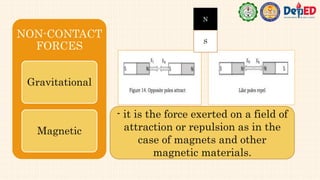
Forces were investigated in relation to how they affect an object's motion. There are two types of forces - contact forces which require touching objects, like applied force, friction, normal force and tension, and non-contact forces which act over a distance without touching, like gravitational and magnetic forces. Balanced forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction and do not cause changes in motion, while unbalanced forces cause changes in motion and are not equal or opposite. The net or resultant force is the sum of all the individual forces acting on an object.