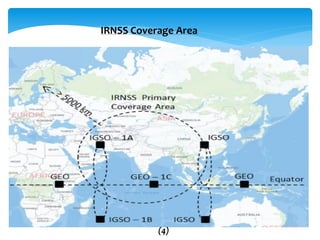
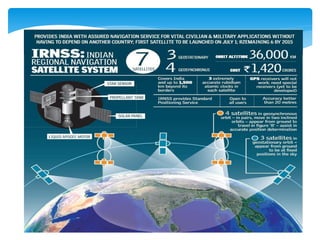
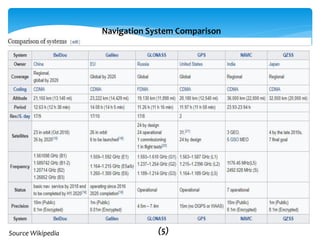
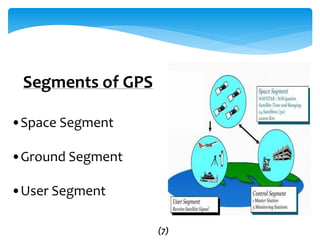
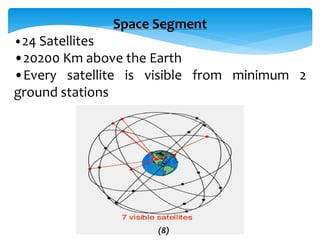
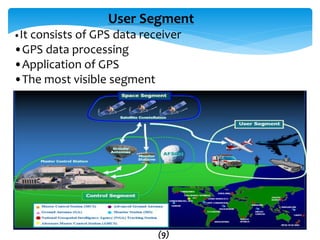
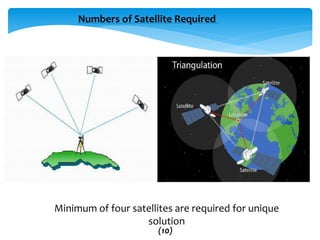
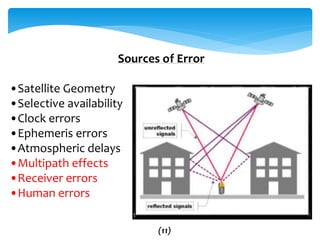
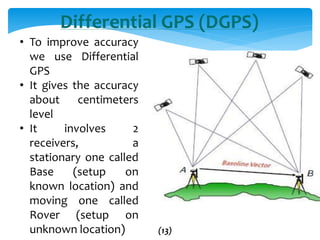
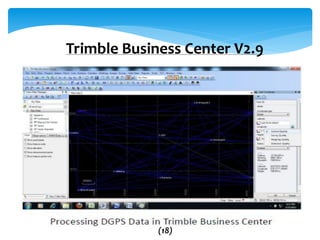
This document provides an overview of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, and regional systems like IRNSS. It discusses the space segment consisting of satellites, ground segment of control stations, and user segment of receivers. At least 4 satellites are needed for positioning. Errors from factors like satellite geometry and atmosphere are reduced with Differential GPS (DGPS) using a stationary base station. DGPS allows centimeter-level accuracy and is used for applications like boundary demarcation, construction surveys, and vehicle tracking. Methods include static, PPK kinematic, RTK, and RTX. The document presents information on IRNSS coverage, system comparisons,