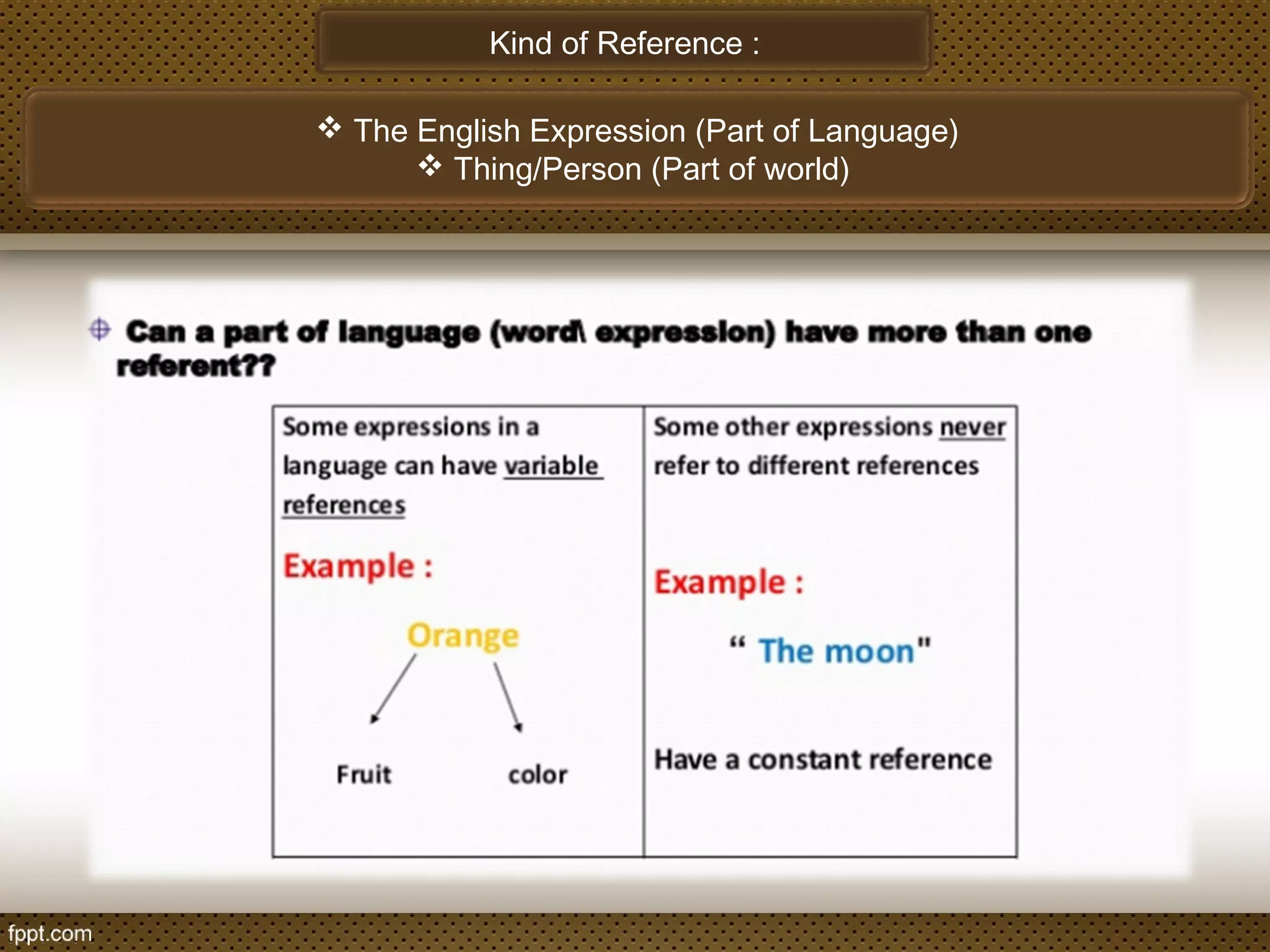
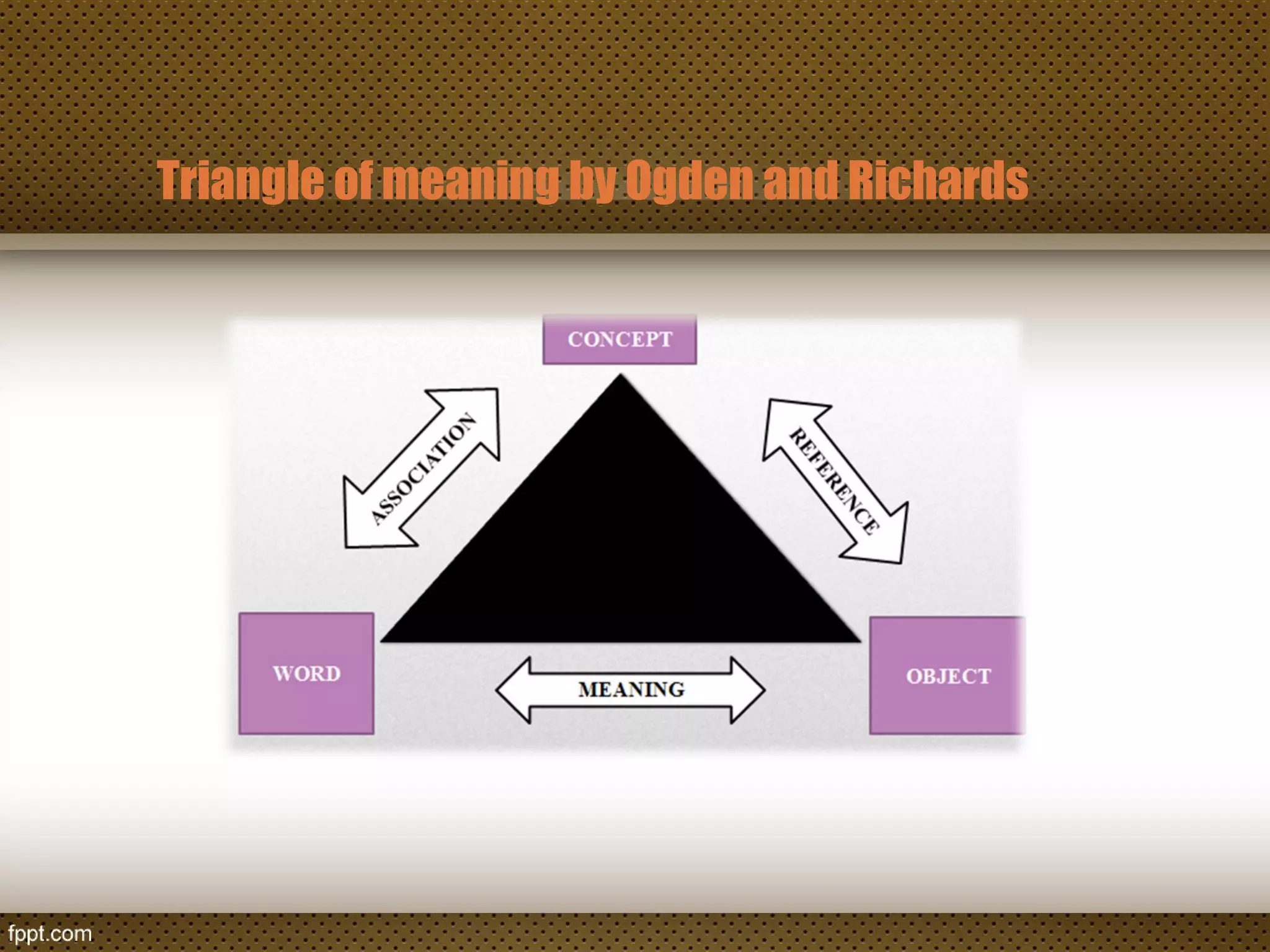
