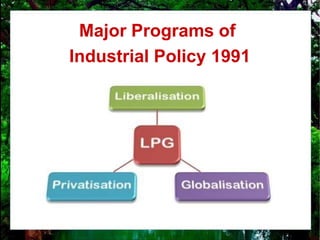
The document discusses the business environment in India. It provides details about the industrial policy of 1991 which aimed to liberalize, privatize, and globalize the Indian economy. This included reducing licensing, allowing more private sector participation, encouraging foreign investment, and reducing public sector control. The policy changes led to increased competition, more demanding customers, rapid technology changes, need for continuous improvement and human resource development, and a shift to a more market-oriented approach for businesses.












































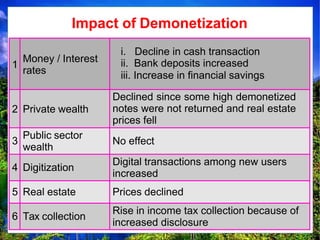
![Cash less economy
Aims and Features of Demonetization
4
Govt. announced demonetization with an aim of
creating a digital economy with the support of formal
financial system / banks. (Internet banking, e-wallets,
PoS [Point of Sale] etc.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade12bs-chapter3businessenvironment-221108232643-78b07a49/85/Grade-12-BS-Chapter-3-Business-Environment-pptx-47-320.jpg)