The document provides an overview of Spanish grammar concepts including:
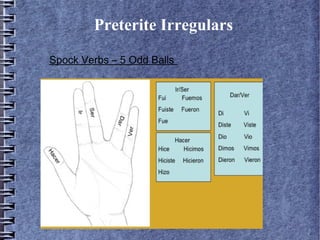
1) Preterite verb forms including regular -ar, -er, -ir endings and irregular verbs.
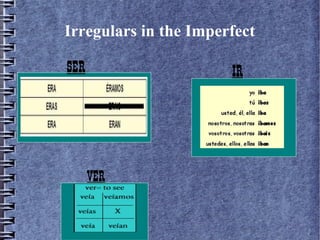
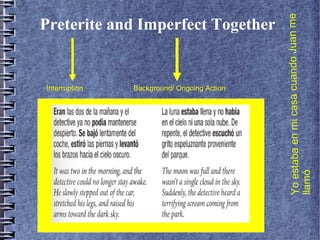
2) Imperfect tense uses and forms.
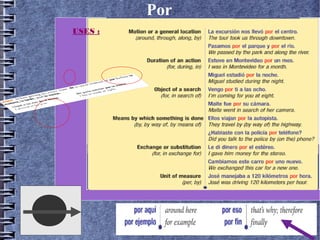
3) Por and para uses which can change sentence meaning.
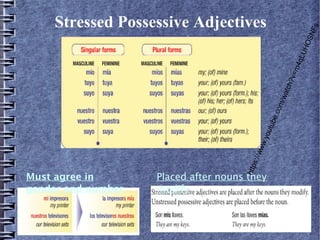
4) Formal command forms including irregular verbs and uses of stressed possessive adjectives.
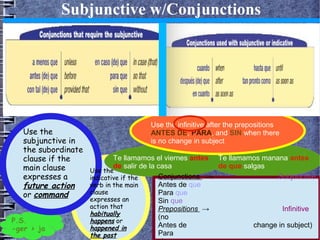
5) Subjunctive mood triggers and uses including will/influence, emotion, doubt/denial, and indefiniteness.