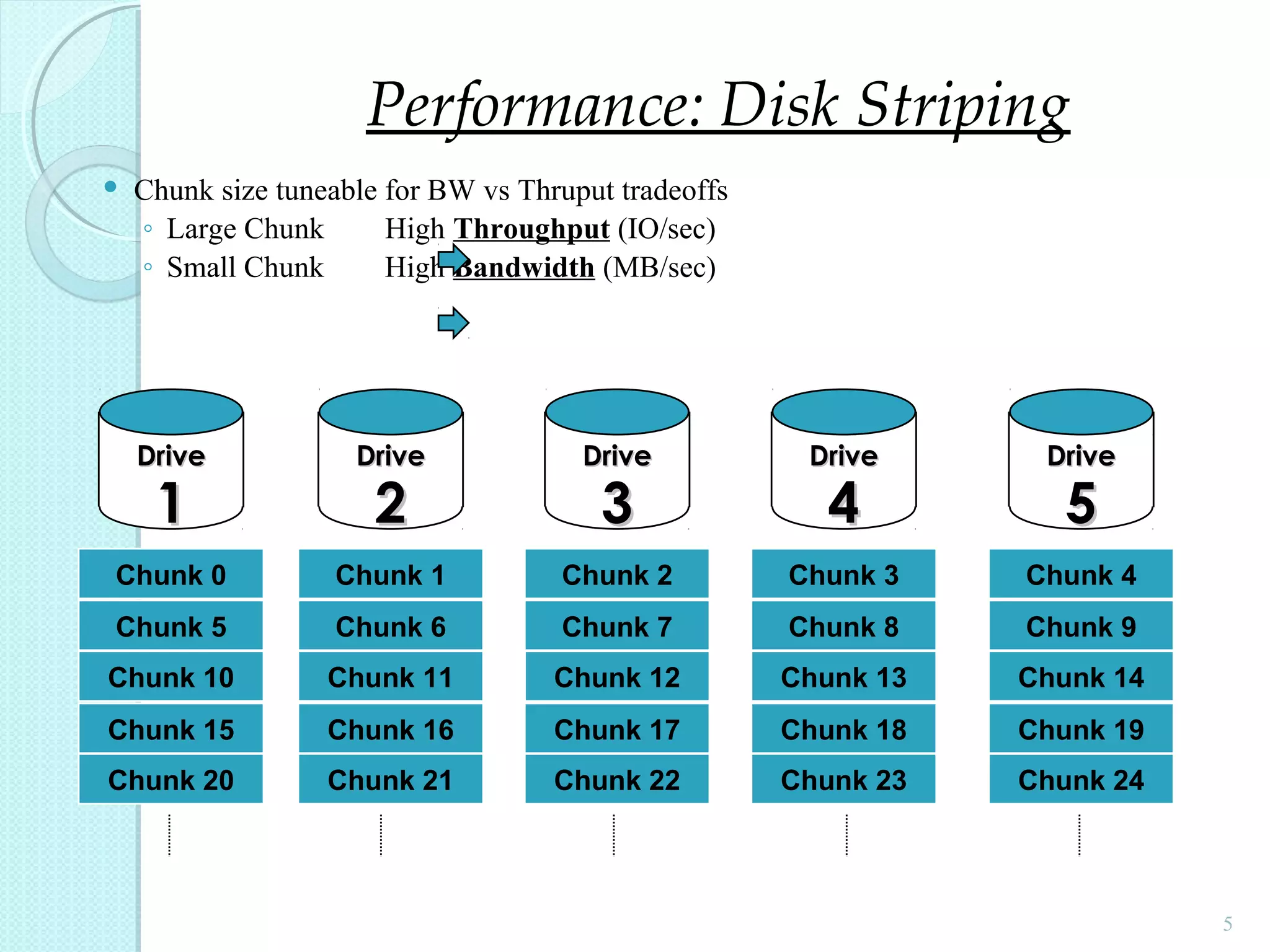
