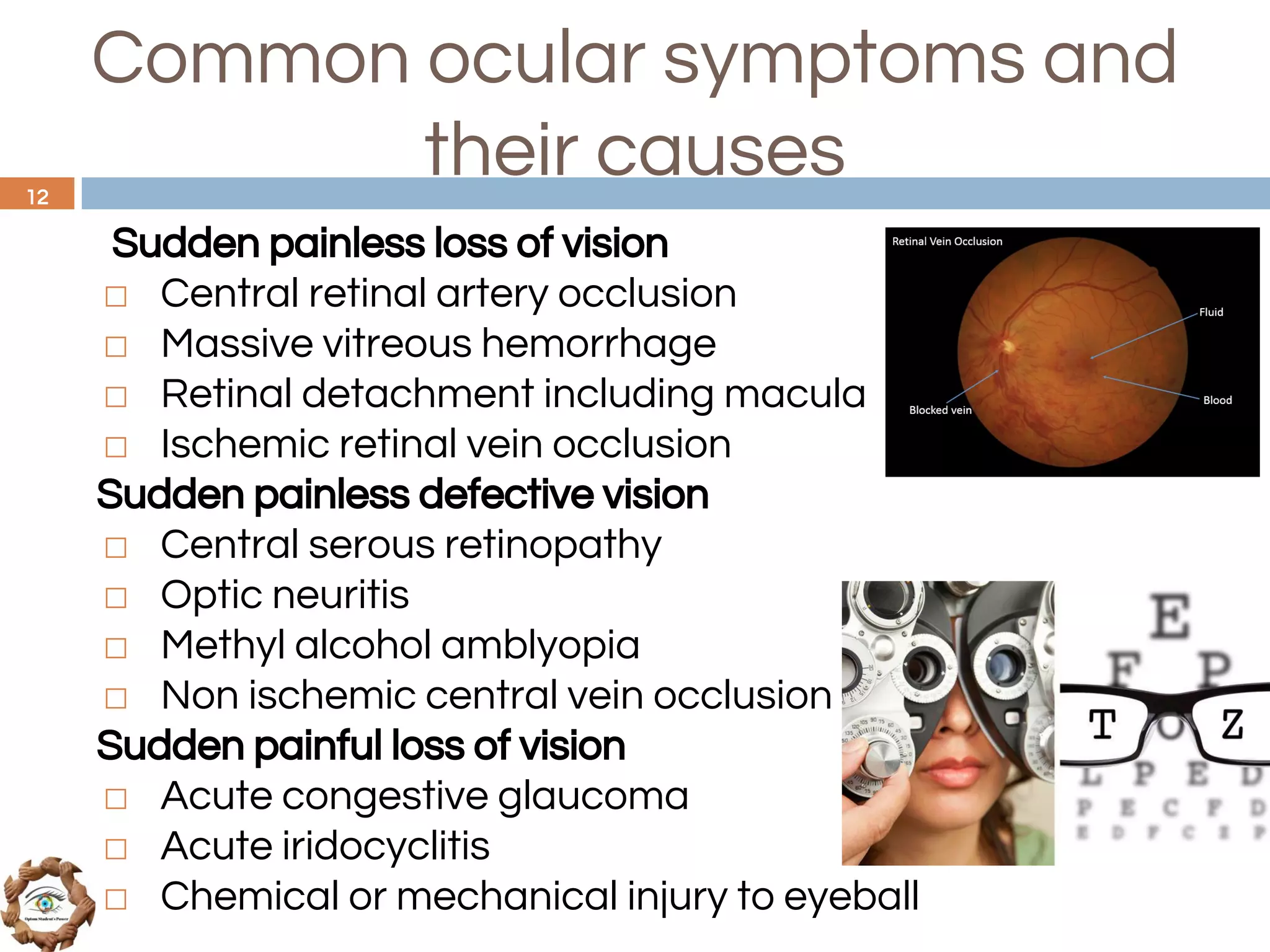
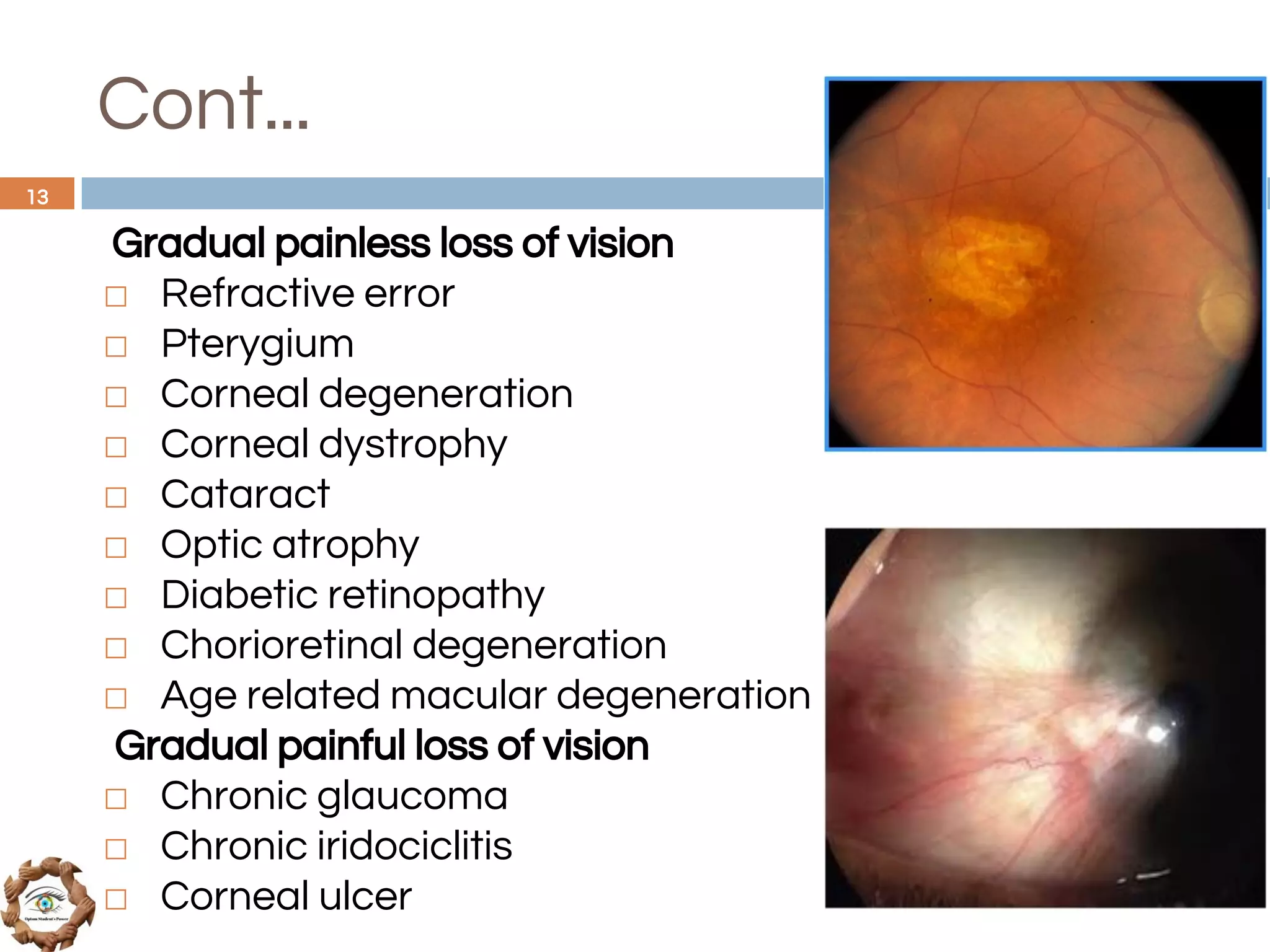
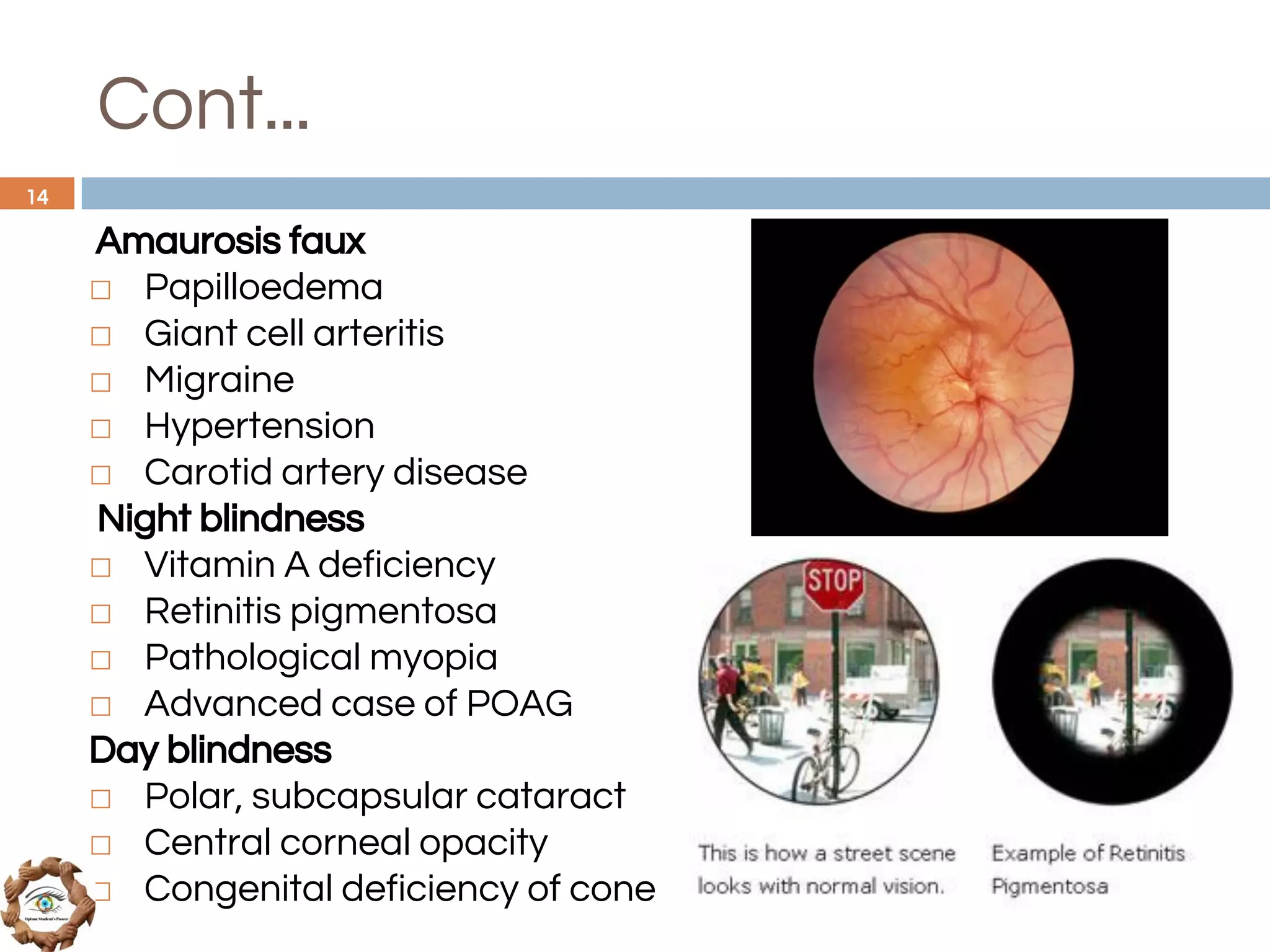
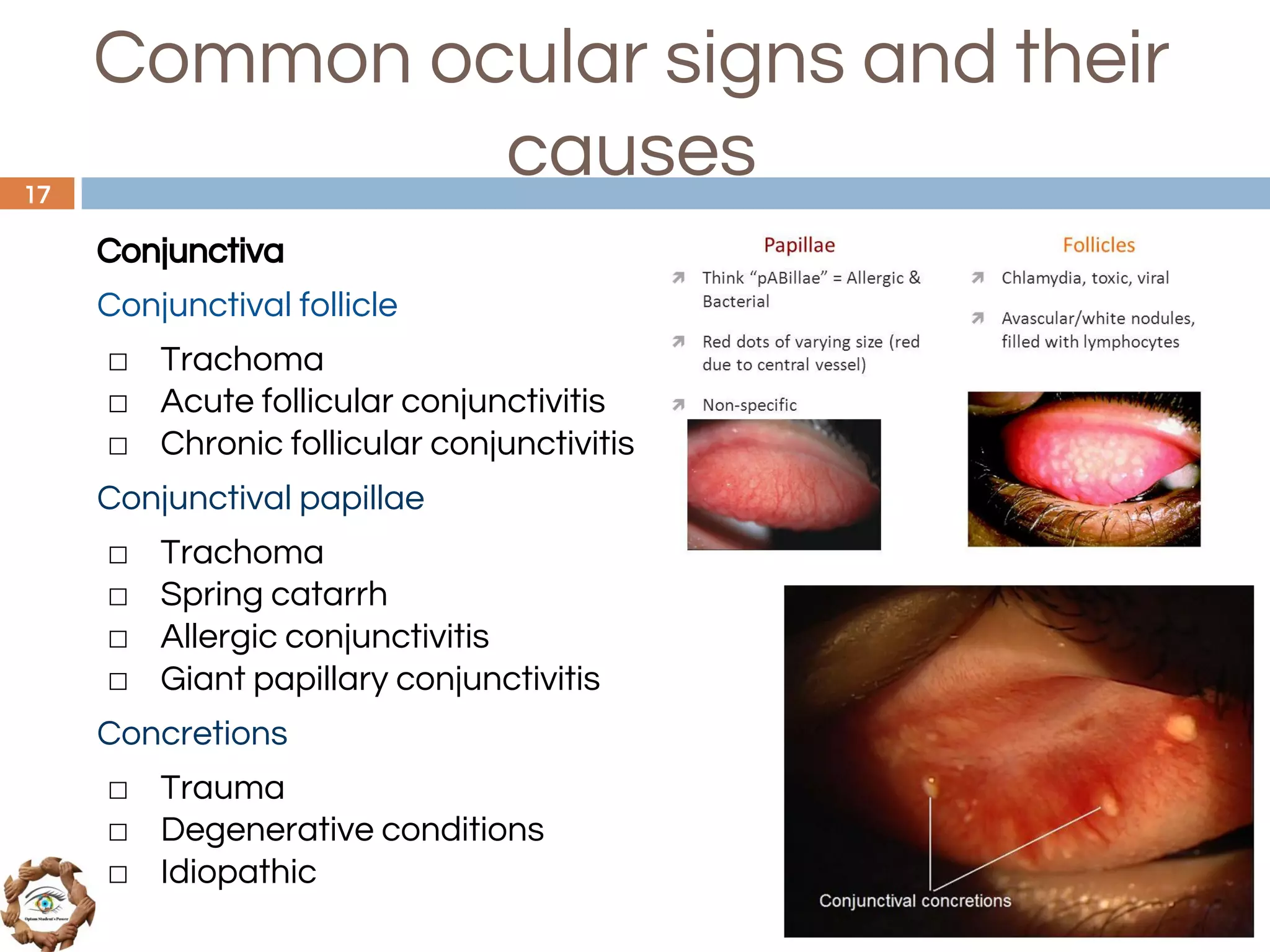
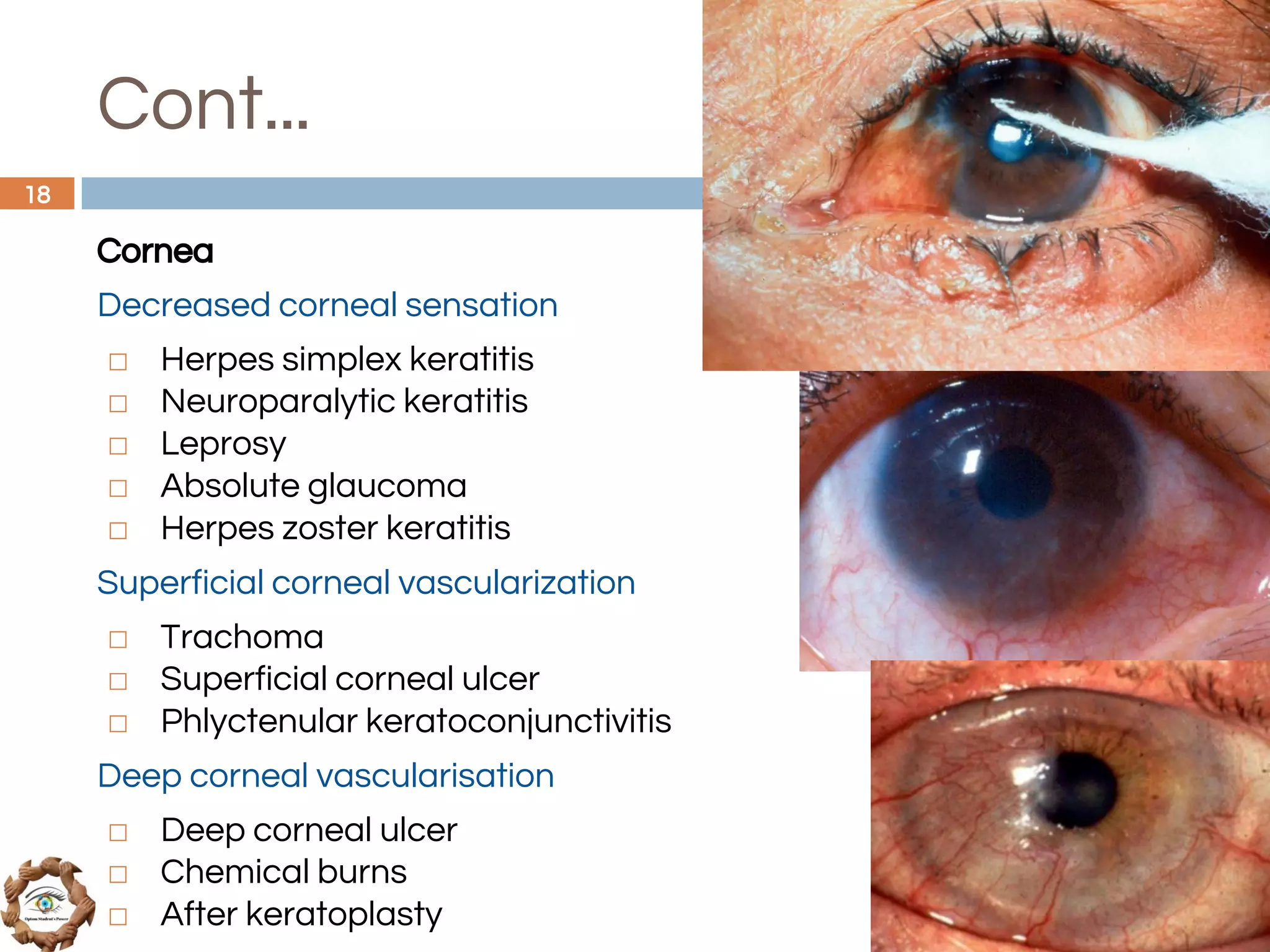
