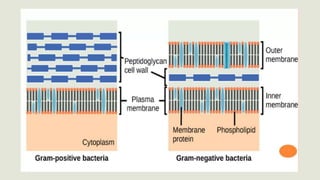
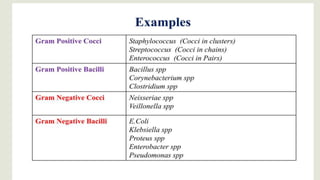
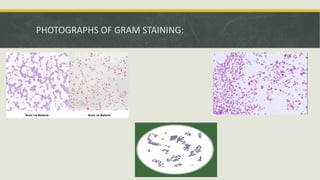
Gram staining is a method used to differentiate between two large groups of bacteria - Gram-positive and Gram-negative. It works by identifying differences in the chemical and physical properties of bacterial cell walls. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan cell wall and appear violet after Gram staining, while Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane and appear red. Gram staining is often the first step in bacterial identification and can help determine initial treatment approaches. The procedure involves applying crystal violet, iodine, decolorizer like alcohol, and counterstain safranin to identify differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria under a microscope.