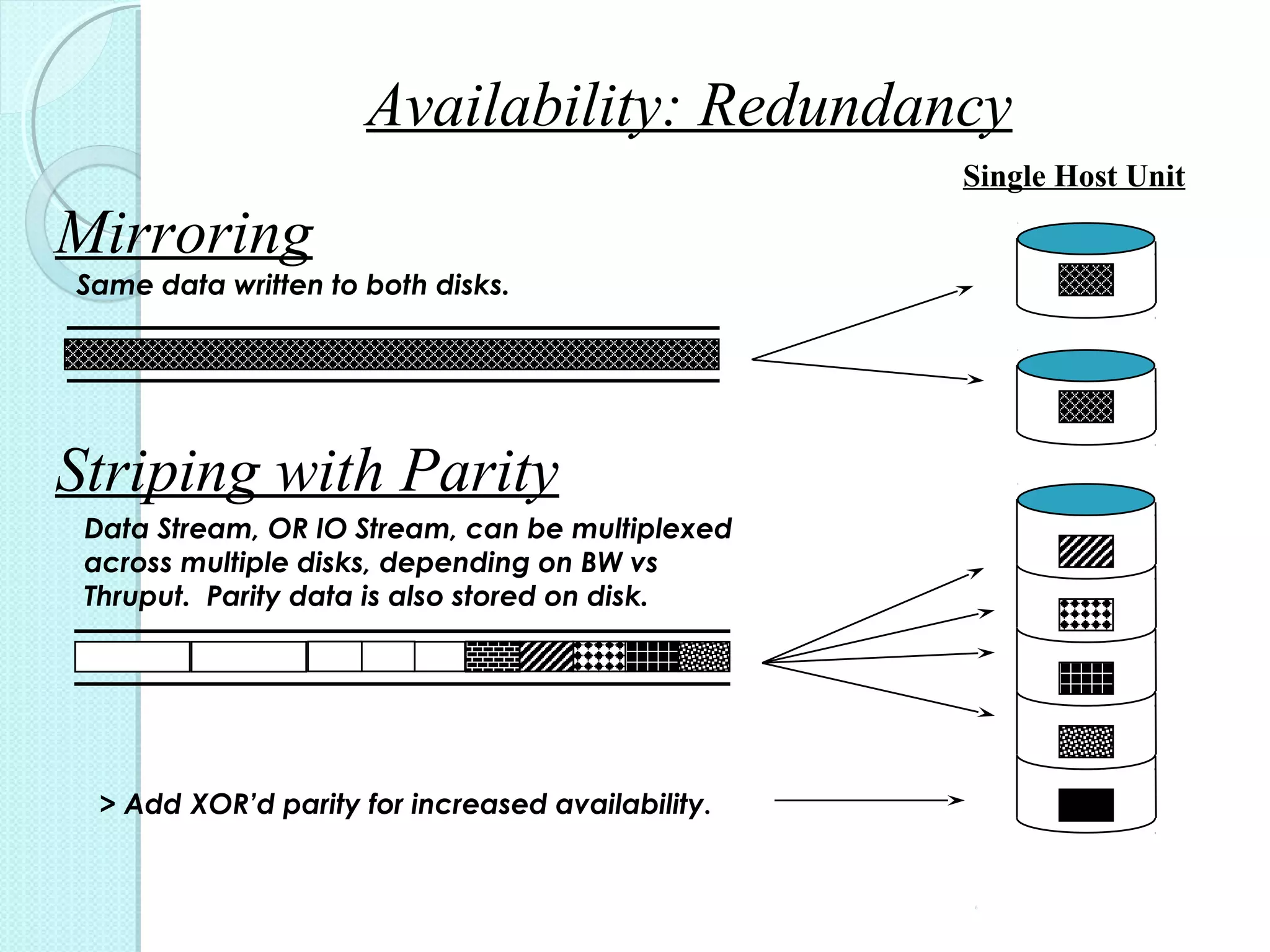