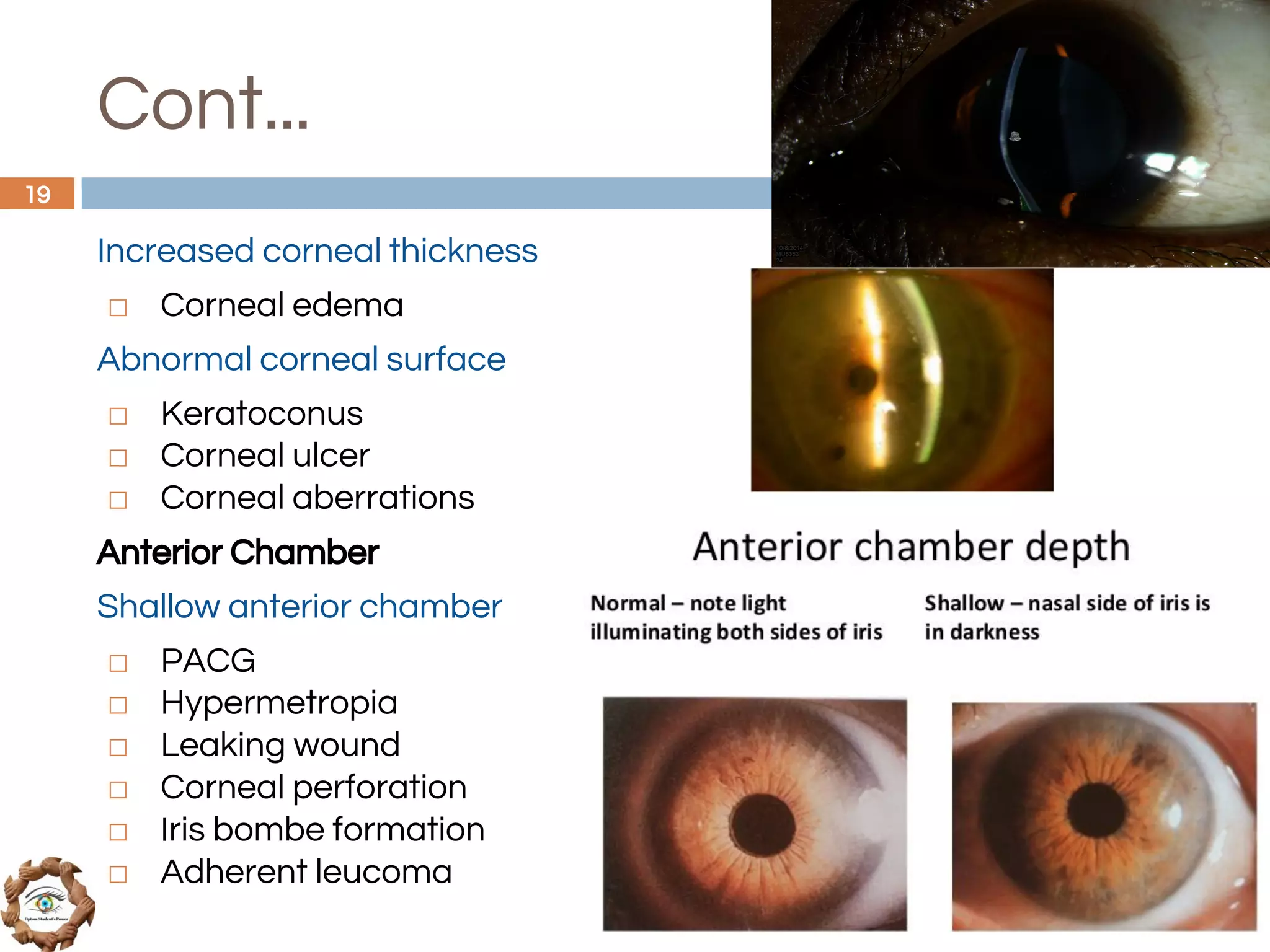
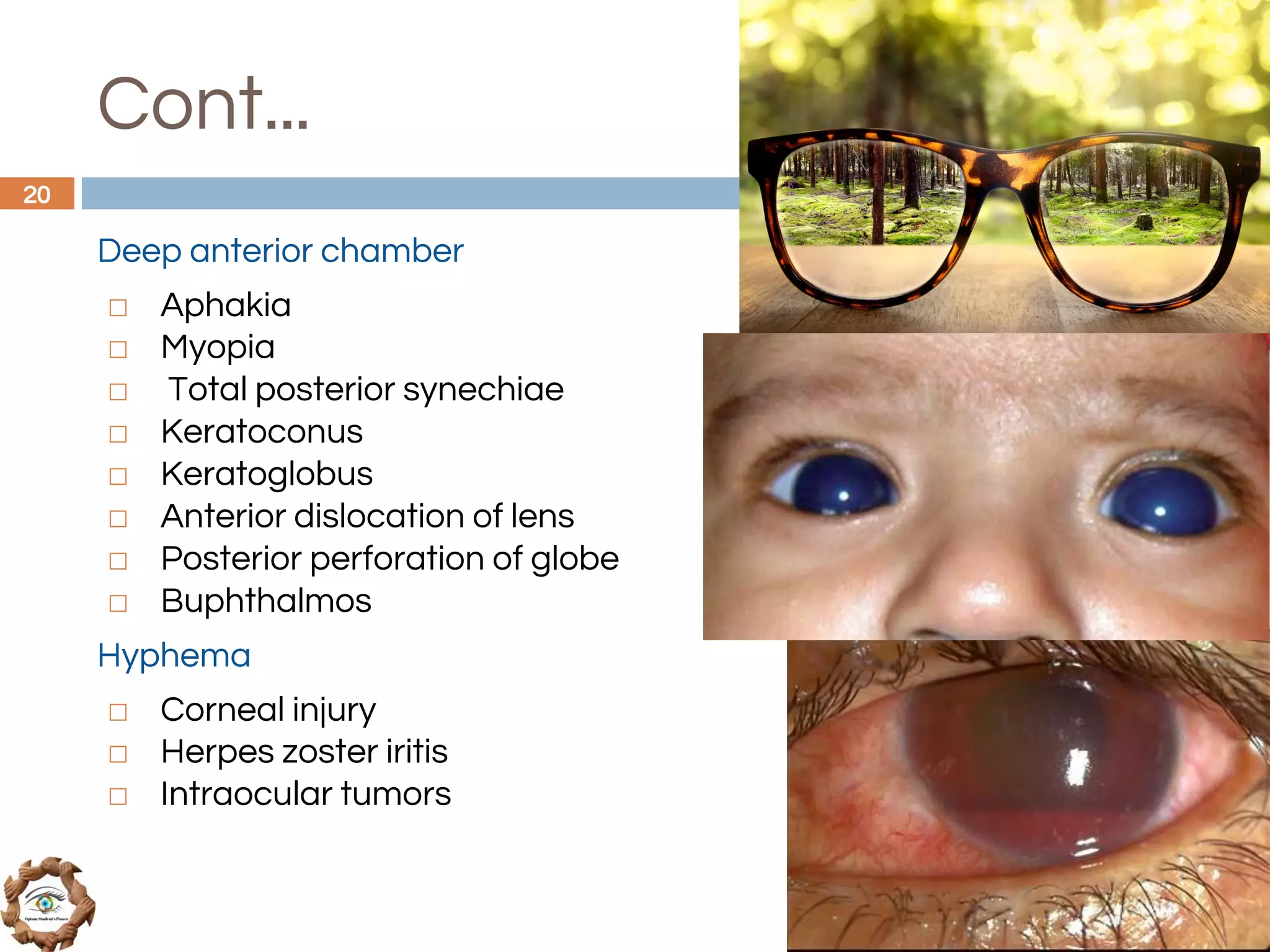
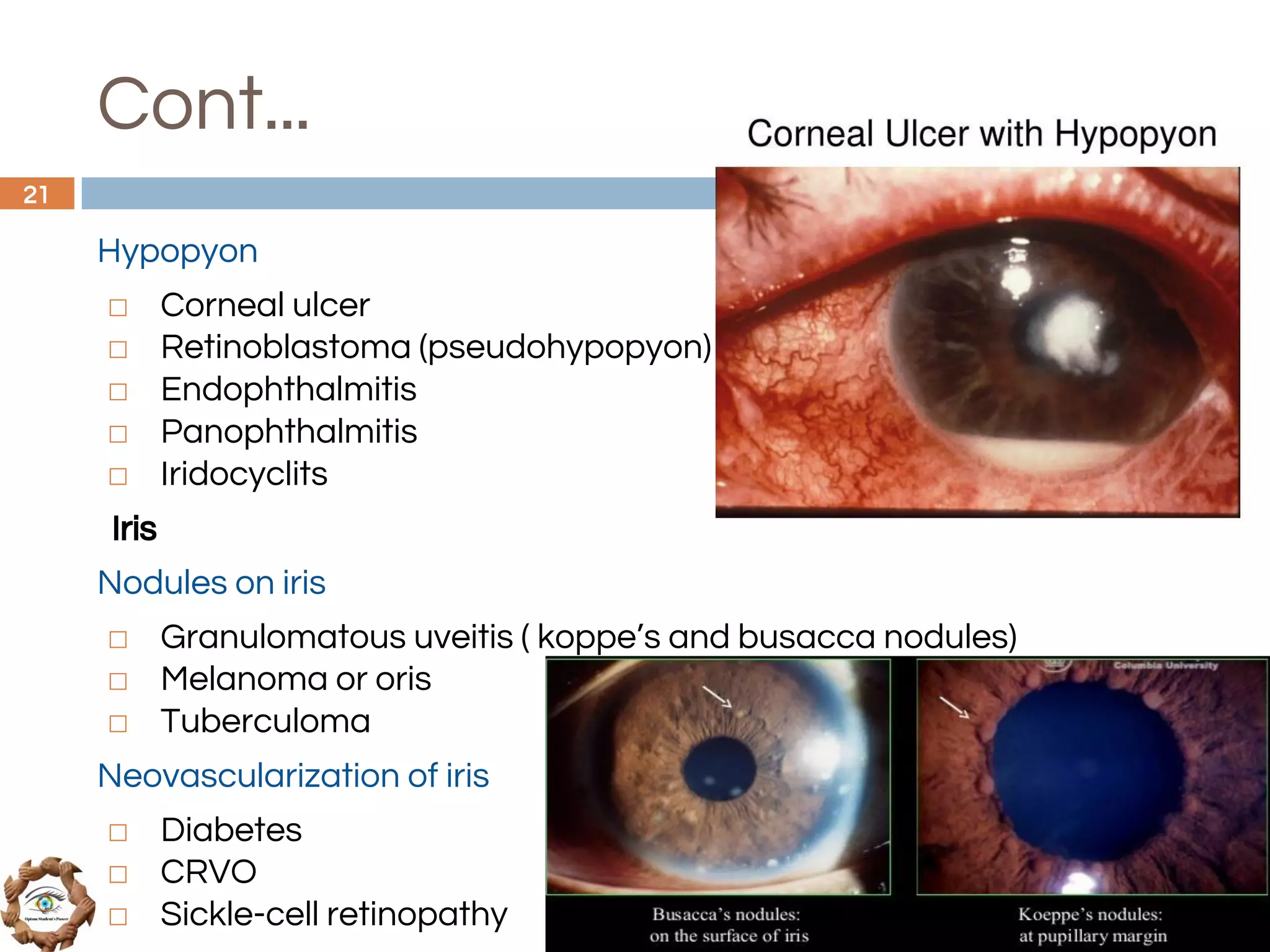
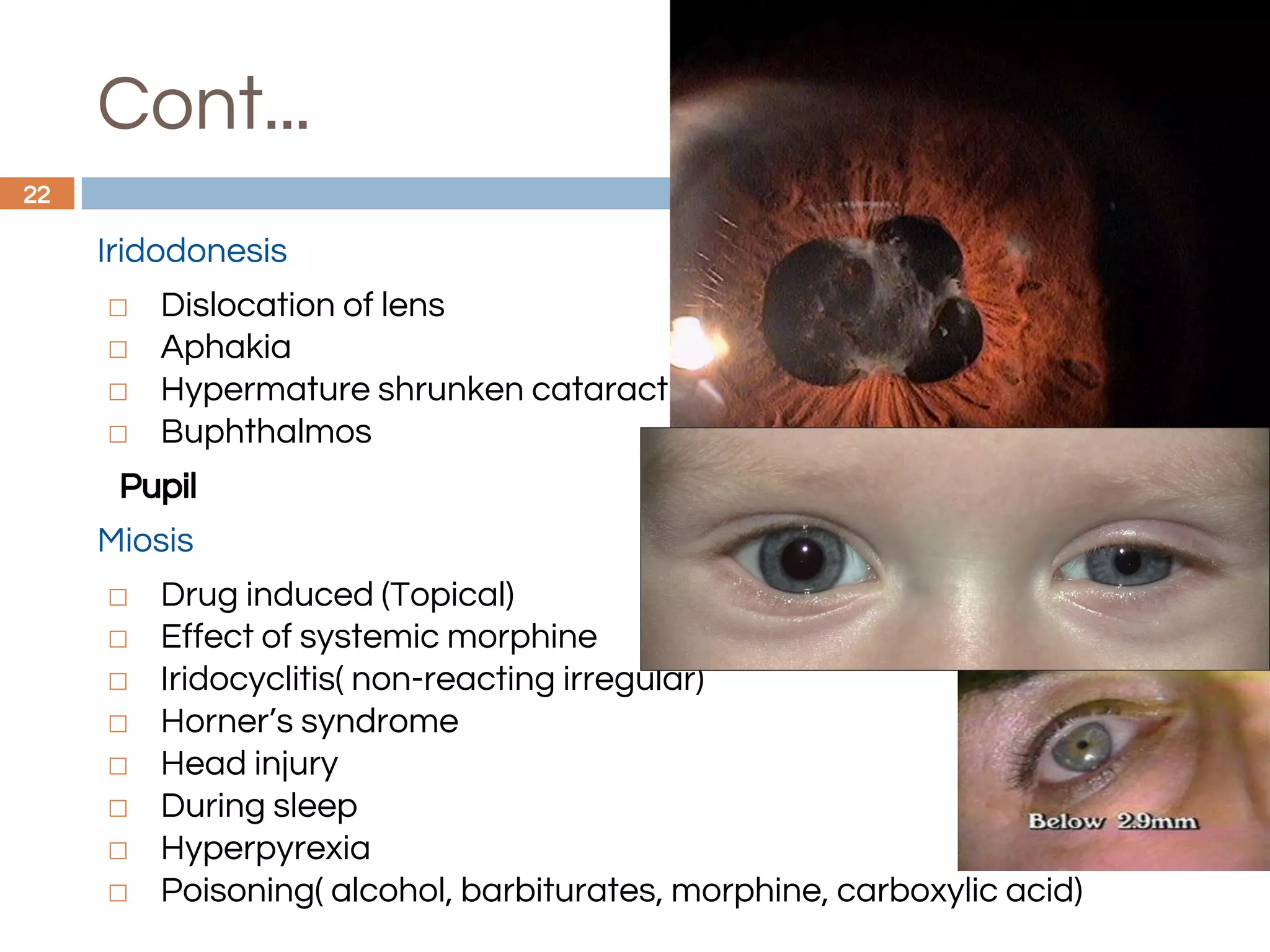
