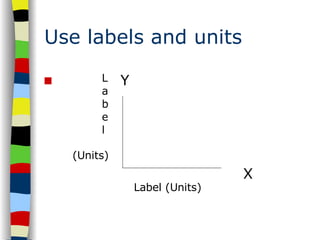
The document provides instructions for graphing data, including using graph paper and proper tools, determining the independent and dependent variables to place on each axis, labeling the axes with units, spreading data out on the page, determining the value of each line, and plotting the data points and connecting them for line graphs.