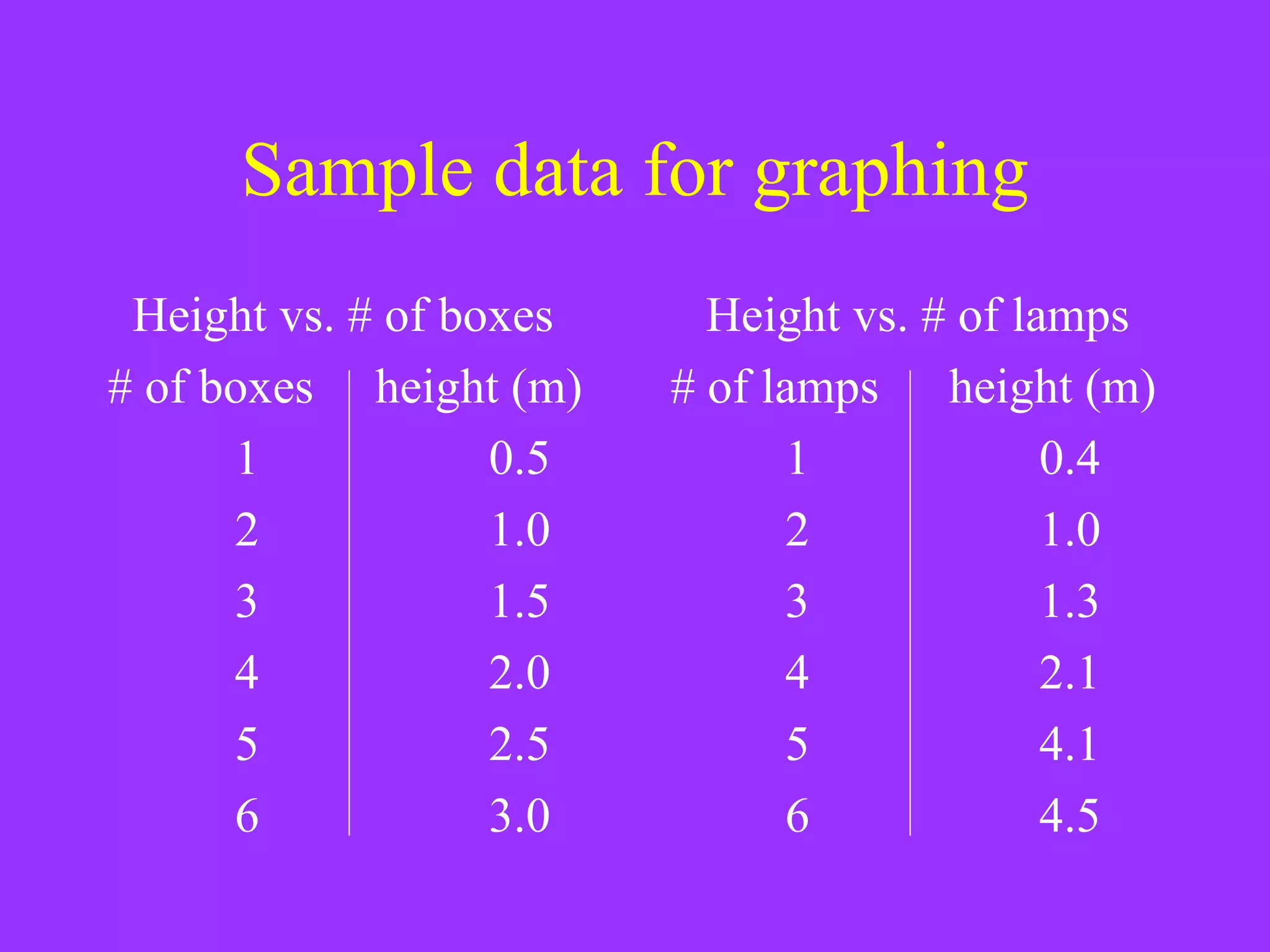
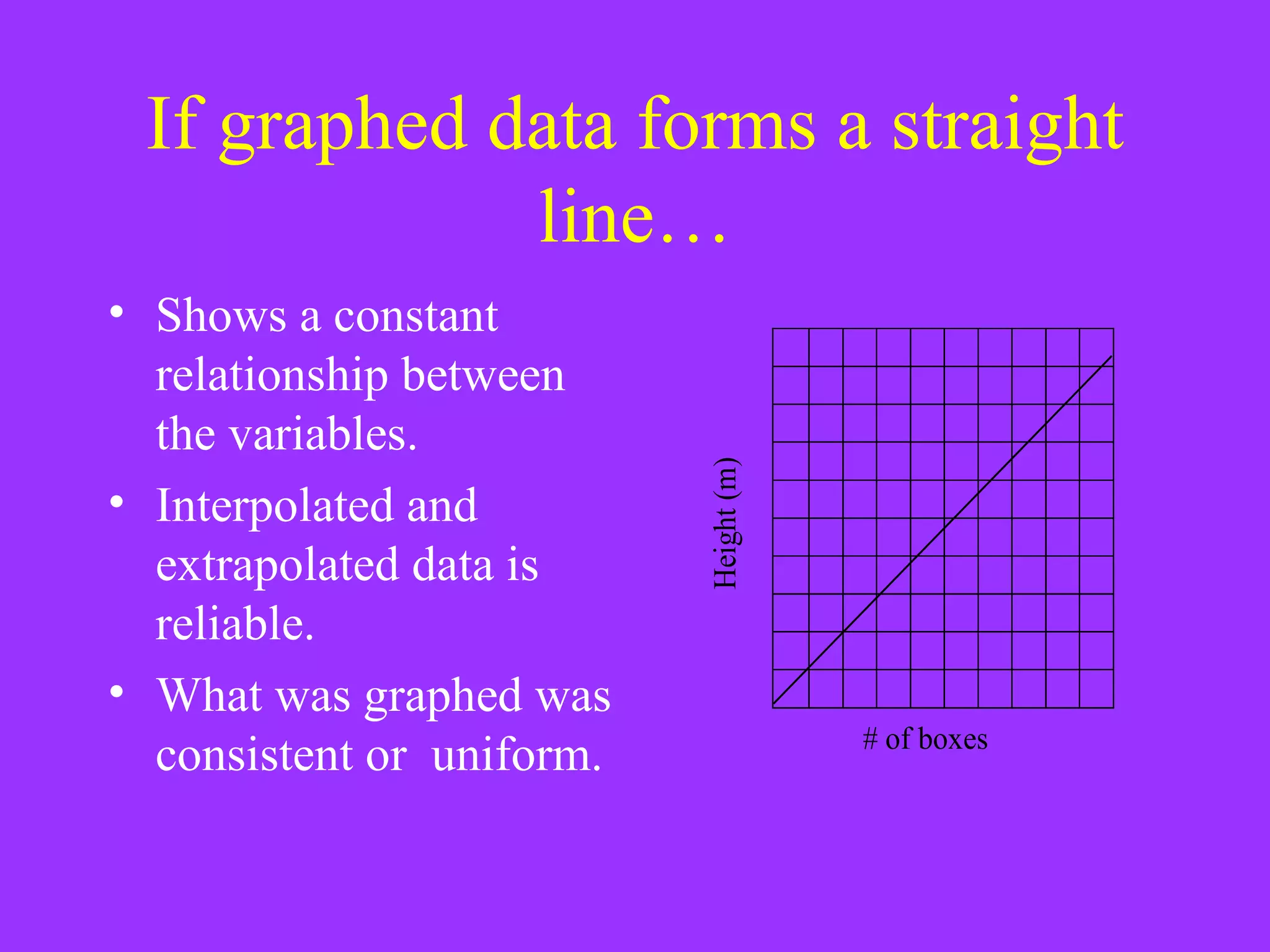
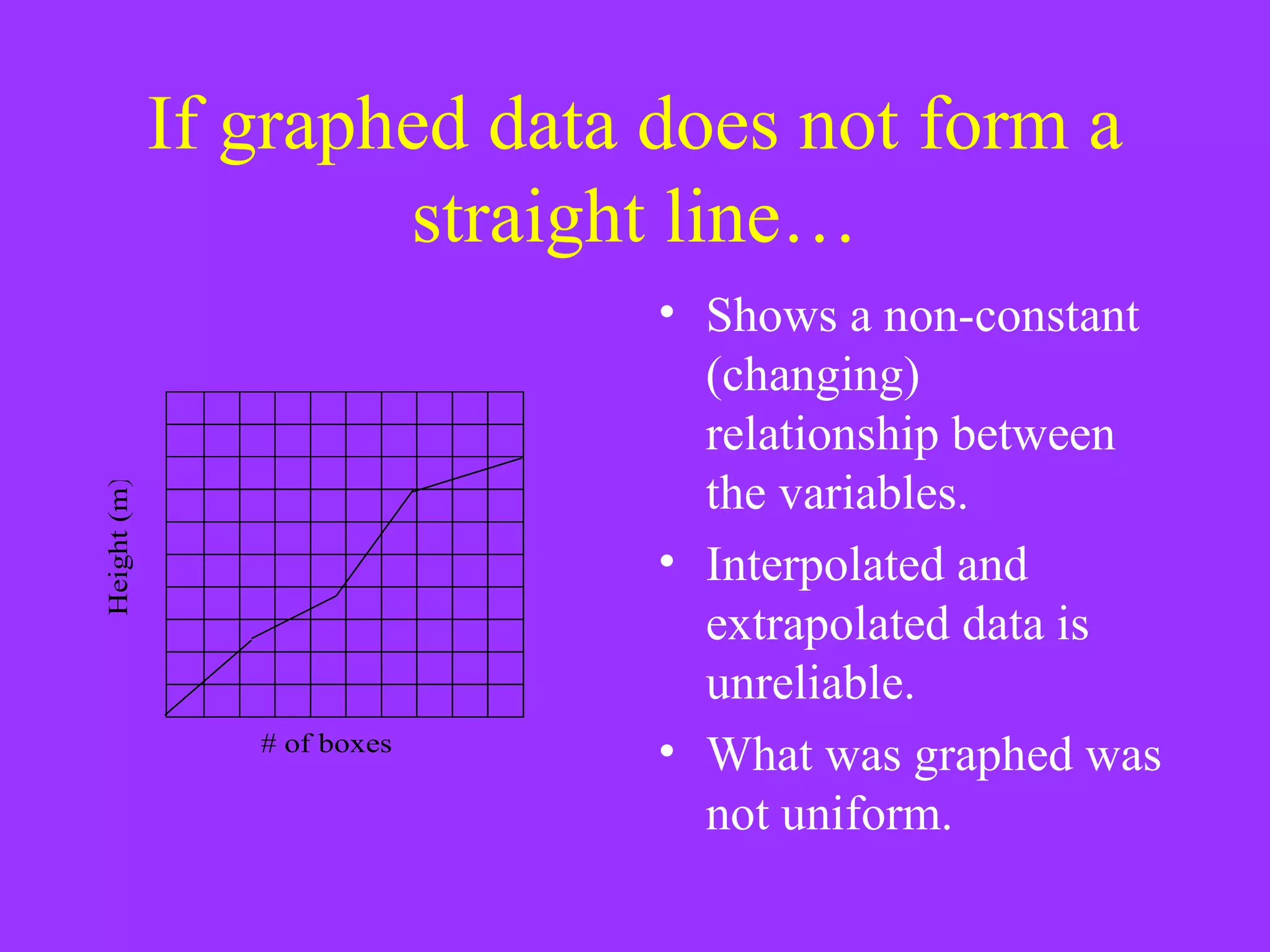
The document discusses key concepts related to graphing data, including the purpose of graphing, dependent and independent variables, and interpolating and extrapolating. It defines dependent and independent variables and provides examples of graphing height against number of boxes and lamps. It also explains that a straight line graph indicates a constant relationship between variables, while a non-straight line shows a changing relationship, and interpolated/extrapolated data is more reliable for a straight line graph.