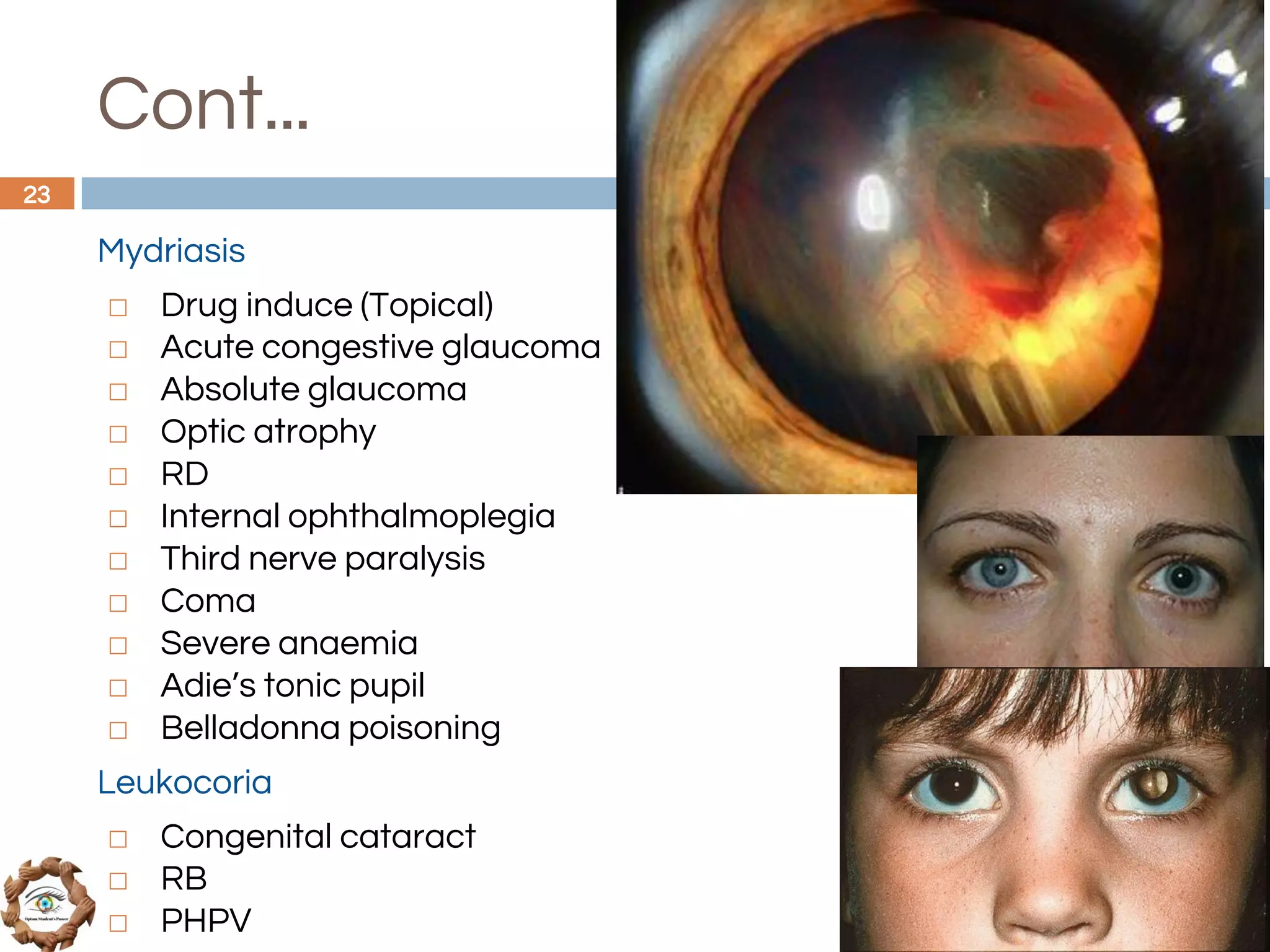
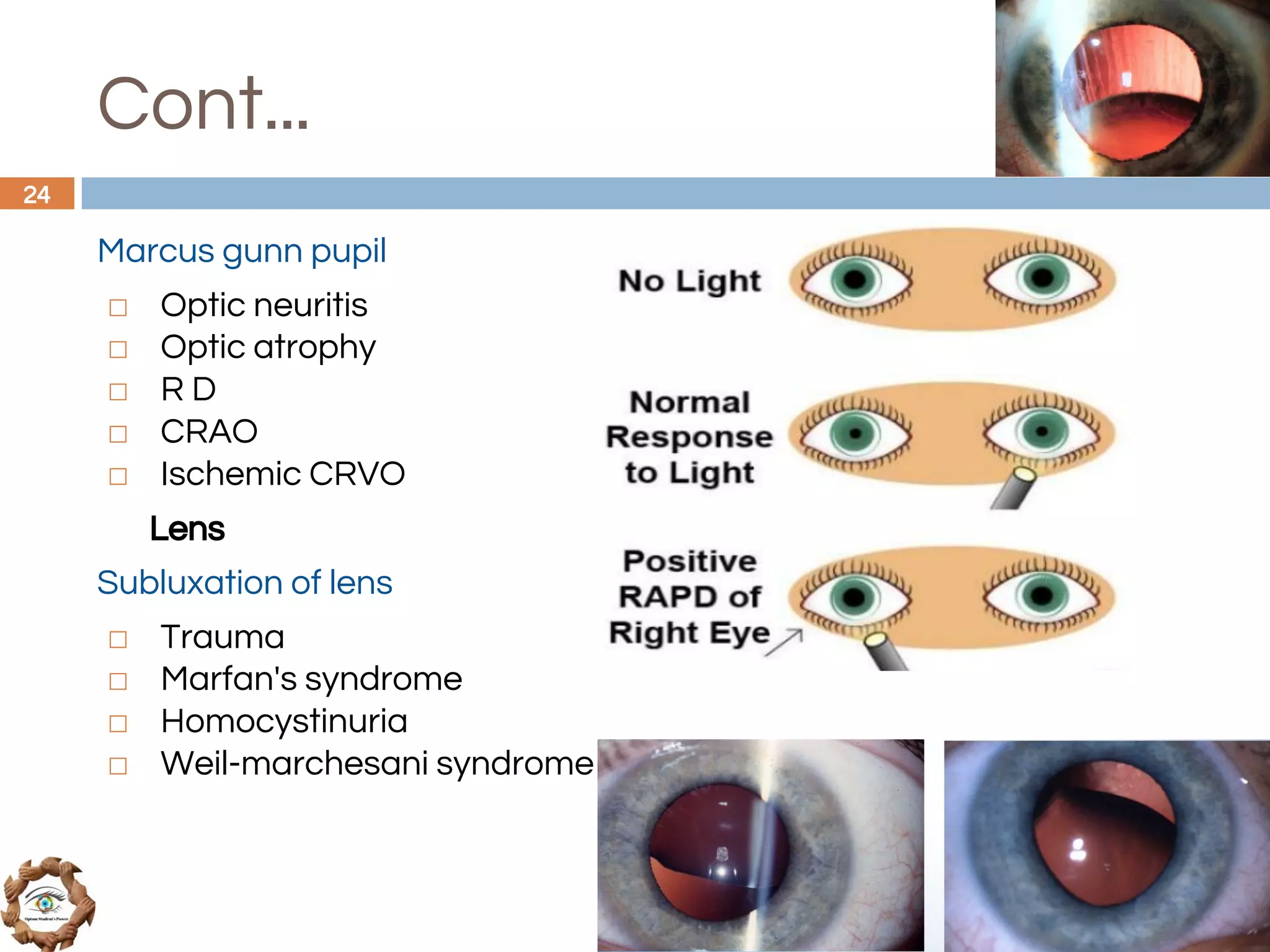
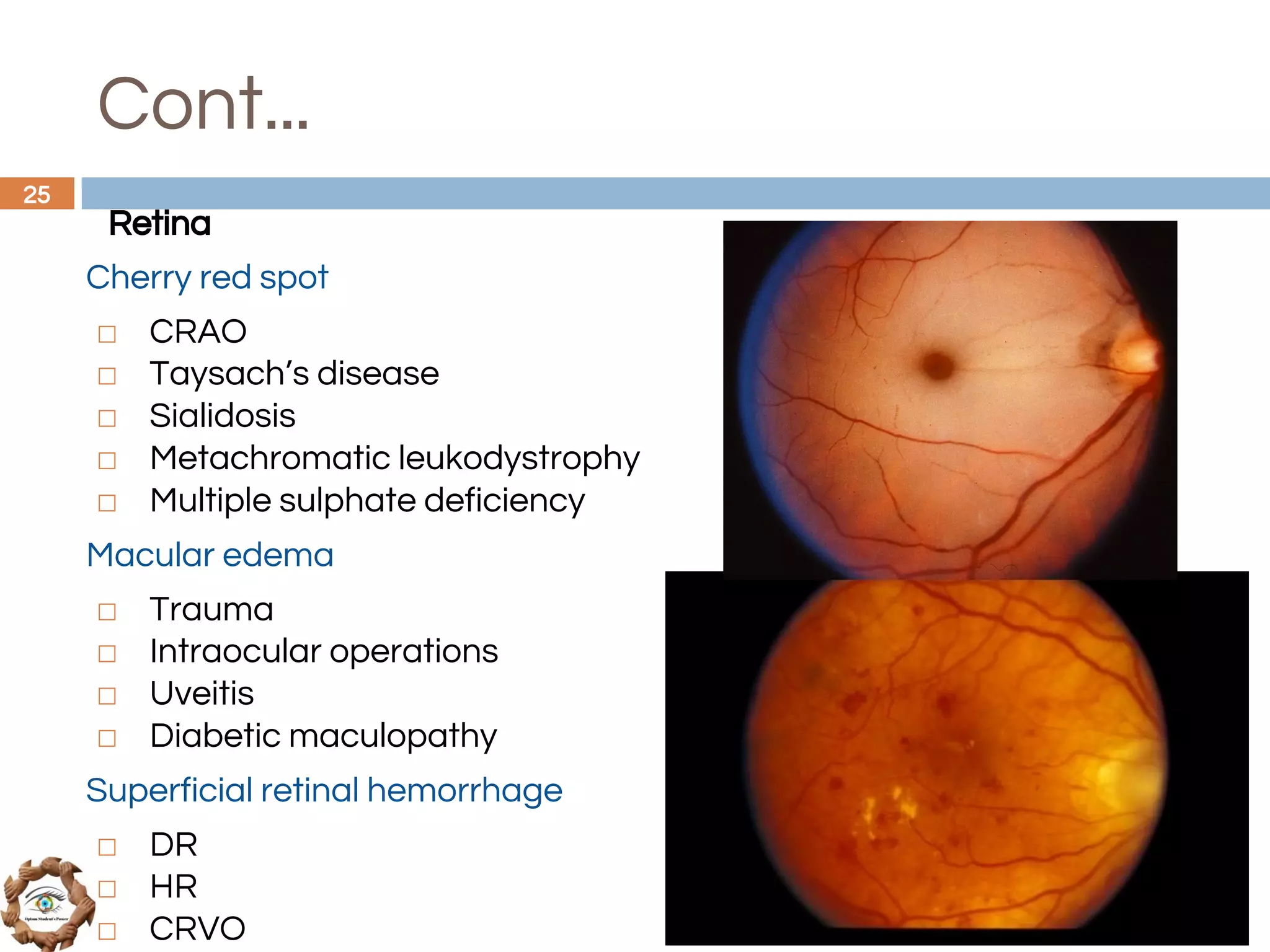
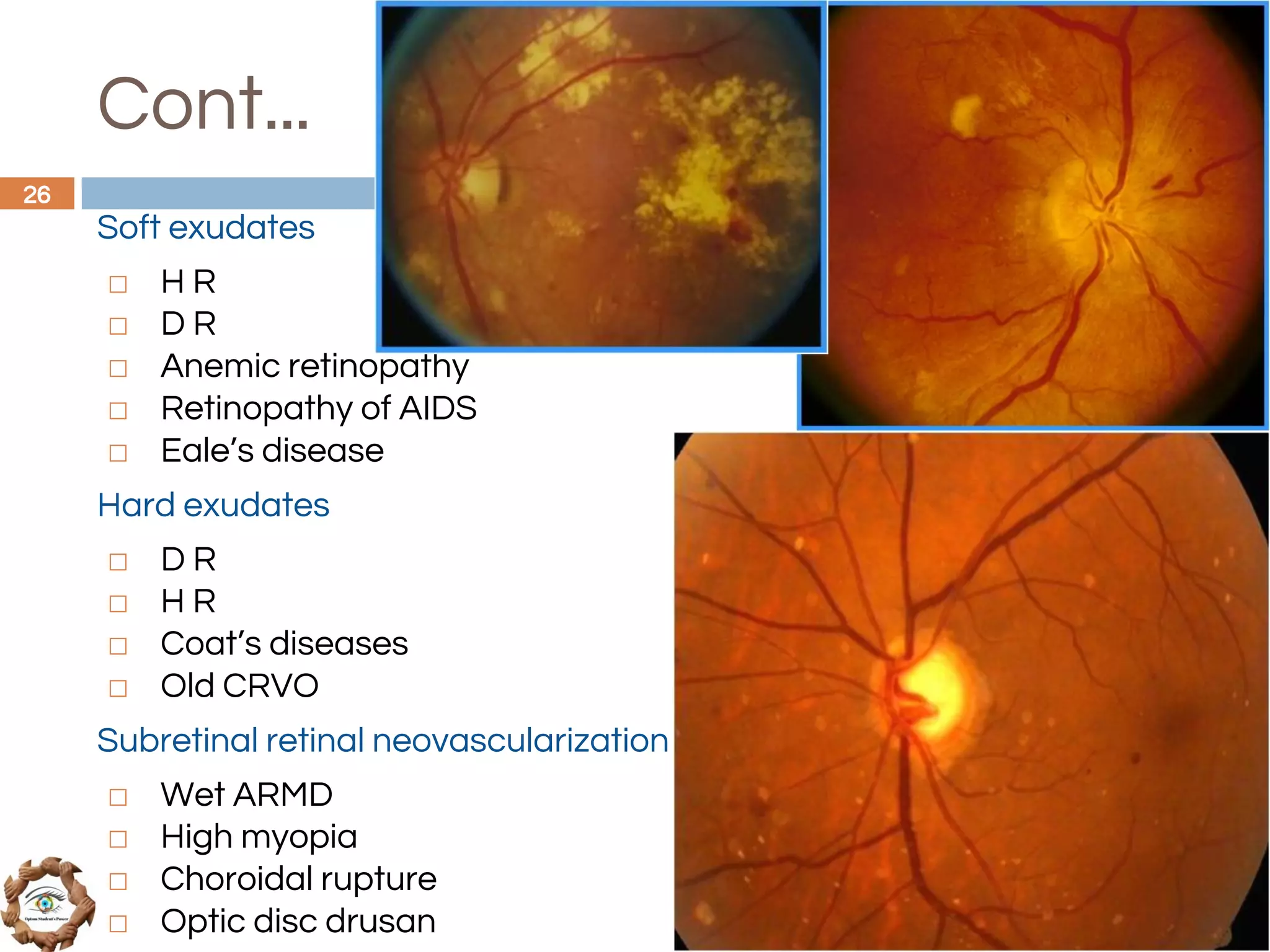
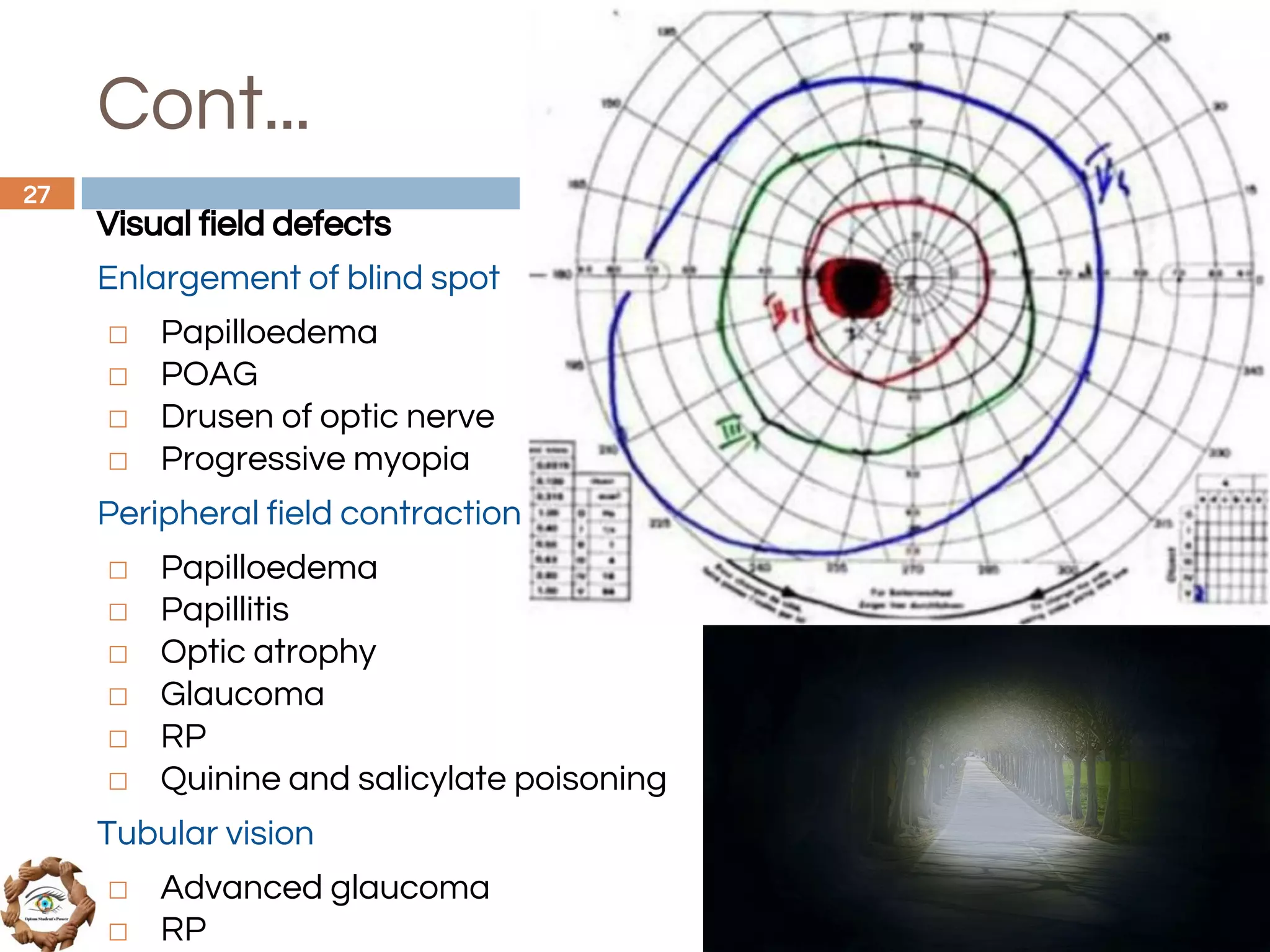
