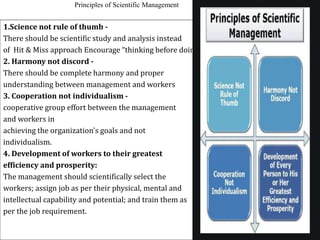
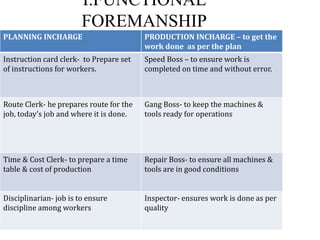
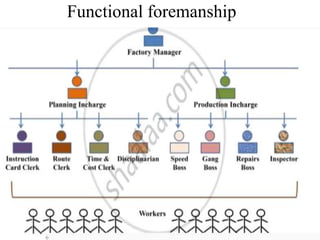
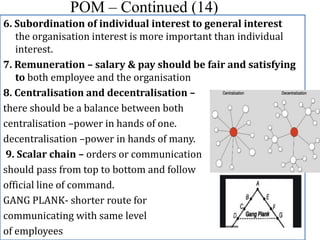
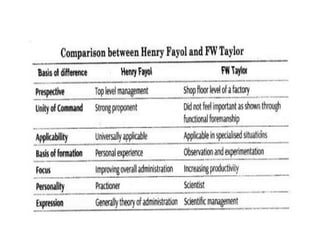
This document discusses several key principles of management. It begins by explaining the meaning and nature of principles of management, noting that they are general guidelines derived from experimentation and observation that can guide managerial decisions. It then outlines several principles, including their universal application, flexibility, role in optimal resource utilization, and ability to adapt to changing environments. The document also summarizes Taylor's scientific management approach and its emphasis on standards, harmony, and worker efficiency. It discusses Fayol's 14 principles of management and the importance of mental revolution among managers and workers for successful implementation of scientific principles.