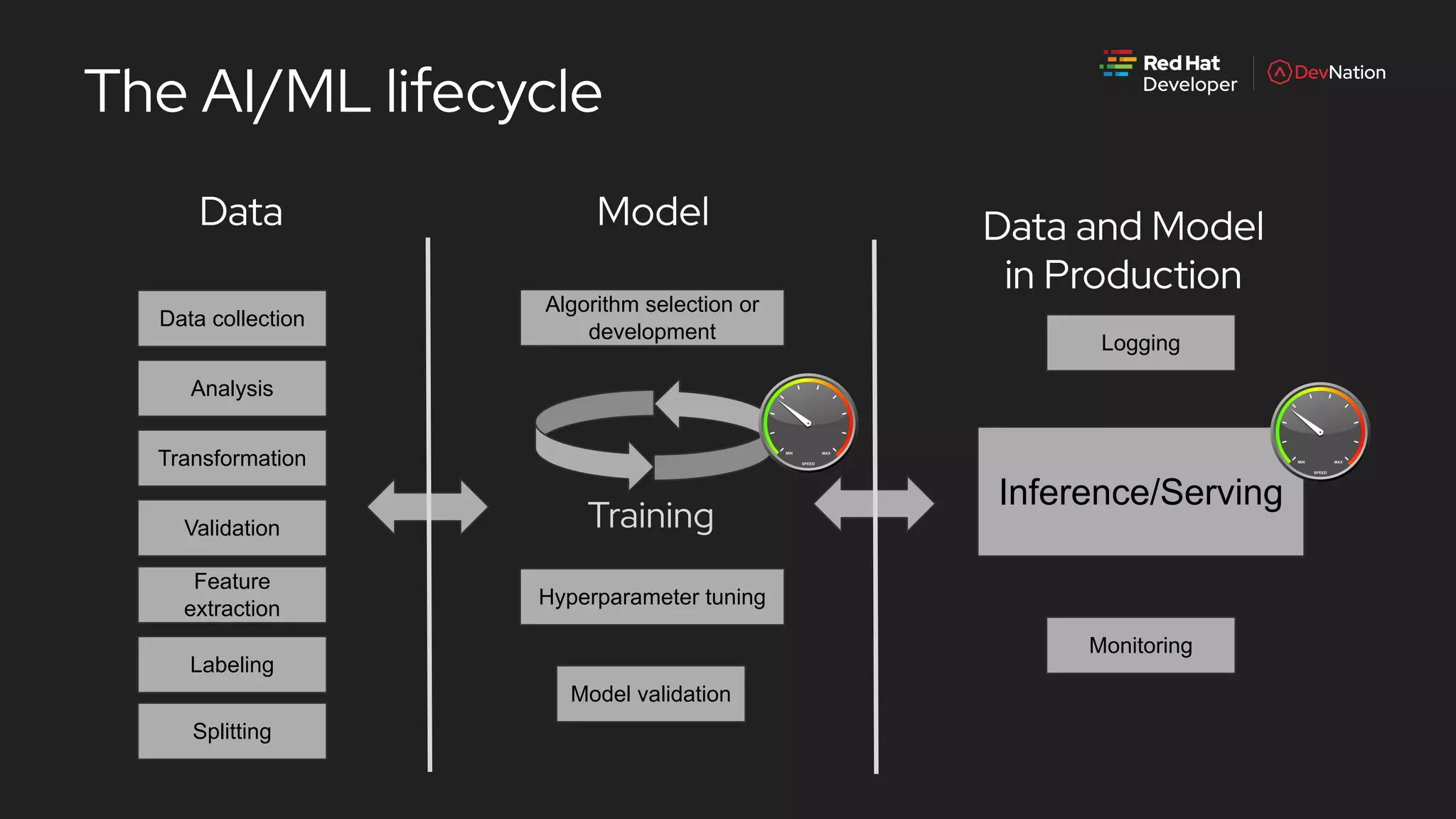
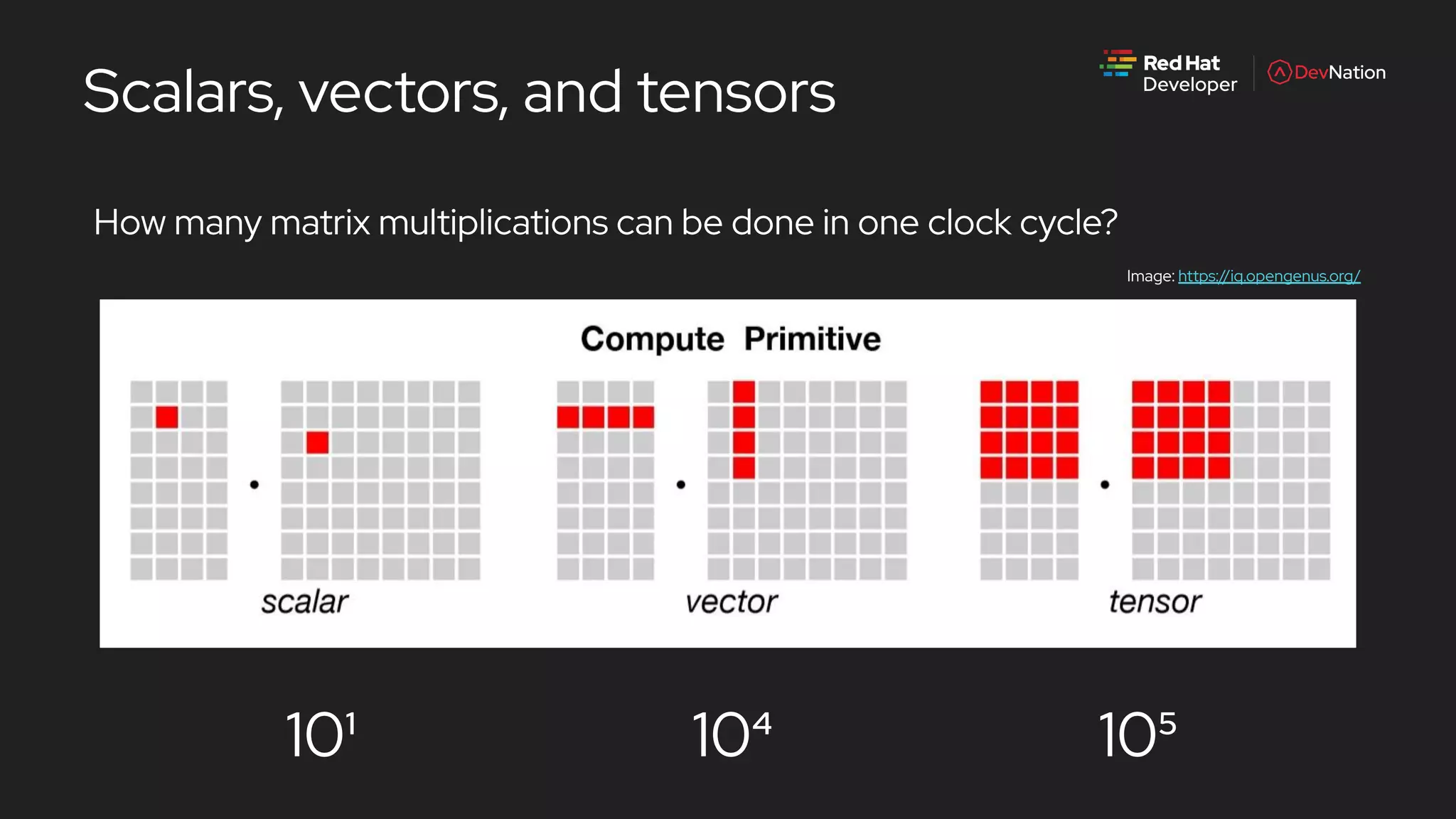
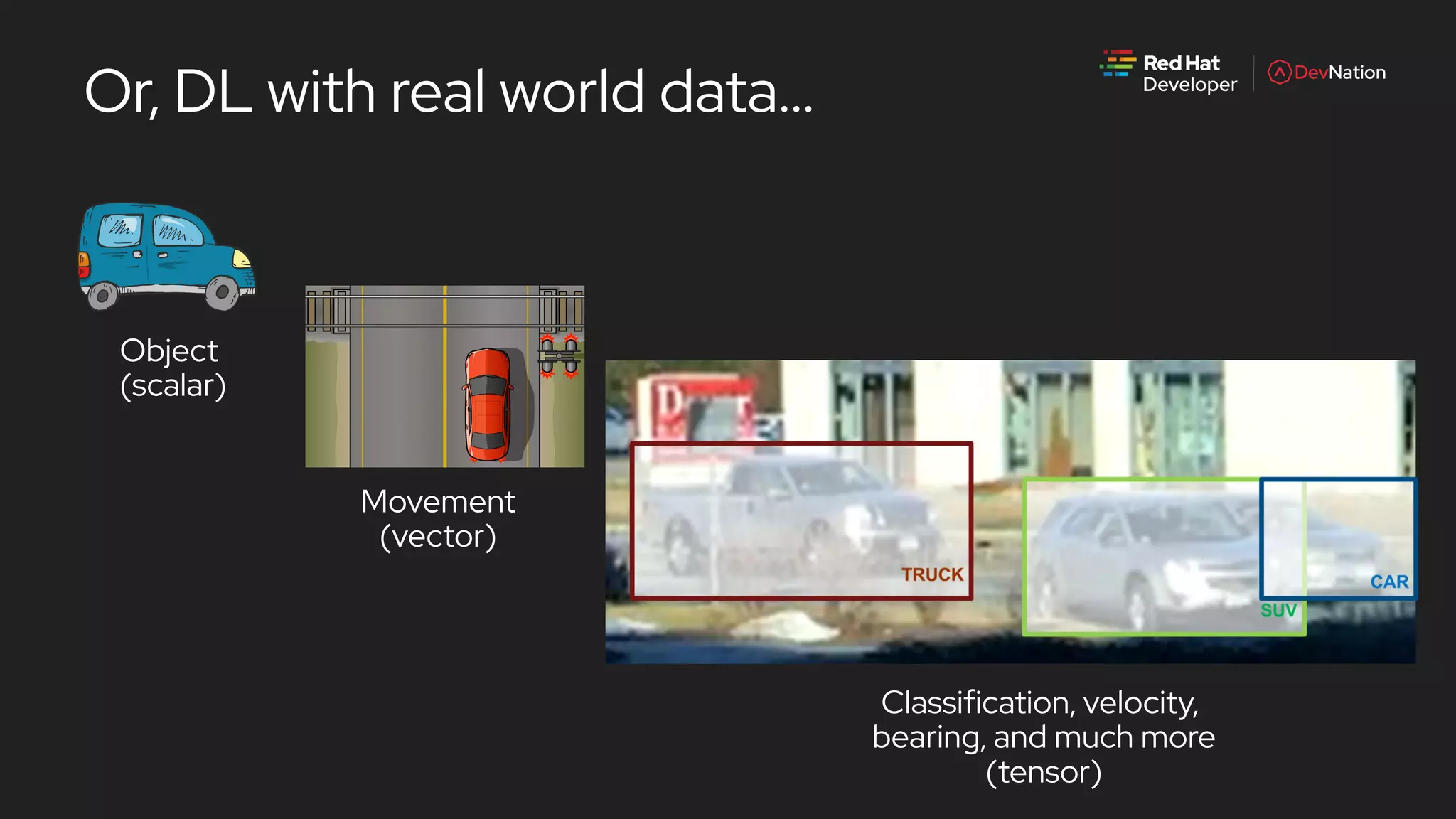