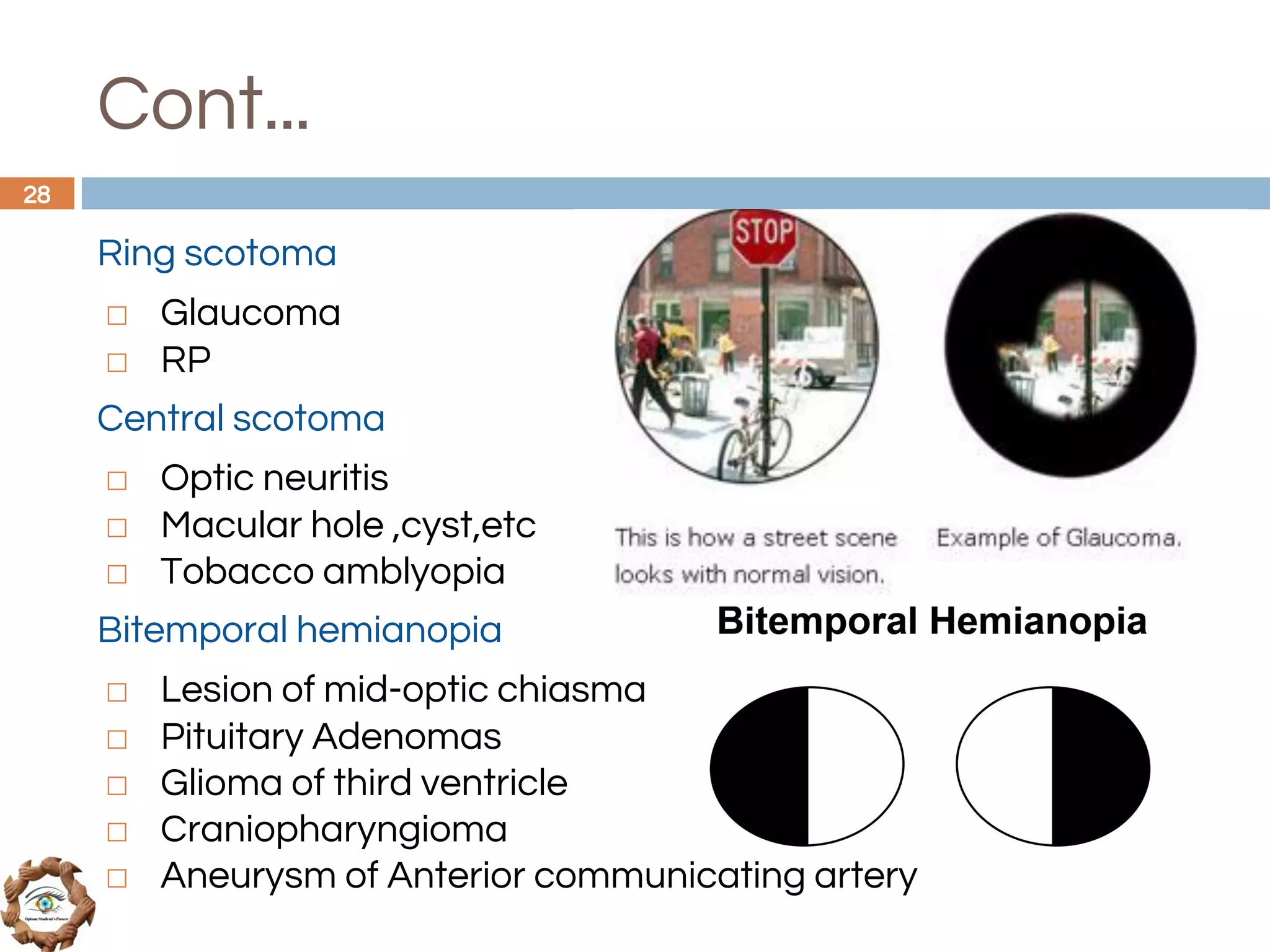
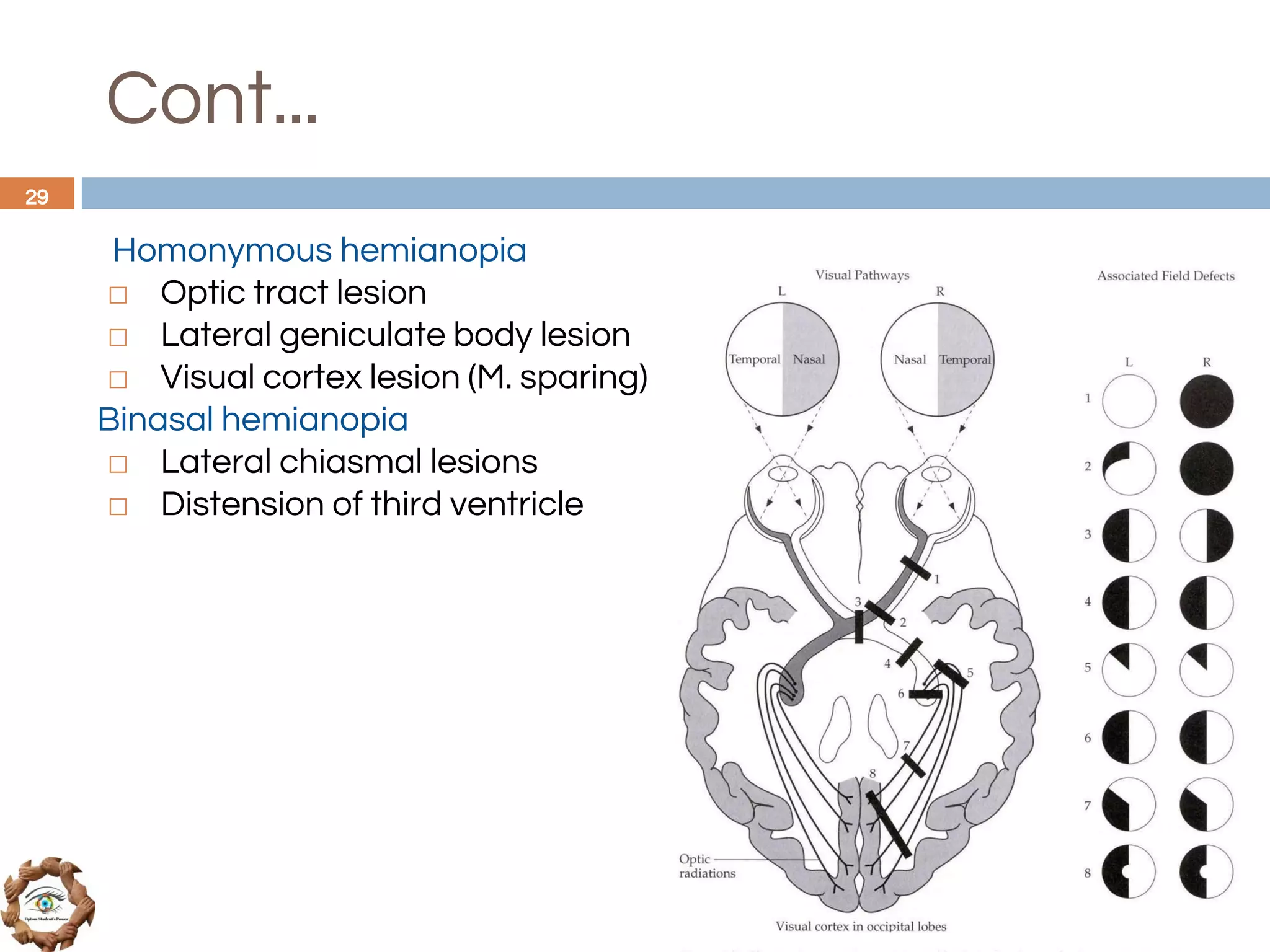
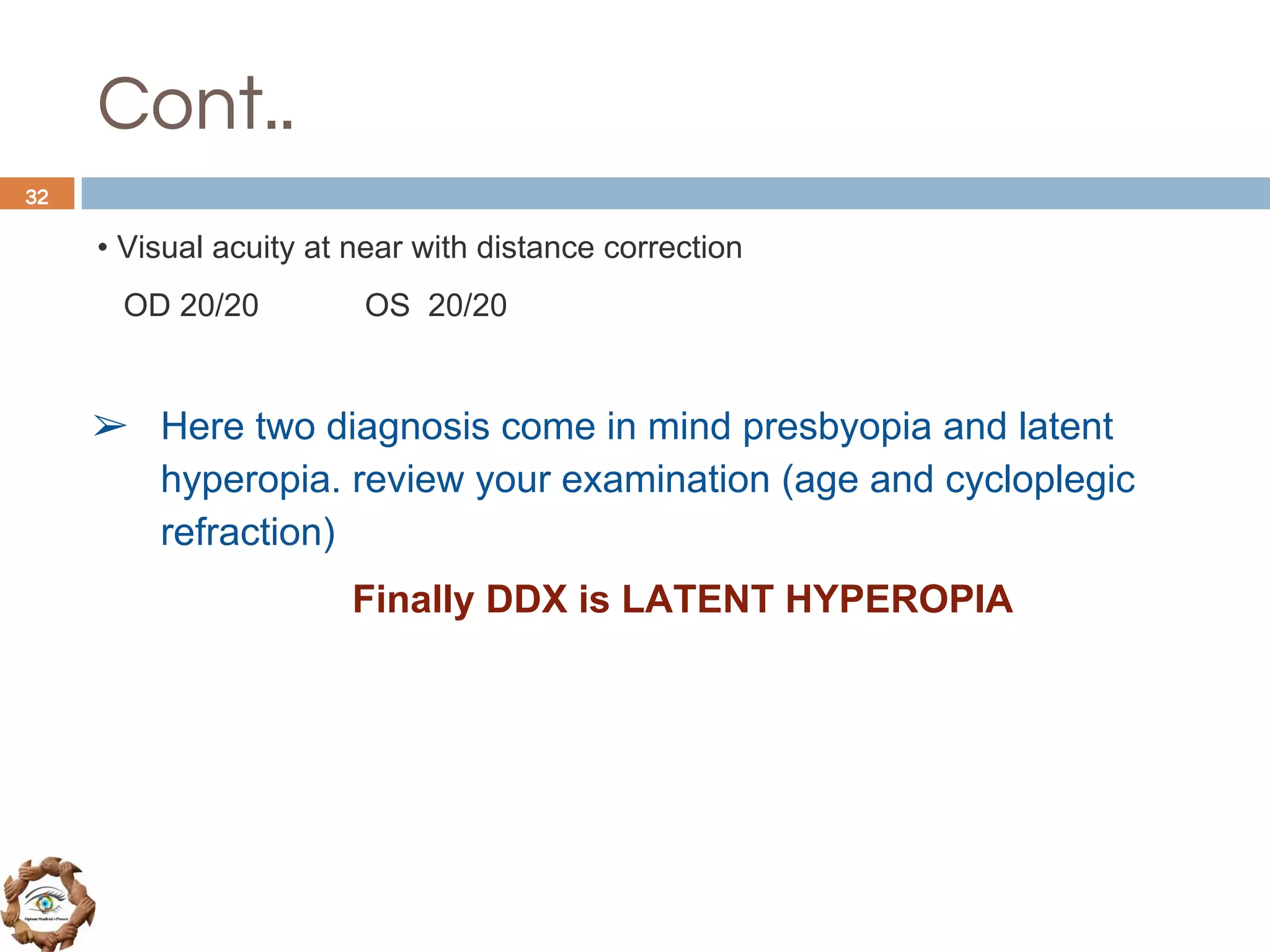
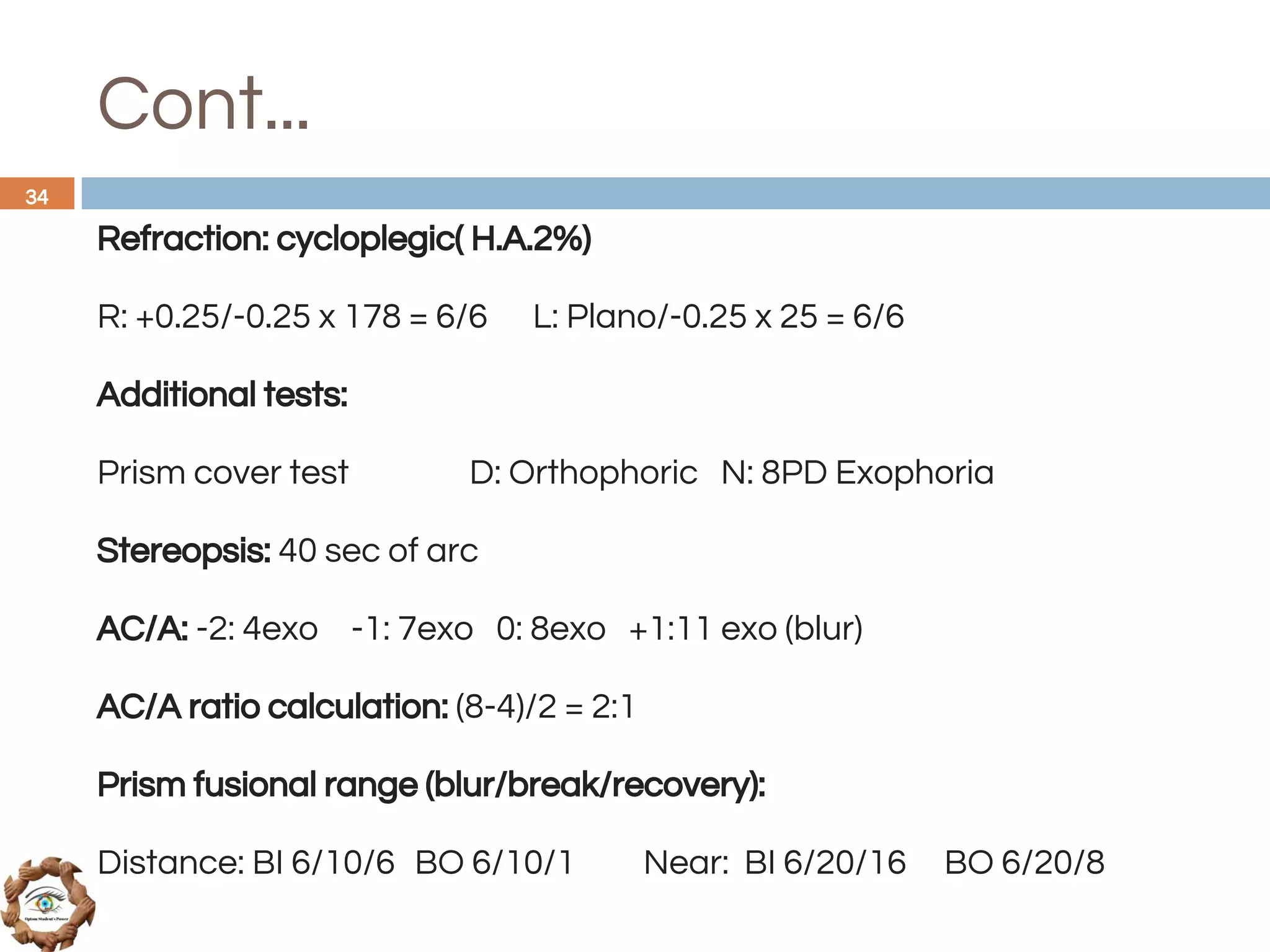
