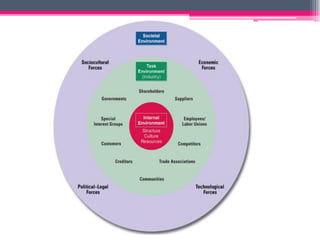
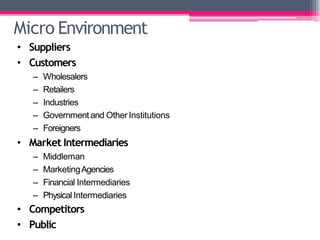
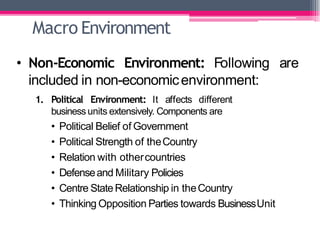
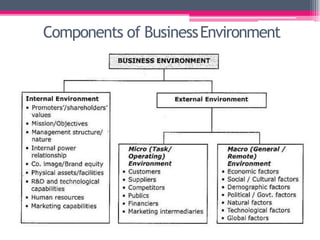
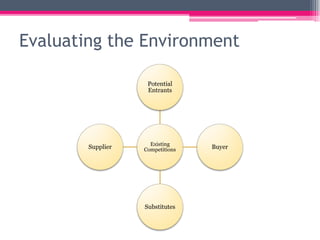
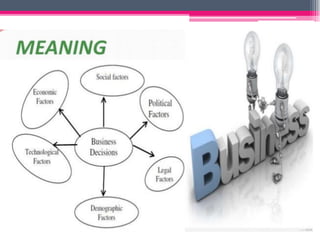
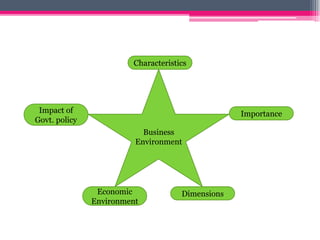
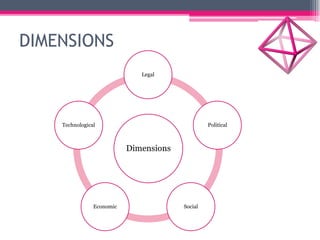
This document provides an overview of business environment. It defines business and its objectives, which include profit, growth, customer satisfaction, and service to society. It discusses the internal and external factors that comprise a business's environment. The external/macro environment includes political, economic, social, technological, demographic, international, and legal factors. It also describes the characteristics, types, importance and impact of evaluating a business's internal and external environment. Key points covered include the economic environment in India related to privatization, liberalization, and industrial policy changes.