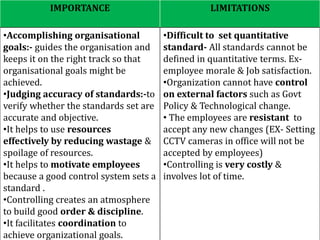
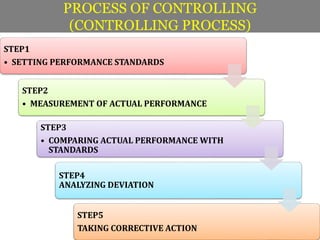
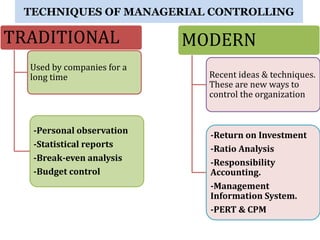
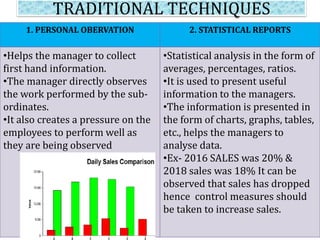
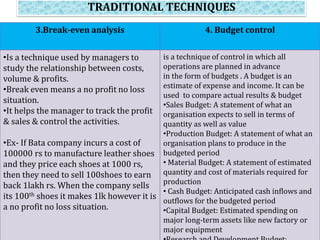
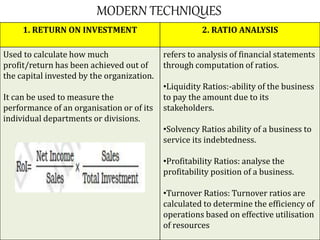
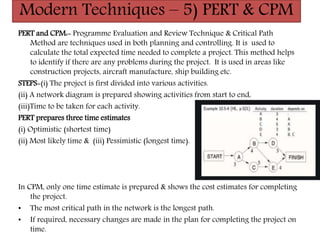
Controlling ensures that organizational activities are performed according to plans and resources are used efficiently to achieve goals. The controlling process involves setting standards, measuring actual performance, comparing to standards, analyzing deviations, and taking corrective actions. Traditional controlling techniques include personal observation, statistical reports, break-even analysis, and budget control. Modern techniques include return on investment, ratio analysis, responsibility accounting, management information systems, PERT/CPM, and management audits. Controlling is an essential function for accomplishing organizational goals, evaluating standards, and motivating employees.