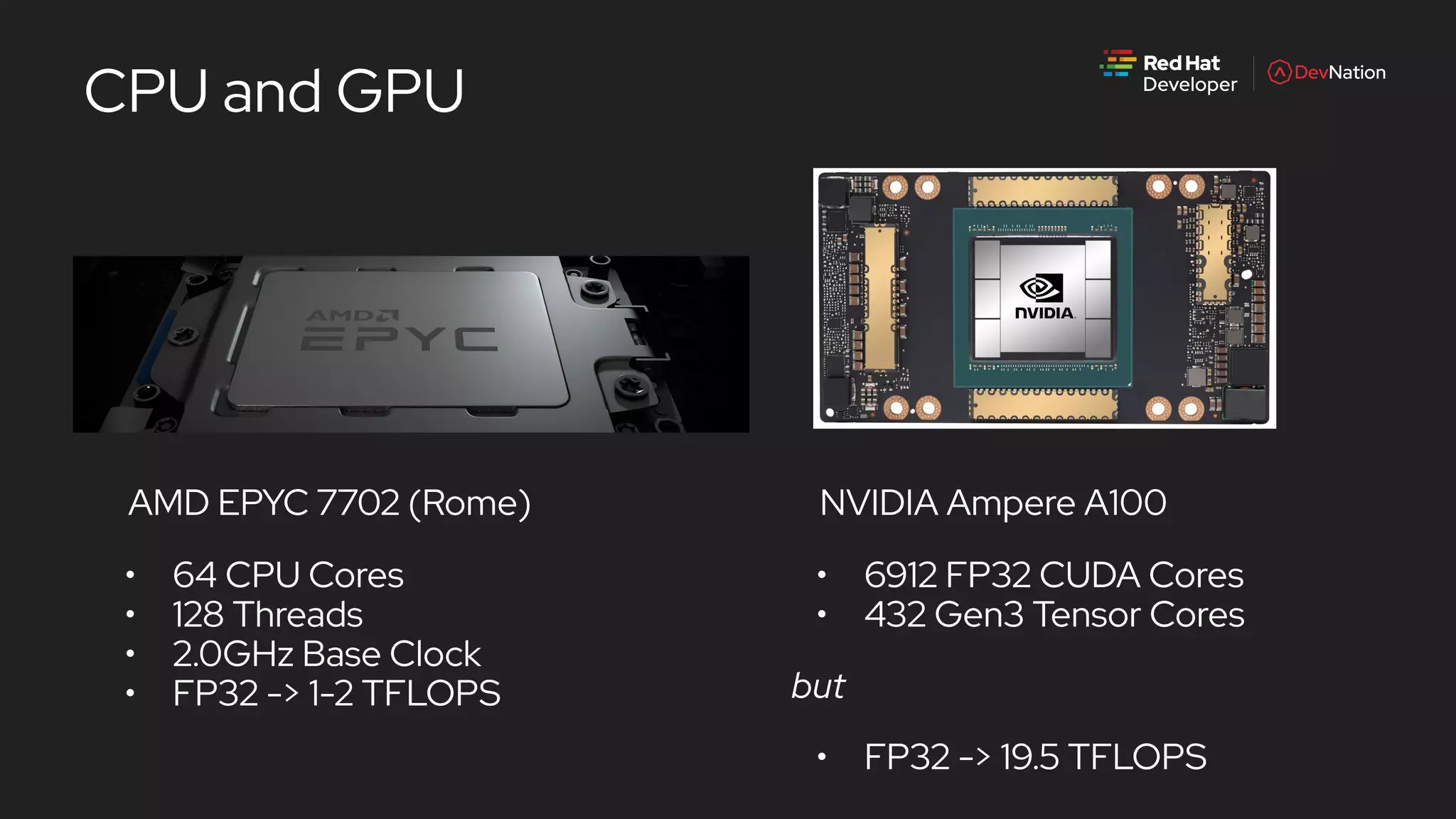
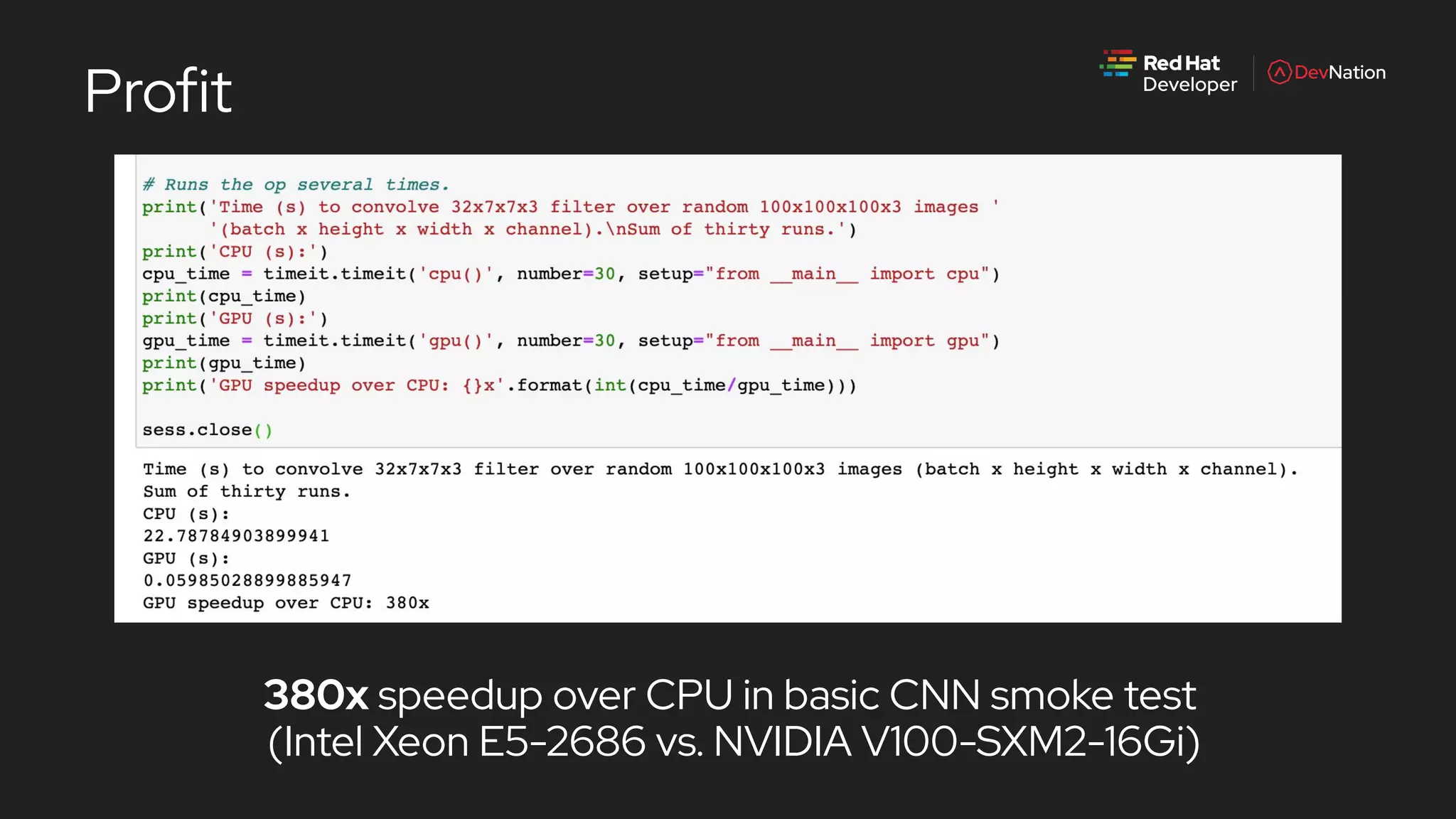
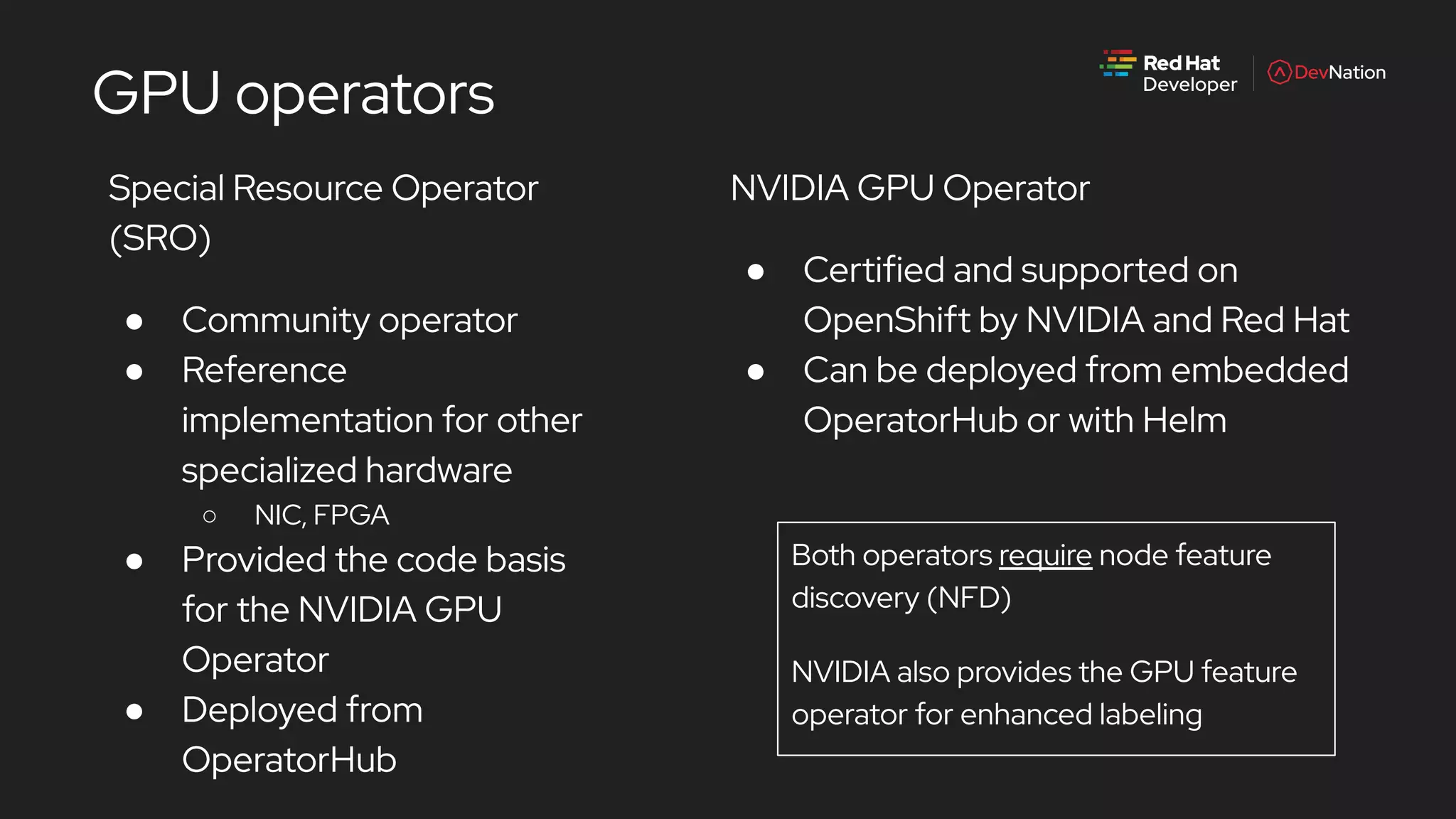