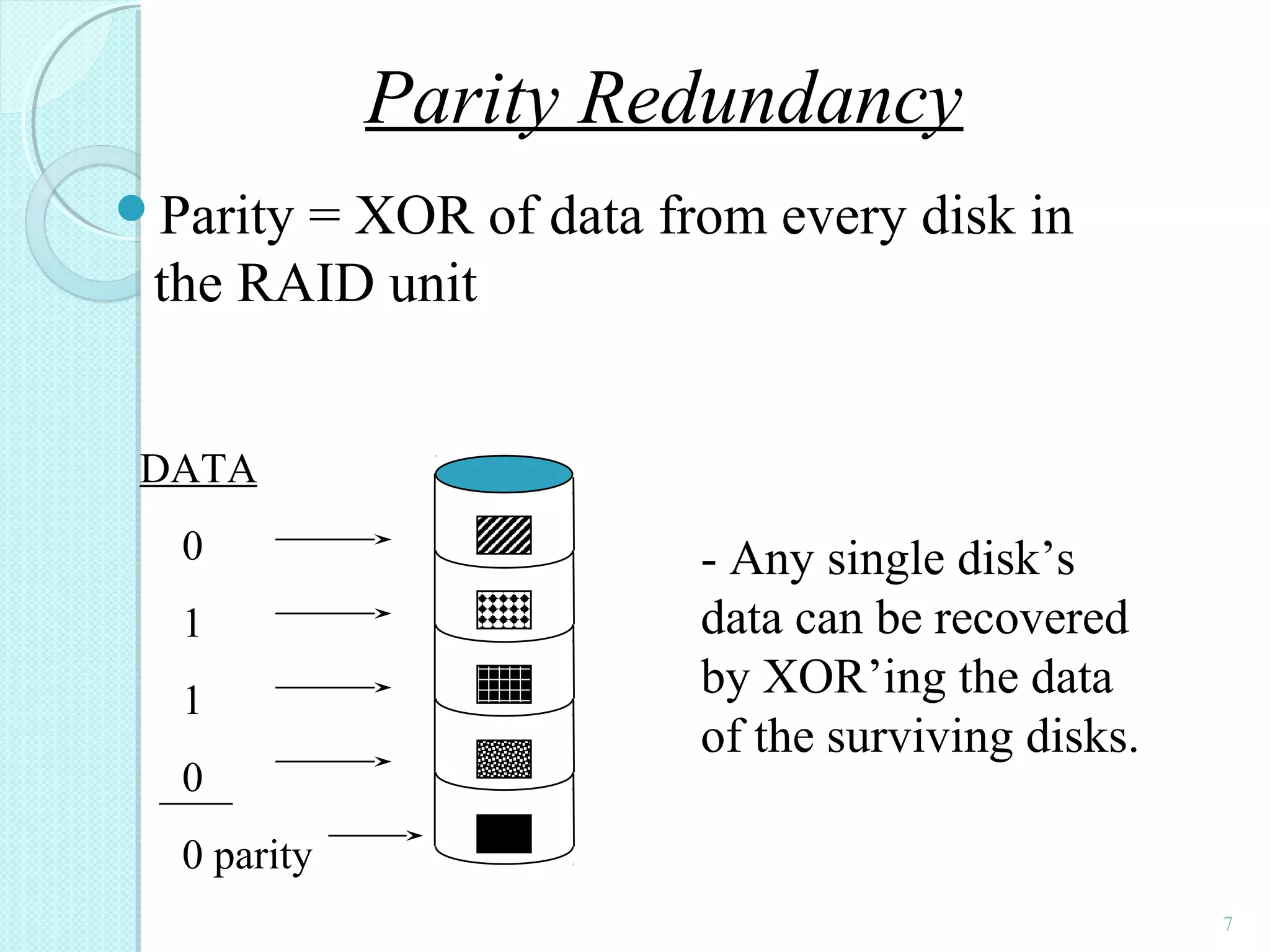
