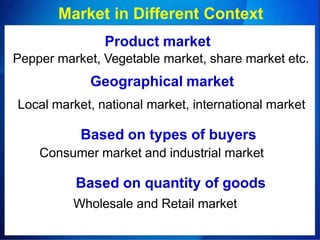
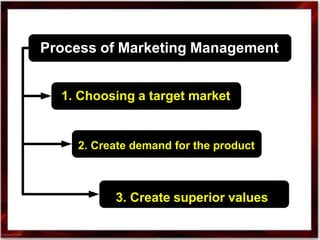
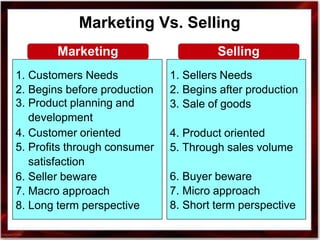
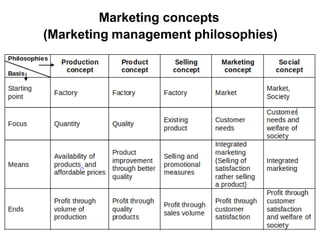
1. Marketing involves identifying consumer needs and wants and satisfying them through the exchange of goods and services. It is a broader concept than just selling.
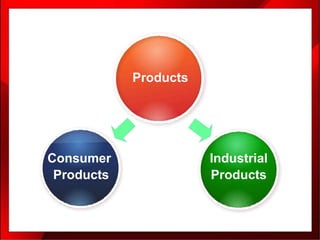
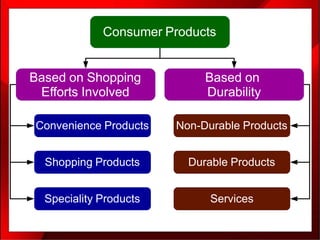
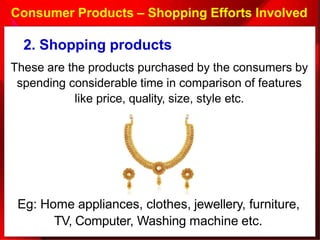
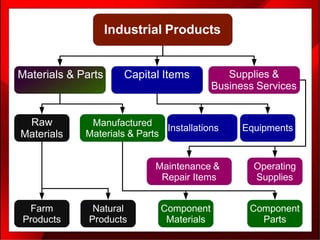
2. The marketing mix, also known as the 4Ps of marketing, refers to the combination of product, price, place (distribution), and promotion that a company uses to bring its product or service to customers.
3. Marketing plays an important role in the economy by helping economic development and raising standards of living through activities like new product development, distribution, pricing, and promotion which increase consumption.