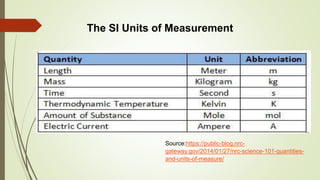
This document discusses different types of graphic/visual aids and their uses in presentations. It identifies 6 main categories: charts, tables, graphs, diagrams, visual images, and maps. Each category is described through definitions and examples. Charts are used to show ranks, levels and classifications. Tables arrange data in rows and columns for easy reference. Graphs present numerical data and trends through visual representations. Diagrams show arrangements and relationships through drawings. Visual images like photographs support information through pictures. Maps are useful for presenting data about places or areas. The document provides guidance on selecting the appropriate visual aid based on the type of data to present and gives activities to practice identifying and creating visual aids.