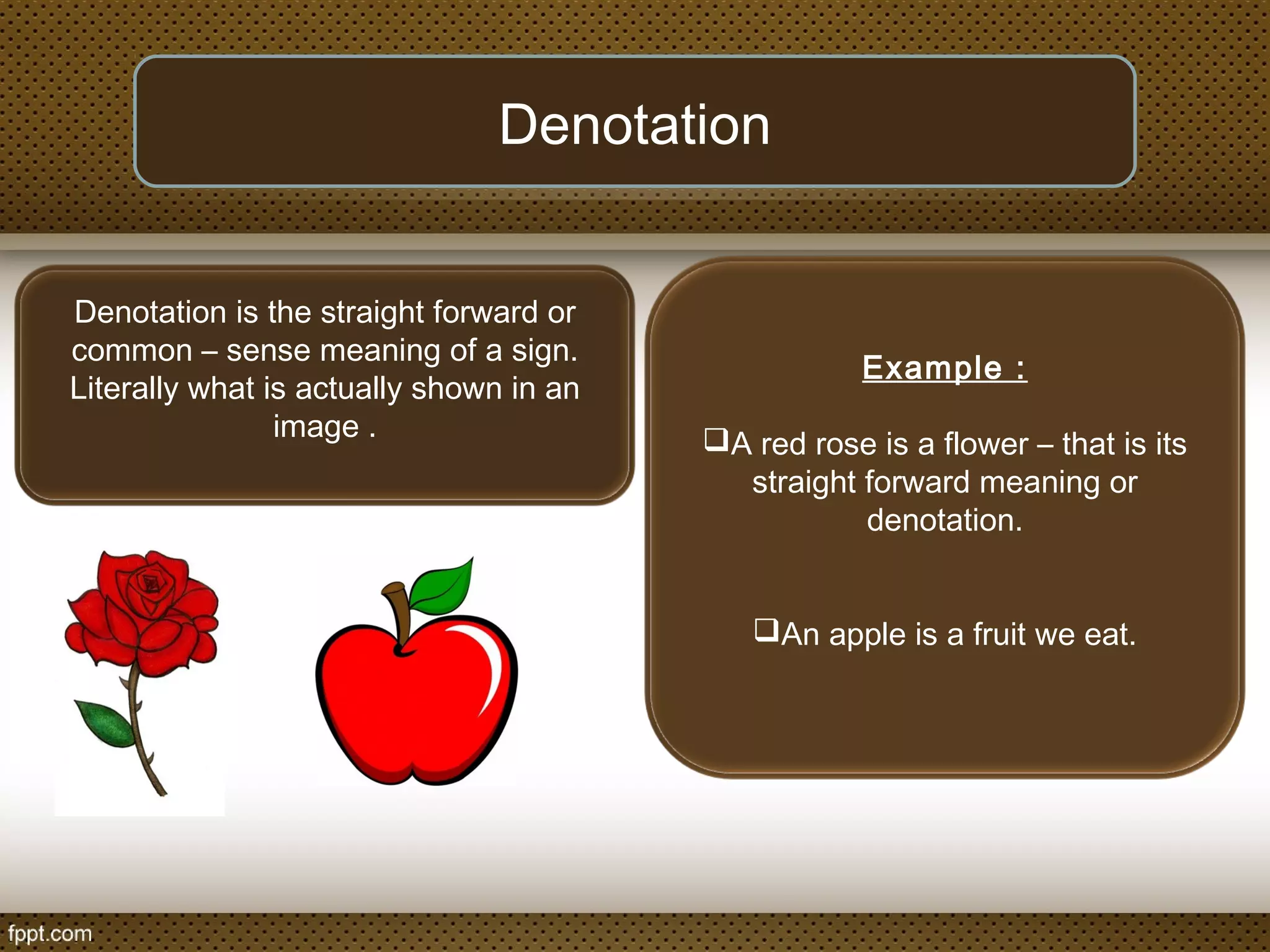
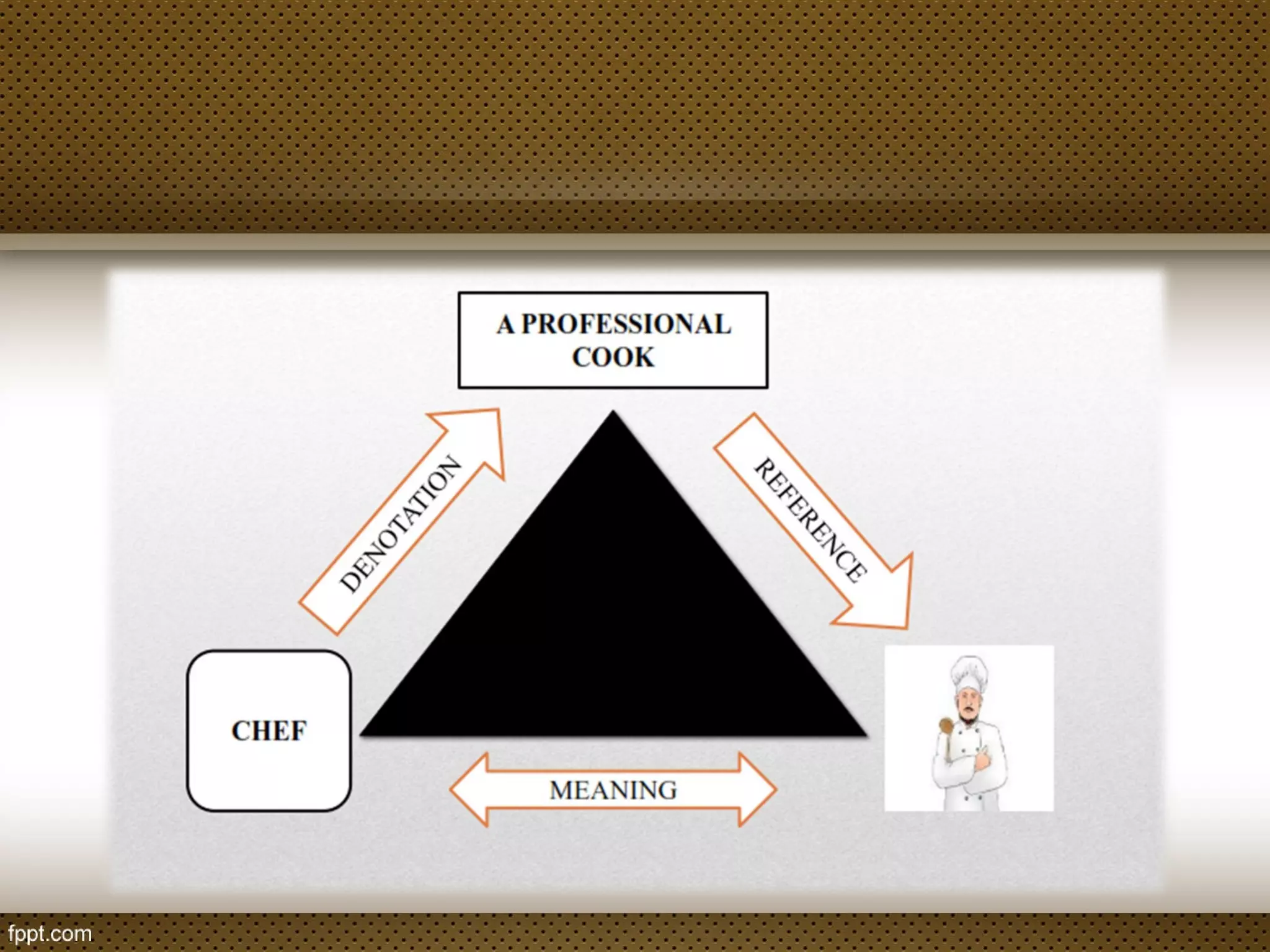
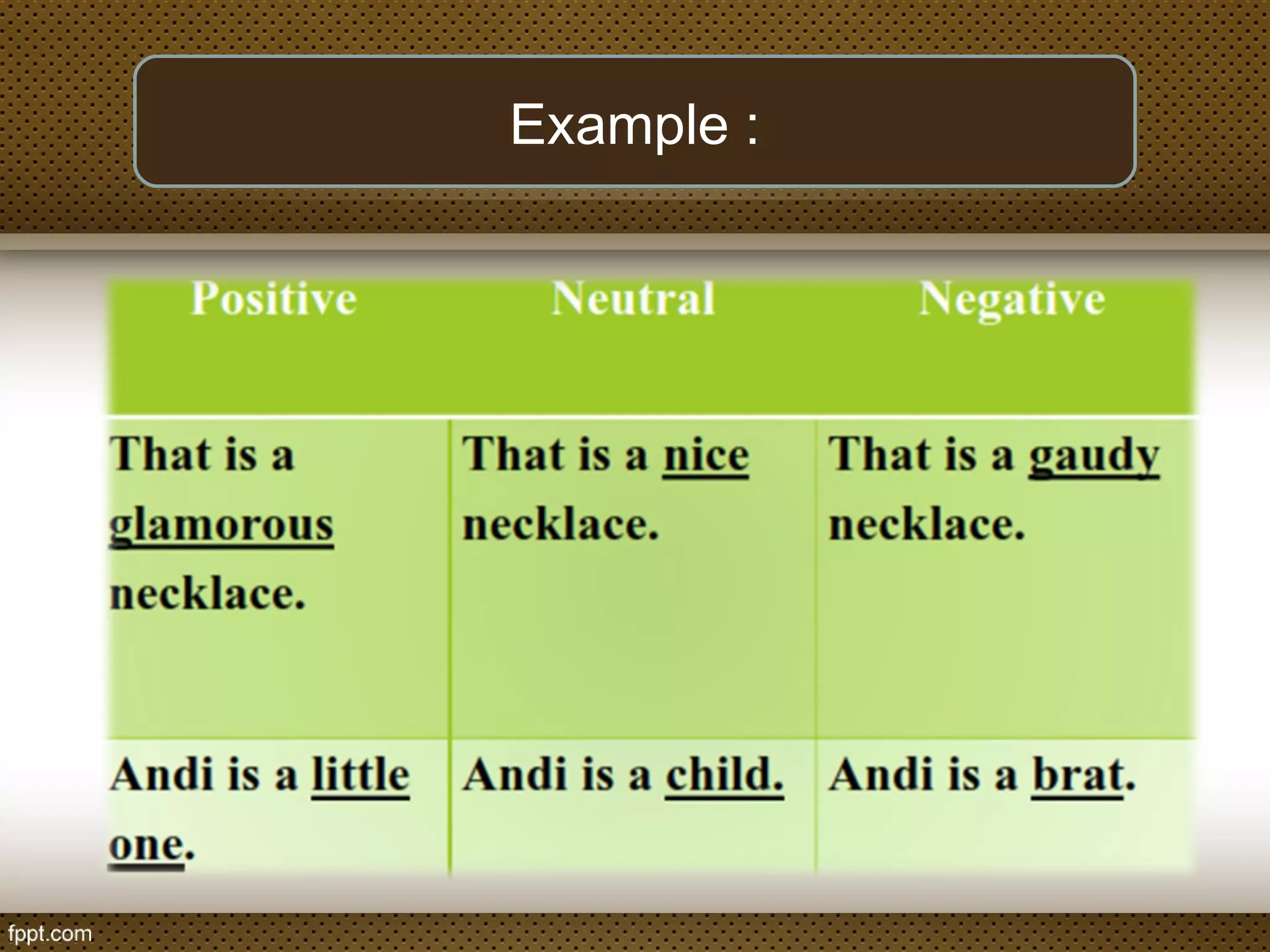