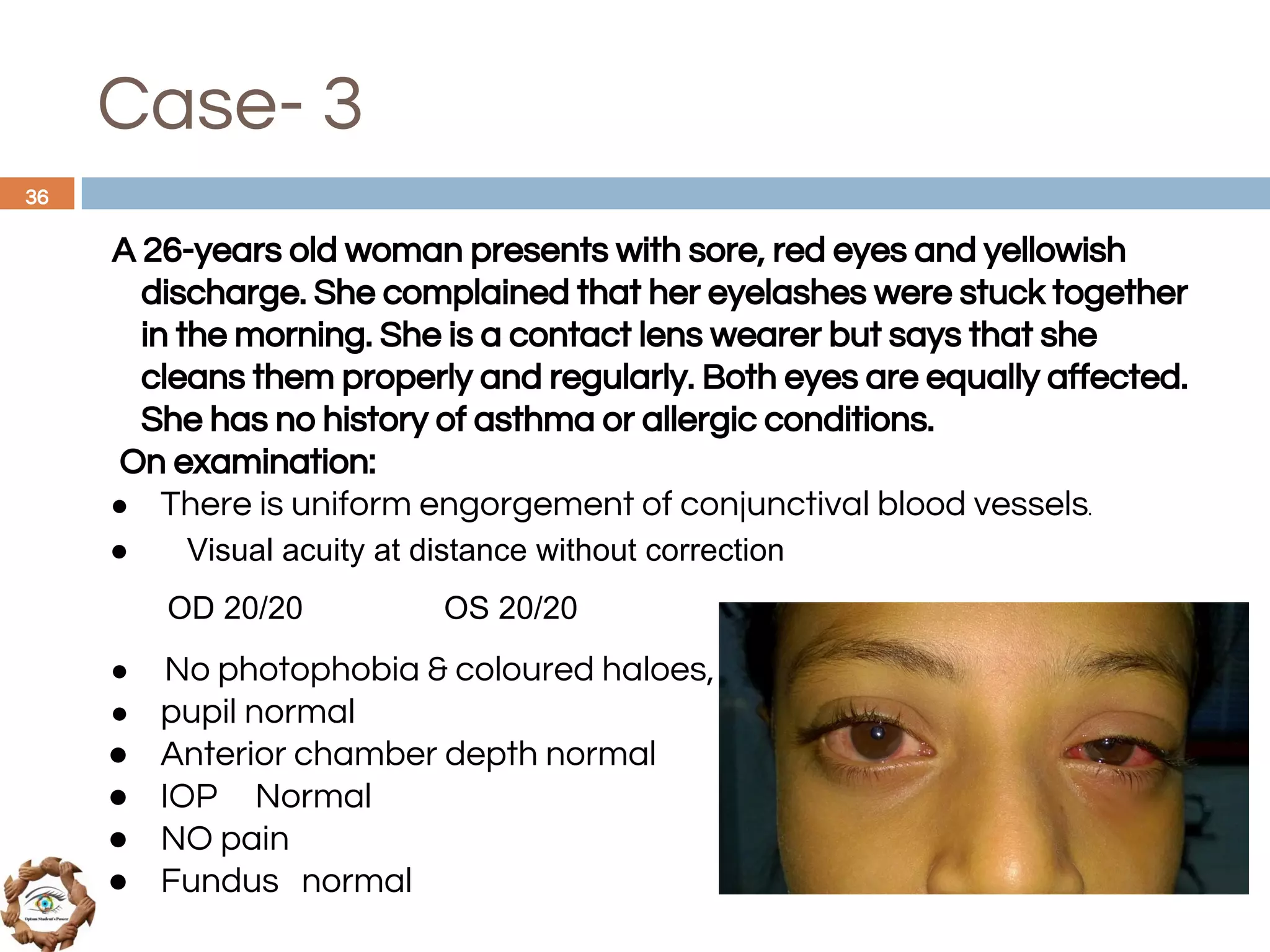
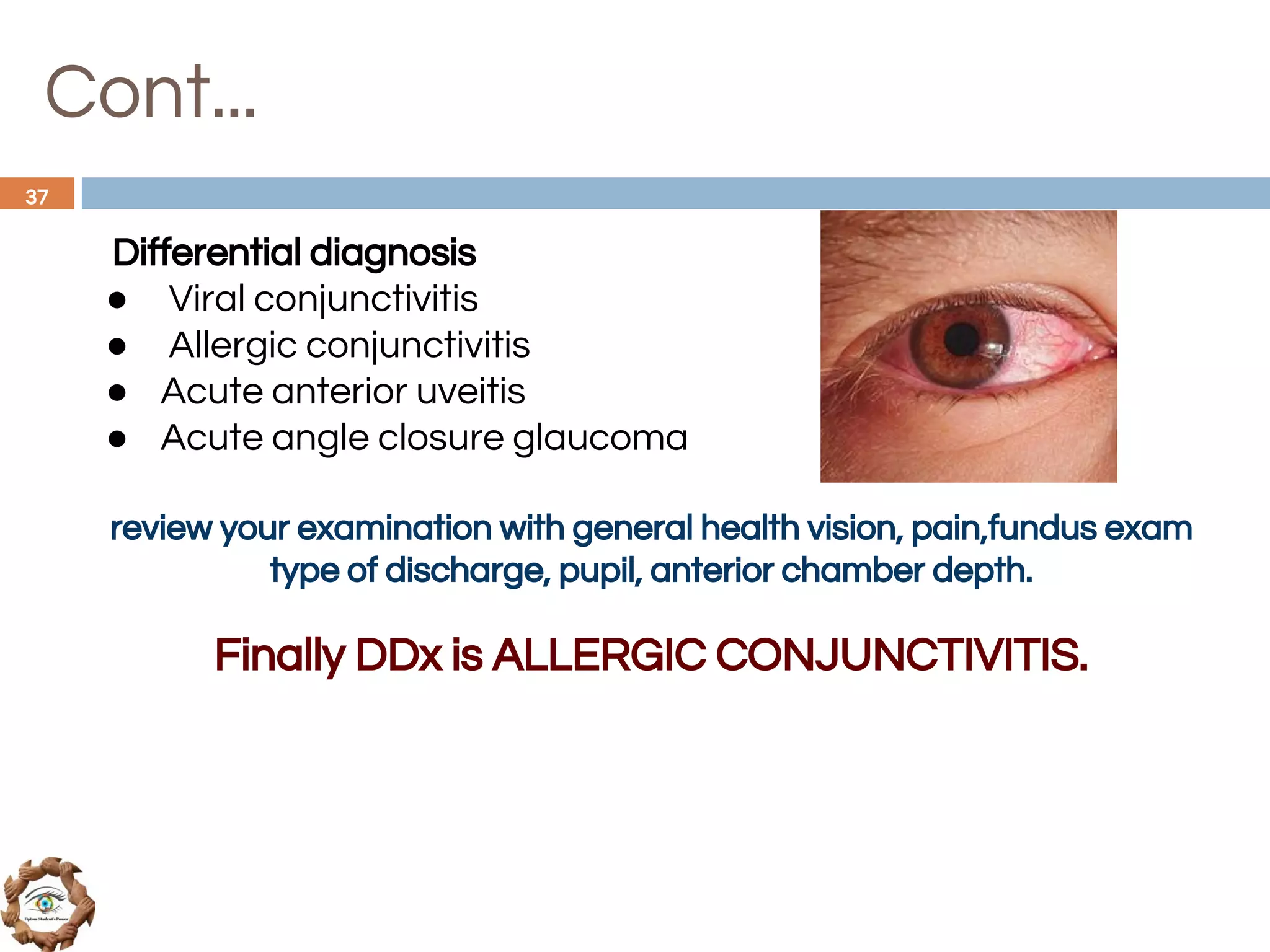
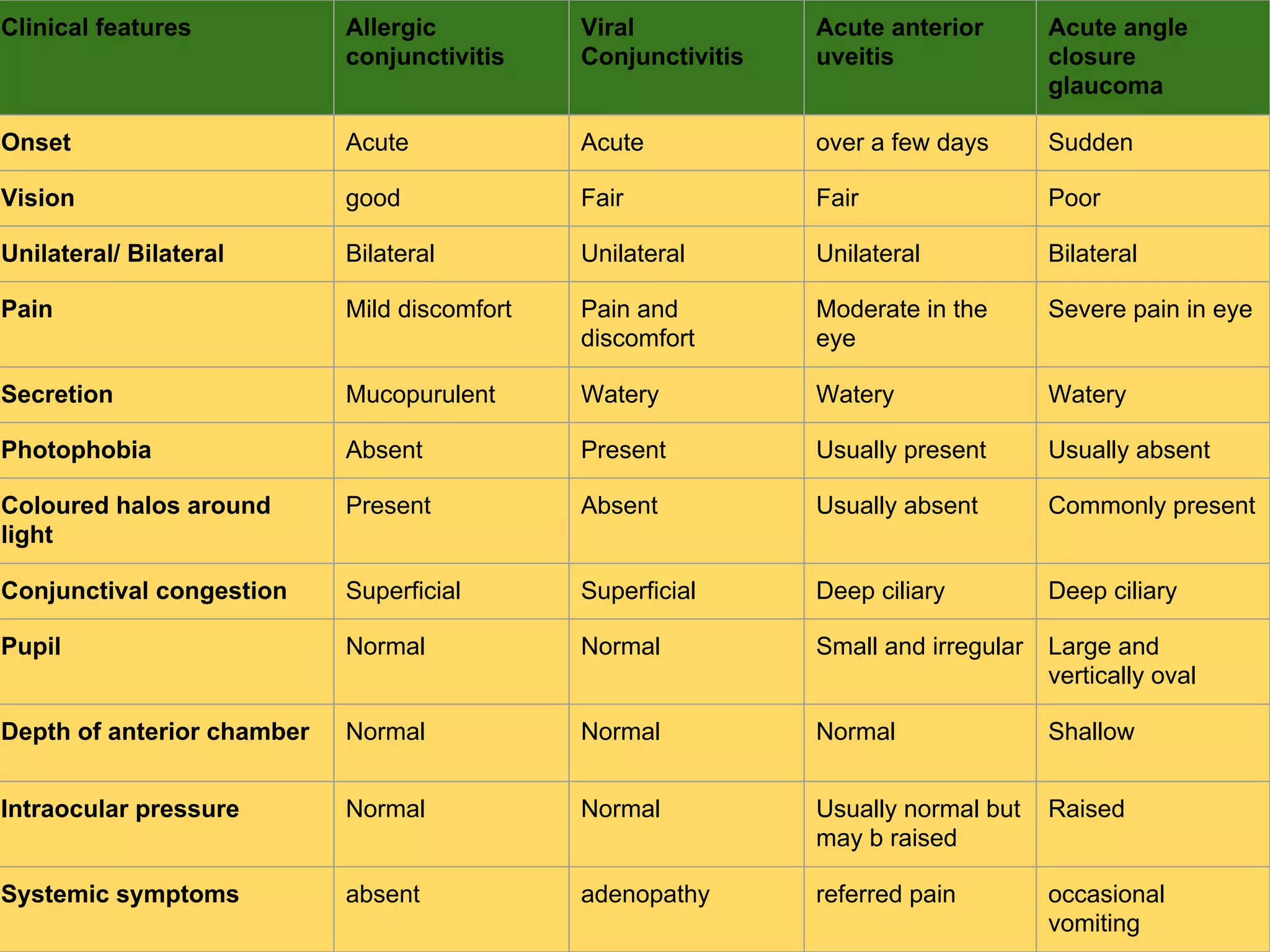
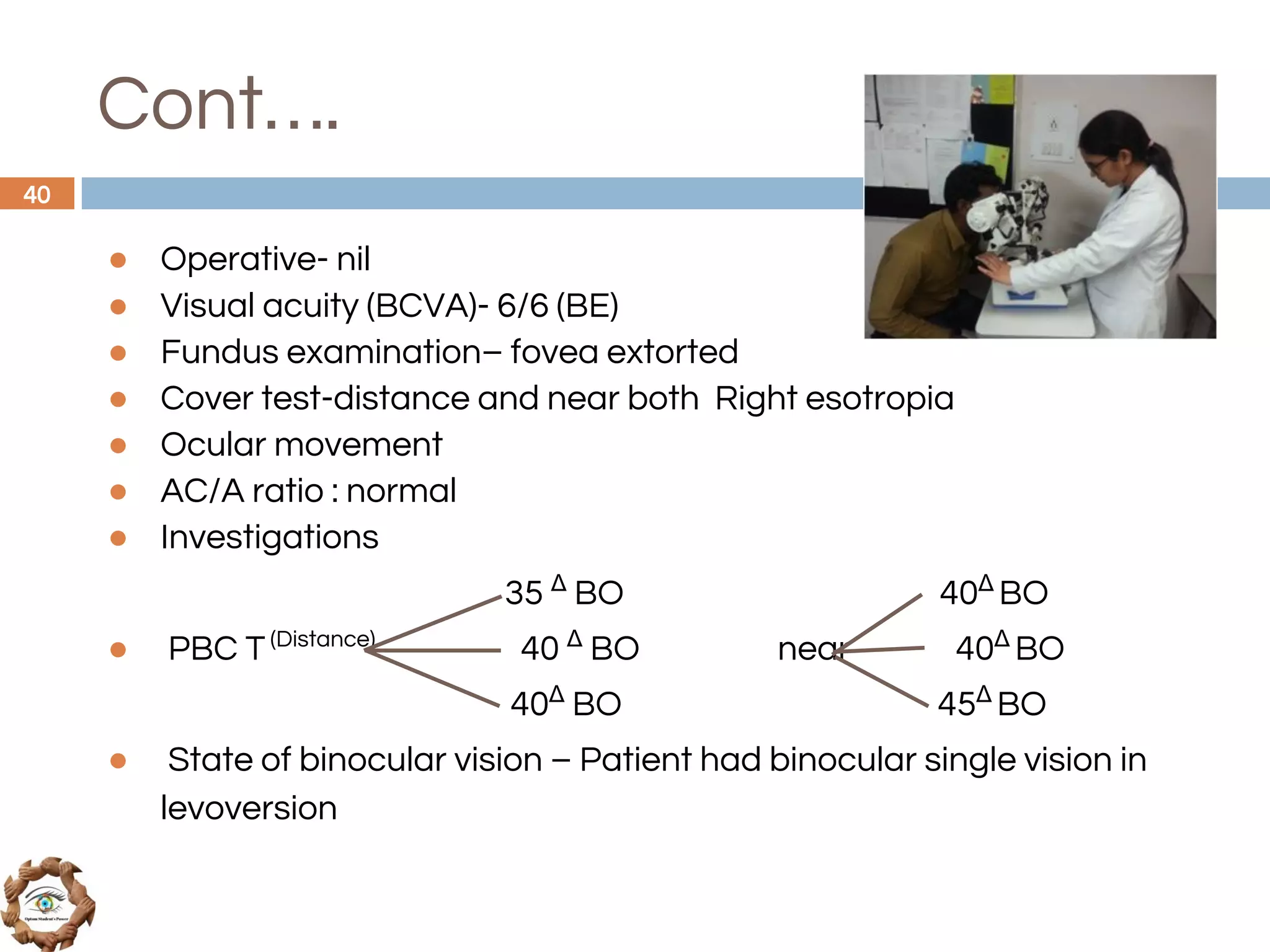
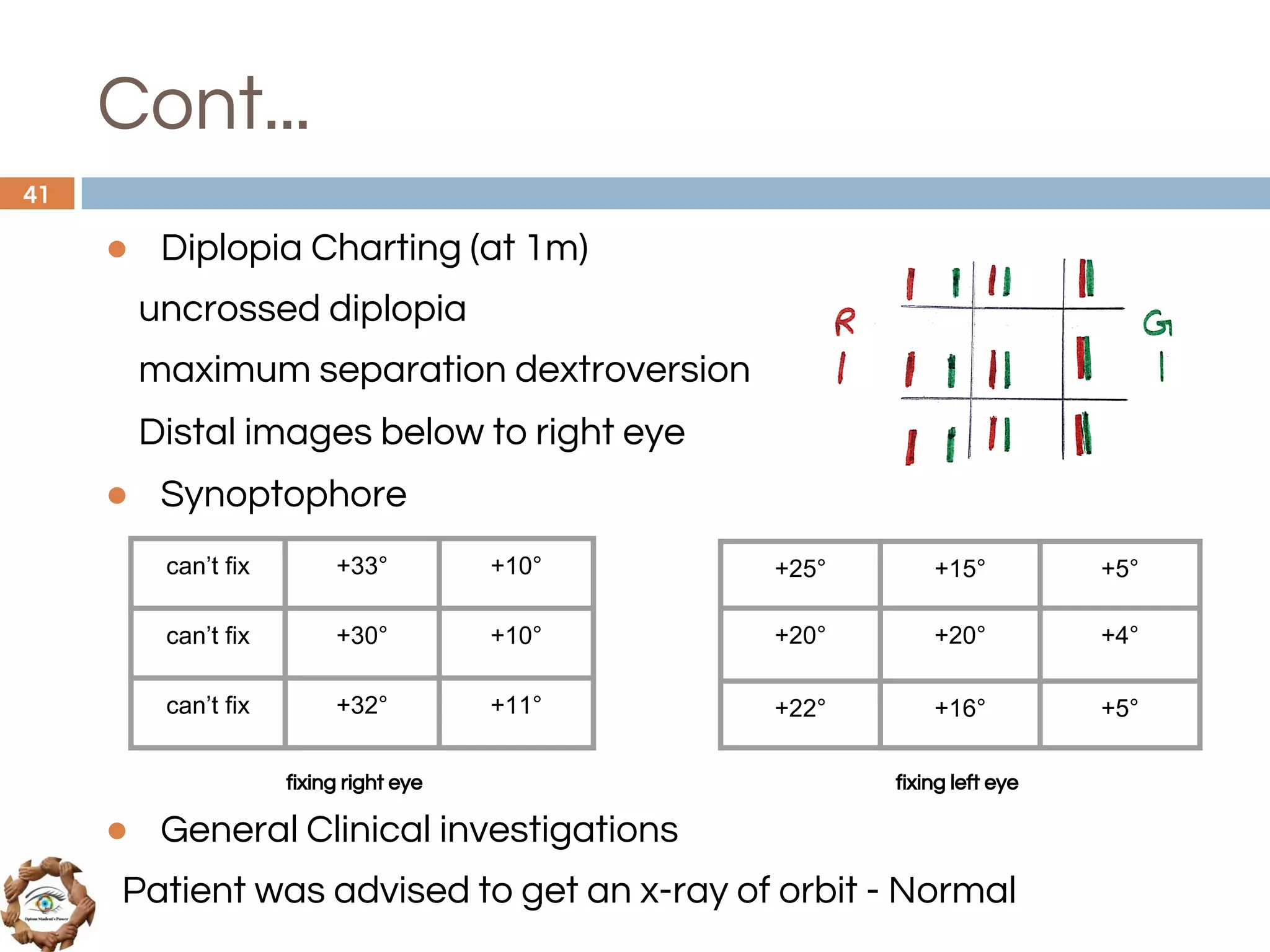
