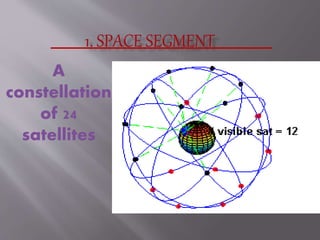
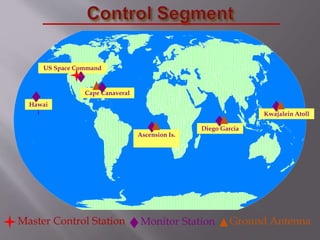
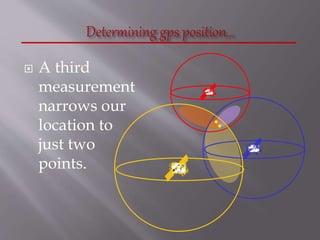
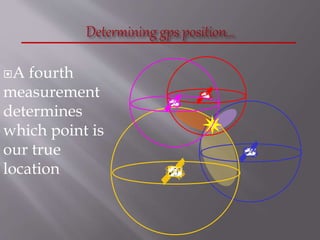
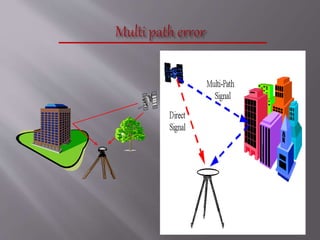
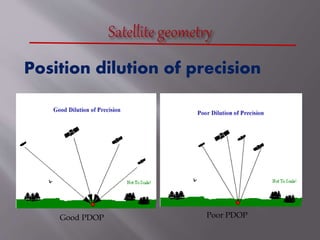
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system developed by the U.S. Department of Defense, consisting of 24 satellites in orbit and becoming fully operational in 1994. GPS is essential for various applications such as navigation, surveying, and emergency services, providing precise location data through a receiver that calculates distances from multiple satellites. The system incurs about $750 million in annual maintenance costs and offers free, reliable, and all-weather services to unlimited users.