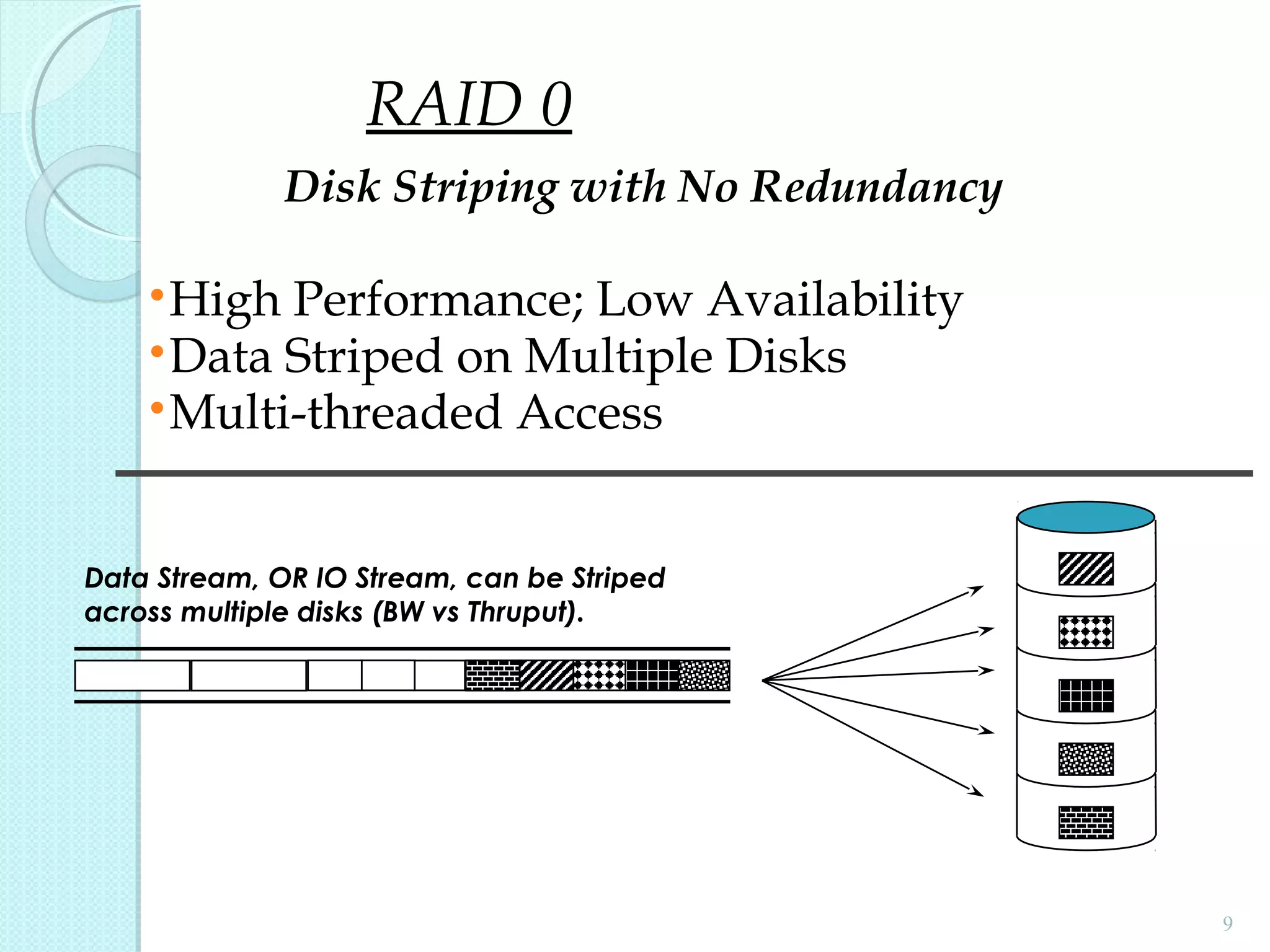