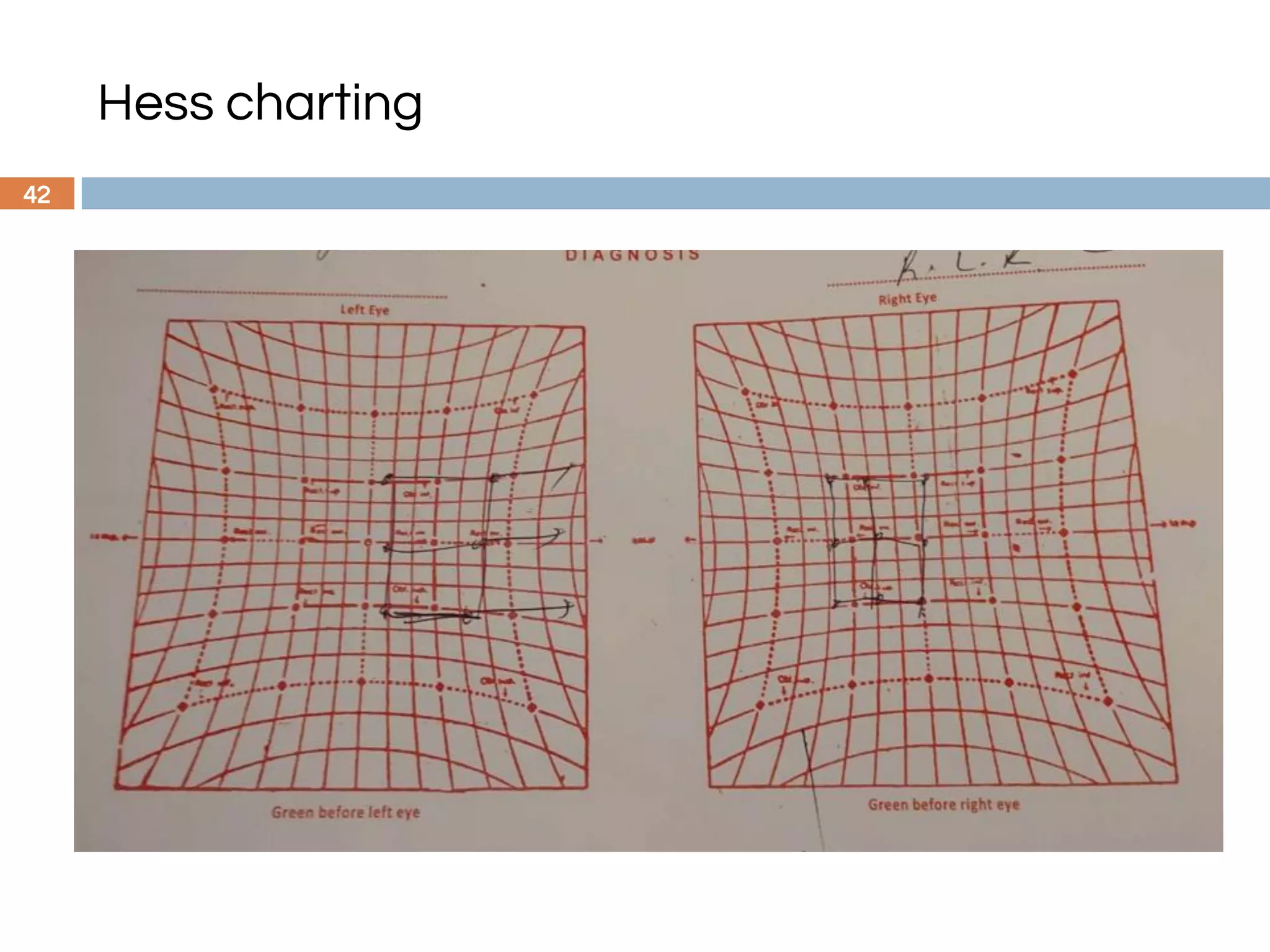
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to differential diagnosis in ocular diseases, emphasizing the systematic collection of patient history and examination findings. It details common ocular symptoms, their causes, and diagnostic errors to avoid, while providing case studies to illustrate the process of generating a differential diagnosis. The structured methodology includes history taking, ocular examinations, and final diagnosis compilation based on patient clinical findings.