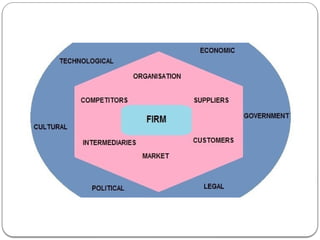
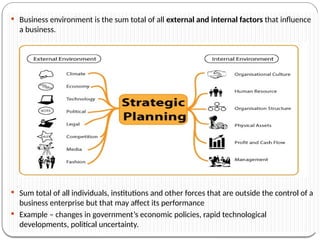
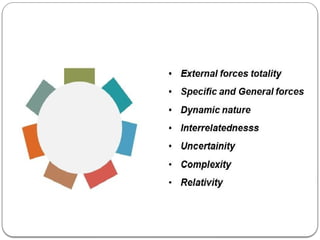
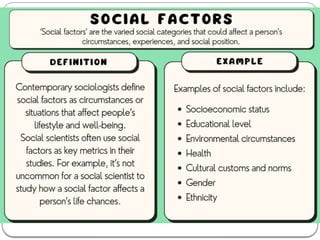
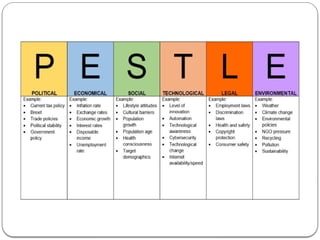
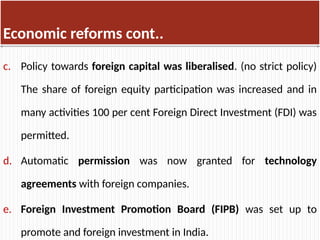
The document discusses the concept of the business environment, which encompasses all external and internal factors influencing a business, including economic, social, technological, political, and legal elements. It emphasizes the dynamic, complex, and uncertain nature of this environment and the importance of adapting to changes to identify opportunities and mitigate threats. Additionally, the document outlines historical economic reforms in India, such as liberalization, privatization, and globalization, alongside the impact of government policy changes on businesses and industries.