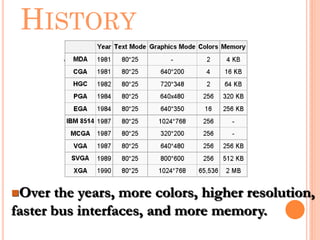
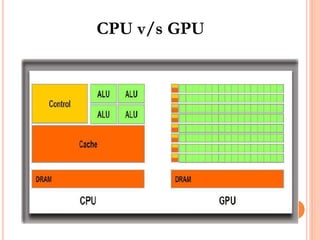
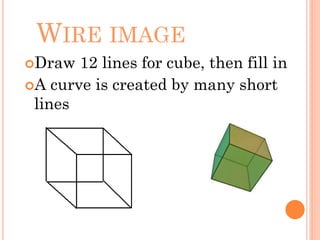
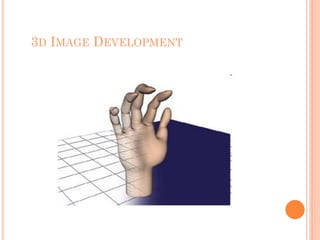
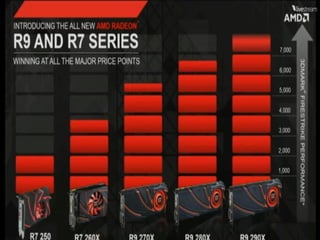
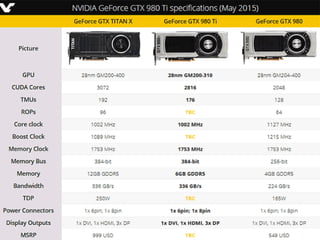
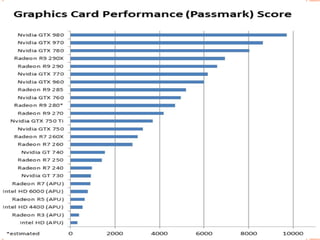
Graphics cards are hardware that produce images on a monitor by converting data into signals. They are used for animation, gaming, design, effects creation, and other tasks requiring fast rendering and high resolution. Over time, graphics cards have provided more colors, higher resolution, faster interfaces and more memory. They work by taking data from the CPU and determining what to do with each pixel to create an image. Key components include the GPU, video memory, and output. Graphics cards are better for gaming and 3D graphics than integrated graphics processors.