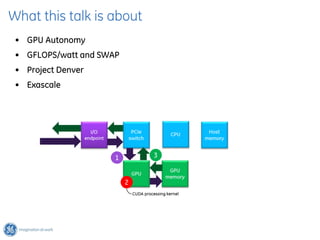
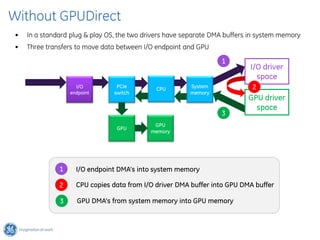
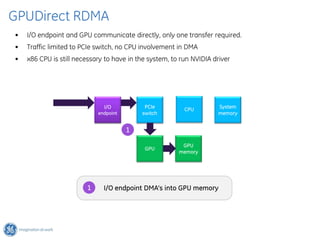
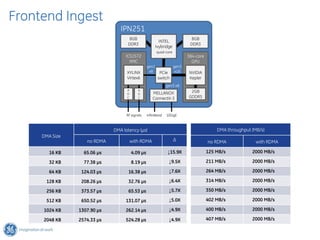
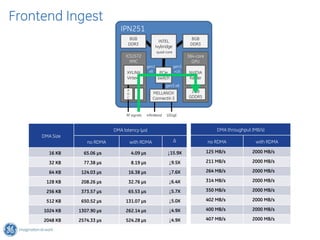
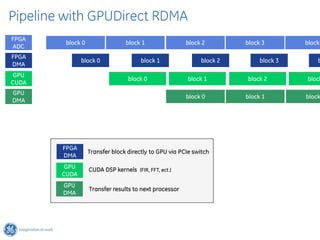
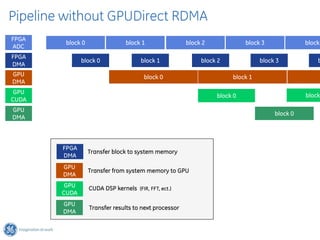
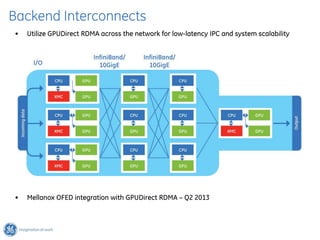
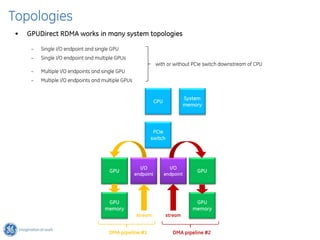
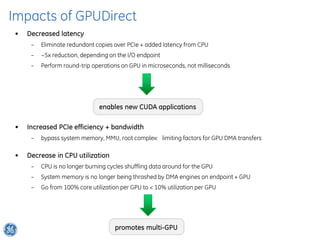
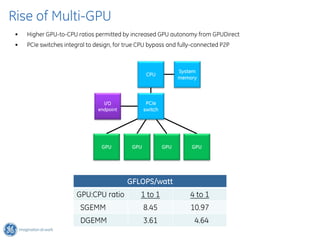
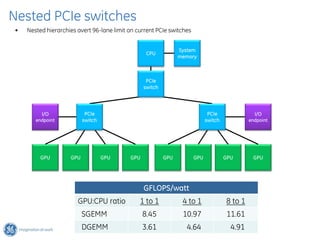
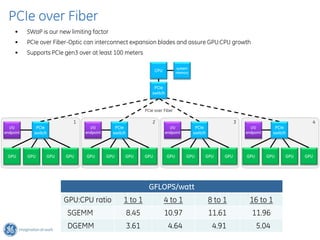
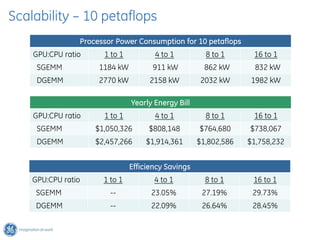
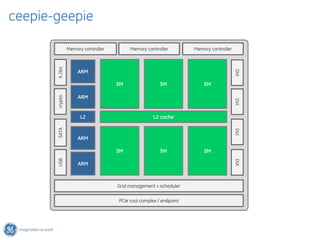
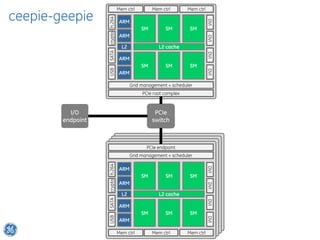
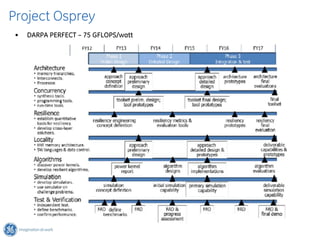
The document discusses GPU Direct RDMA and its relevance to green multi-GPU architectures, emphasizing reduced data transfer latency and improved efficiency through direct GPU communication. By eliminating redundant data copies and CPU involvement, GPUDirect allows for more optimal GPU utilization and scalability in high-performance computing. It also explores advancements in system integration and future projects aimed at enhancing heterogeneous computing capabilities.