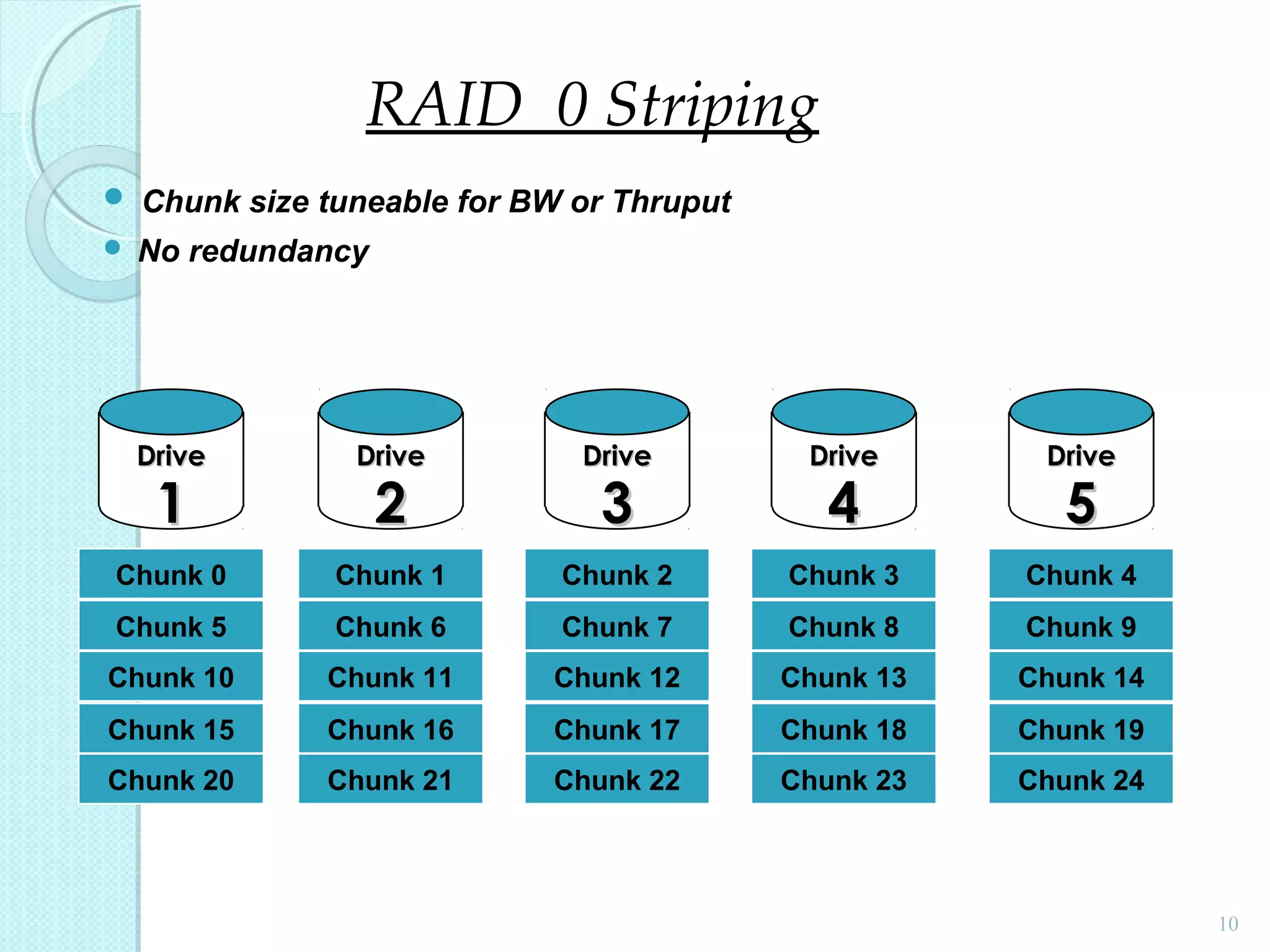
