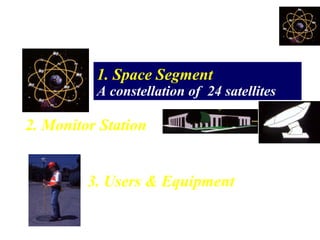
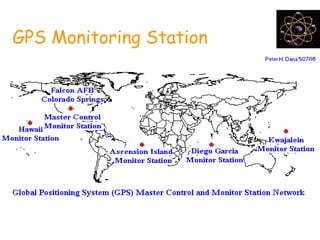
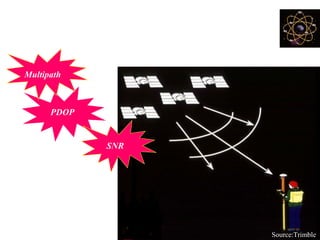
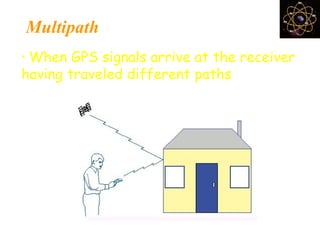
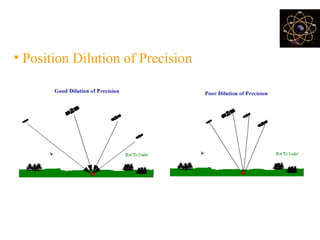
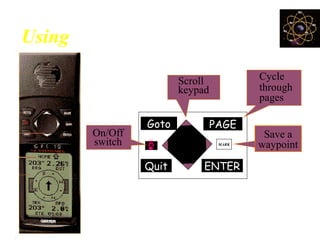
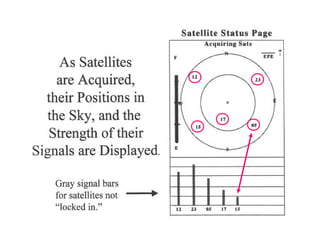
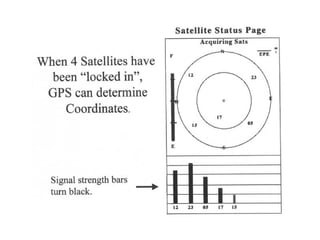
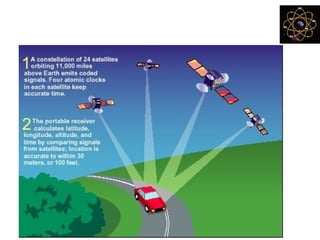
This document provides an overview and review of the book "Global Positioning System" by Akash Deep Sharma. The 232-page book published in 2008 provides a comprehensive guide to GPS technology, explaining how GPS works, its various components and uses for navigation, recreation, and other applications. It covers topics such as satellite positioning, sources of error, augmented GPS, and future improvements and alternatives to GPS from other countries. The review notes that the book is technically detailed and most suitable for readers interested in developing an understanding of GPS systems and applications.