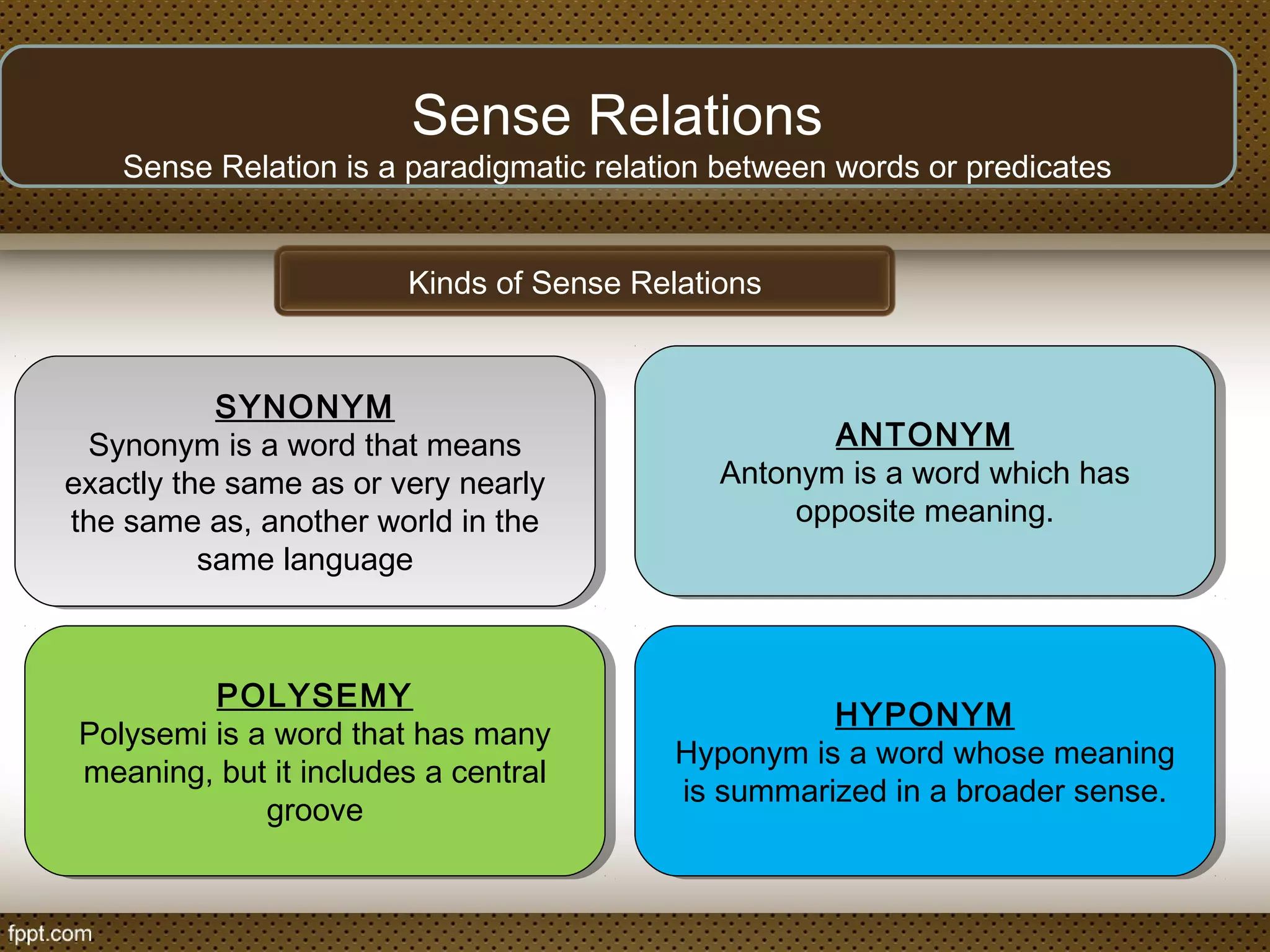
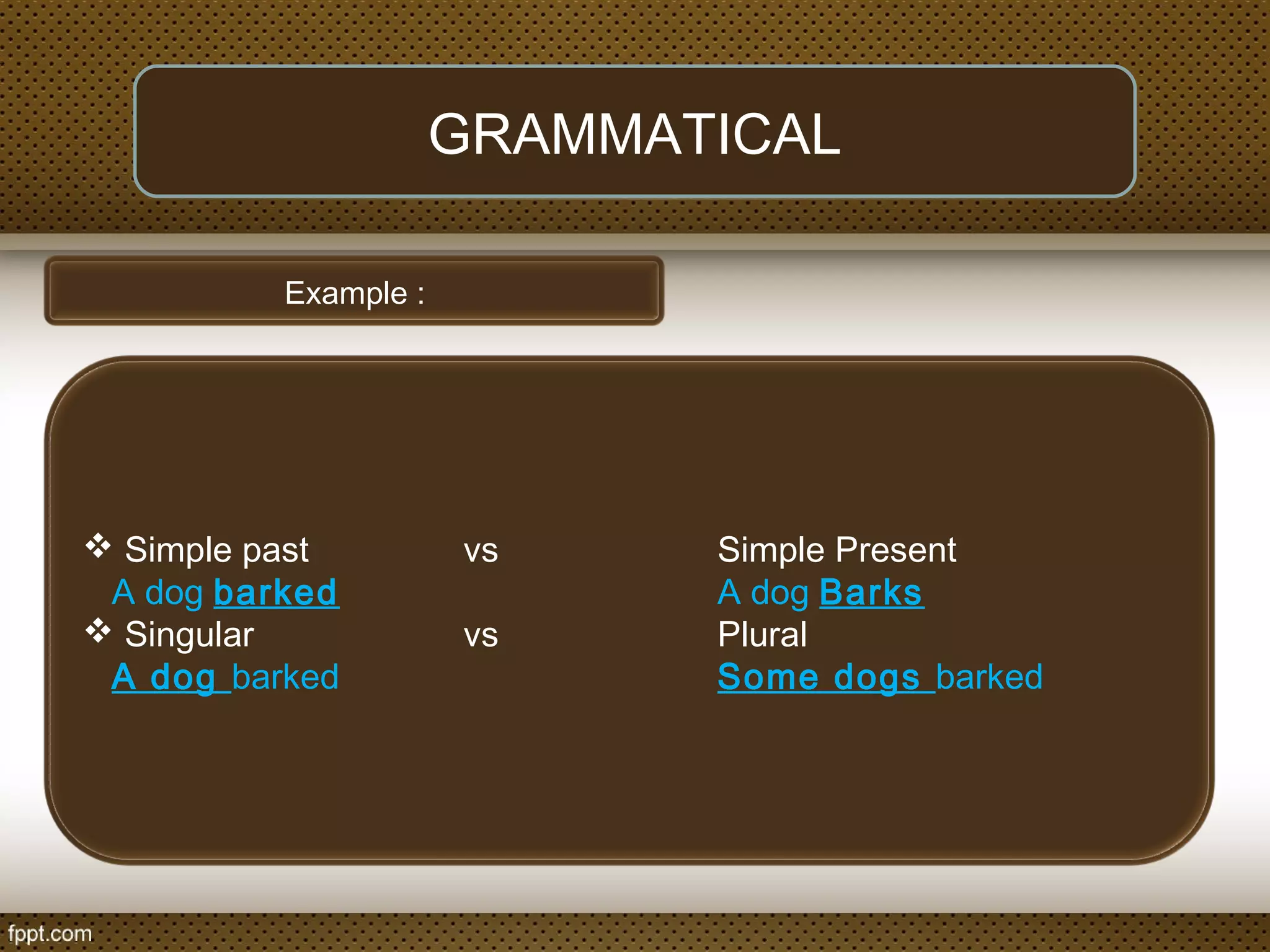
The document discusses linguistic concepts such as reference, denotation, and connotation, explaining how expressions relate to their meanings and implications in language. It defines key terms like synonyms, antonyms, and polysemy along with their relations, as well as differentiating between lexical and grammatical meanings. Examples illustrate how different grammatical forms and meanings interact within language usage.