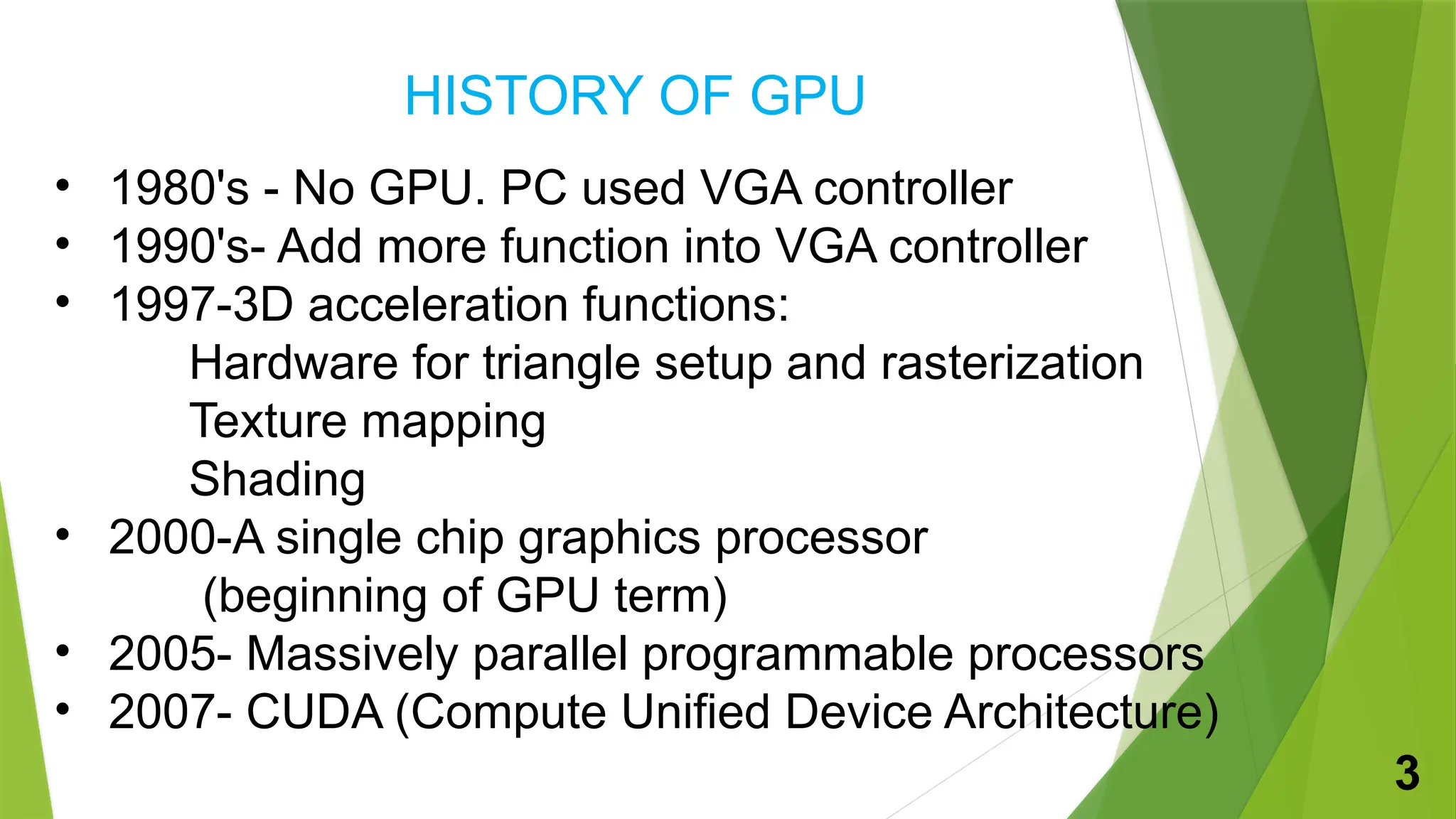
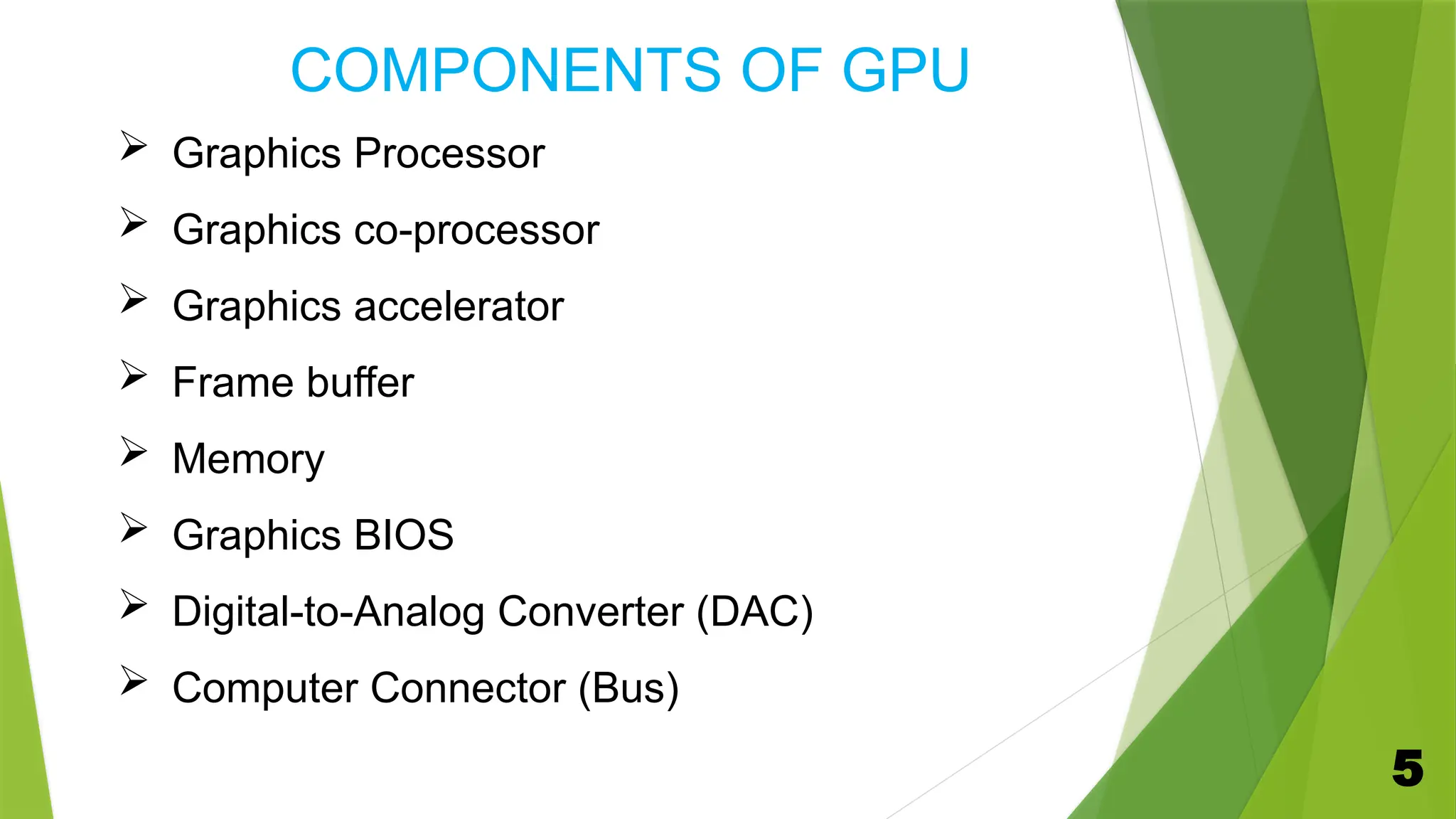
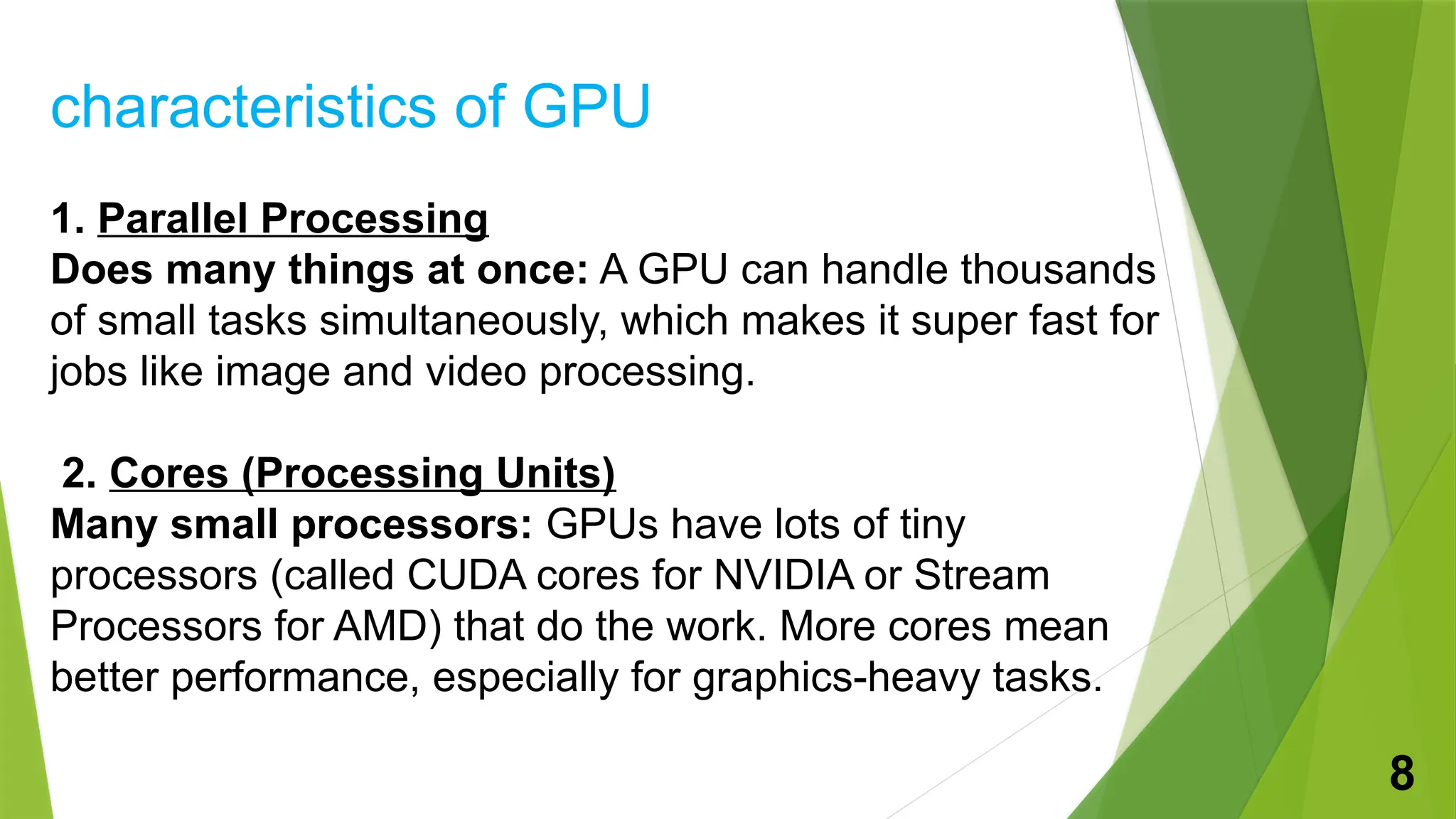
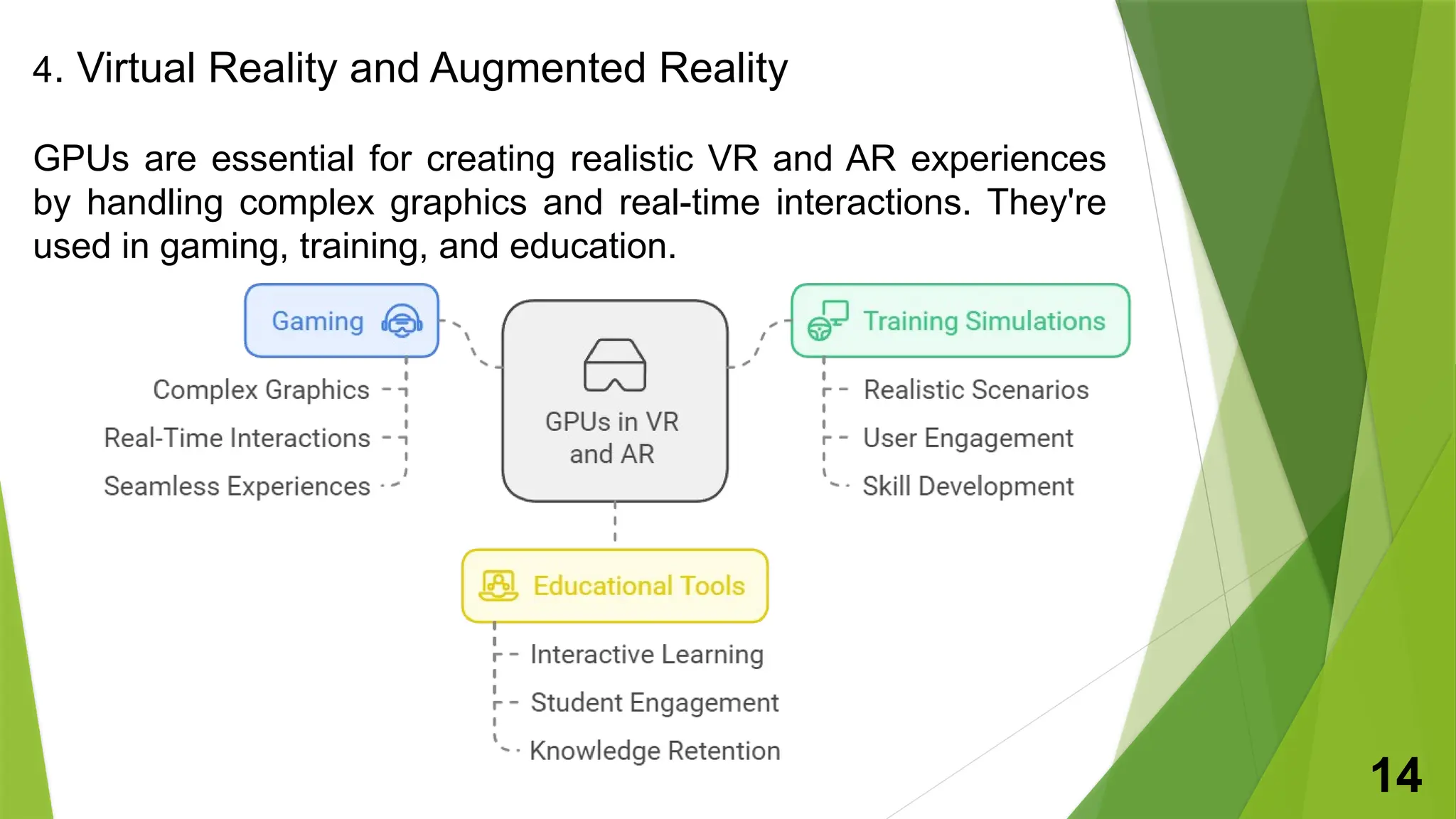
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized microprocessor designed for processing 3D graphics, significantly enhancing image and video rendering while allowing the CPU to focus on other tasks. The document outlines the history, components, characteristics, and various applications of GPUs in gaming, scientific computing, image processing, and virtual reality. It concludes that ongoing developments in GPU technology will lead to more powerful and efficient graphics performance in the future.