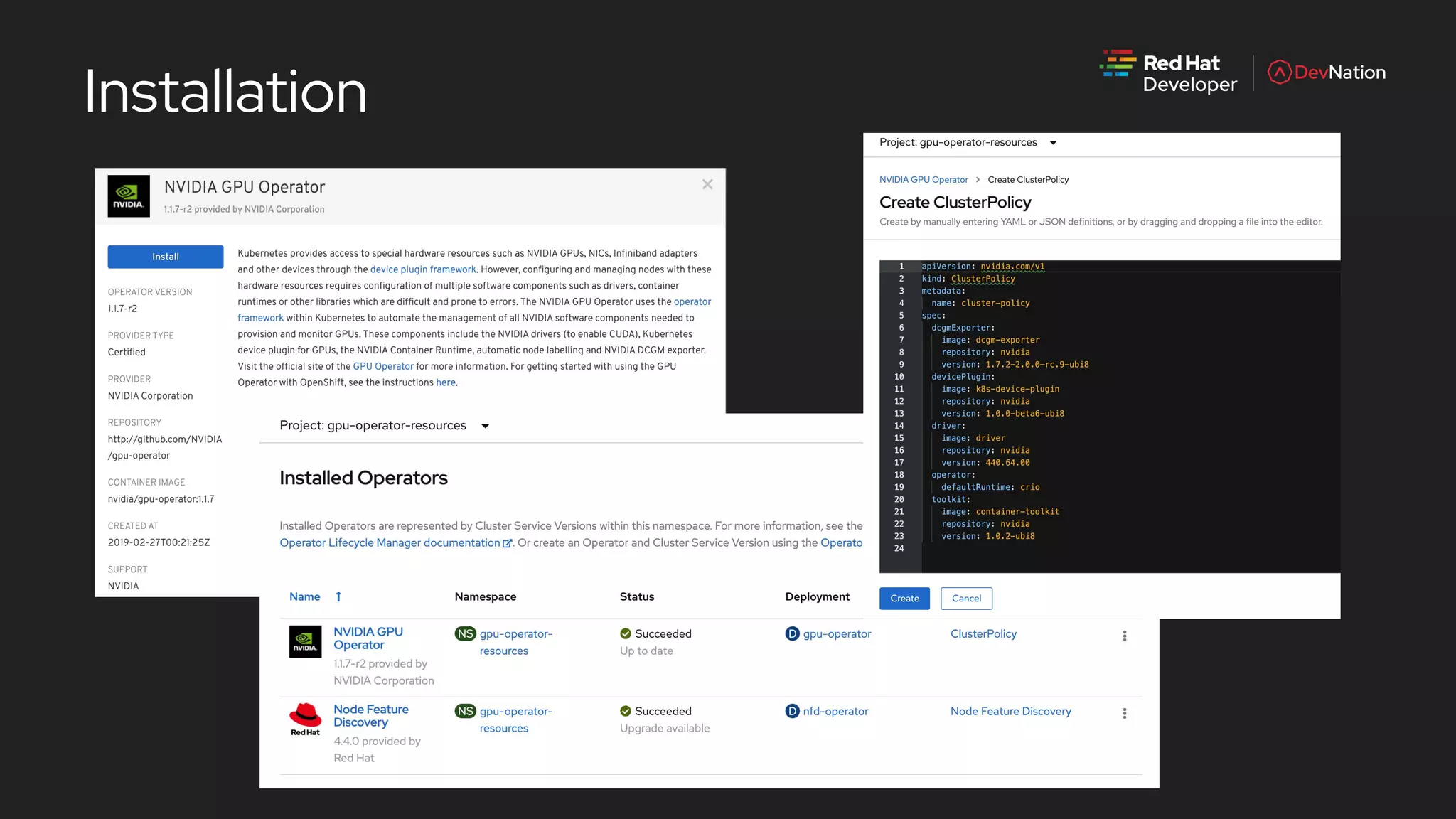
The document is a presentation by Pete Mackinnon on GPU enablement for data science on OpenShift, detailing technical aspects of the AI/ML lifecycle and components of GPU support. It discusses the significant performance improvements GPUs can provide in data processing compared to CPUs, including hardware specifications and examples of accelerated workloads. The NVIDIA GPU operator and its deployment in OpenShift environments are explored, emphasizing its role in facilitating GPU resource management and monitoring.