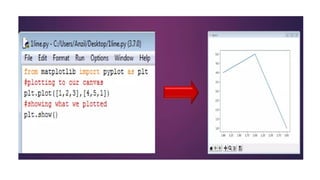
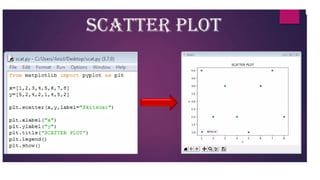
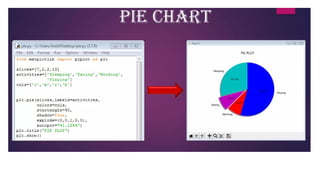
The document provides an overview of different types of graphs and charts in data visualization using the pyplot module from matplotlib. It explains line graphs, bar charts, scatter plots, histograms, and pie charts, detailing their uses, structure, and the types of data they represent. Each graph serves a specific purpose, such as showing trends, comparing categories, or illustrating part-whole relationships.