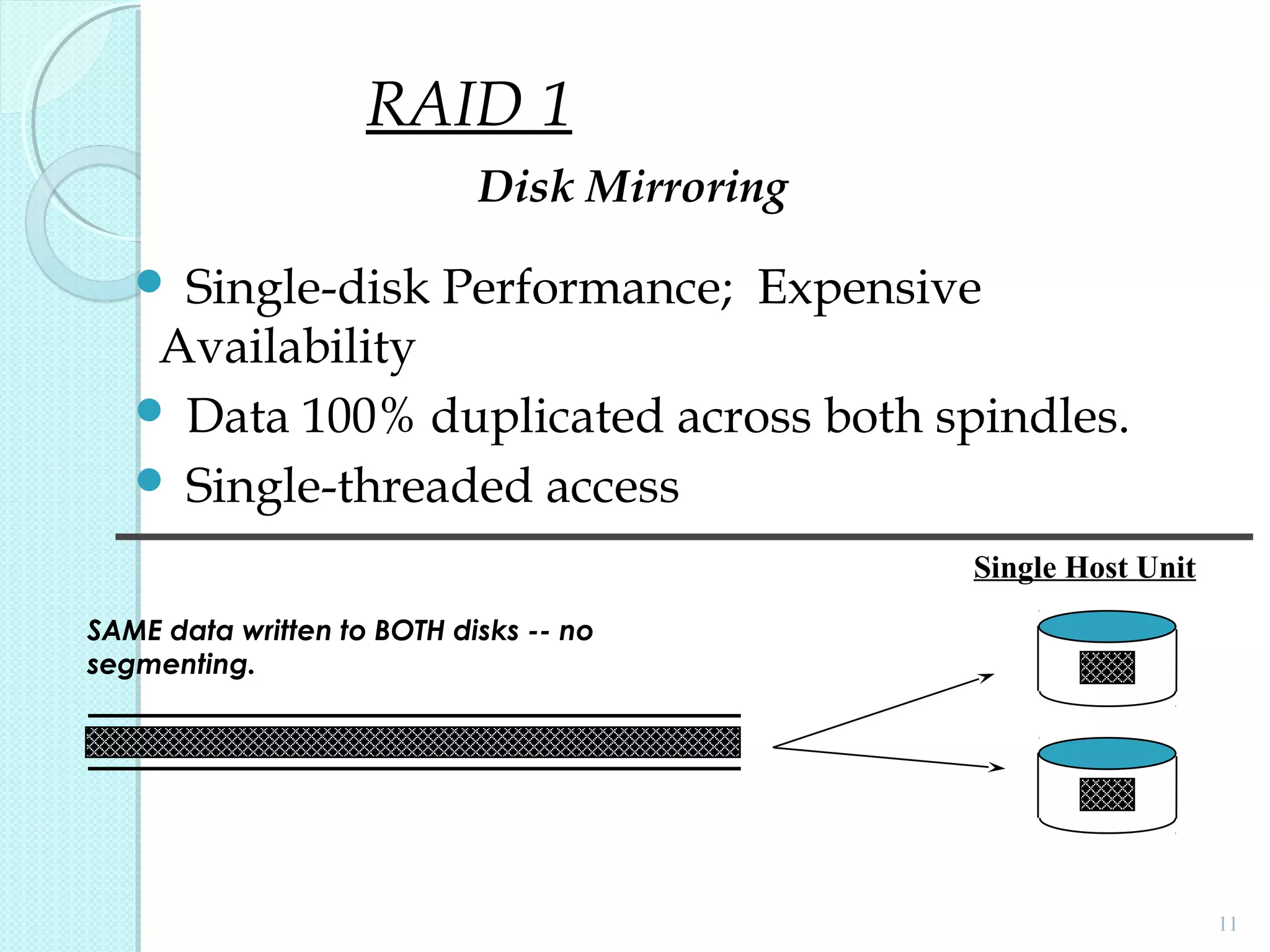
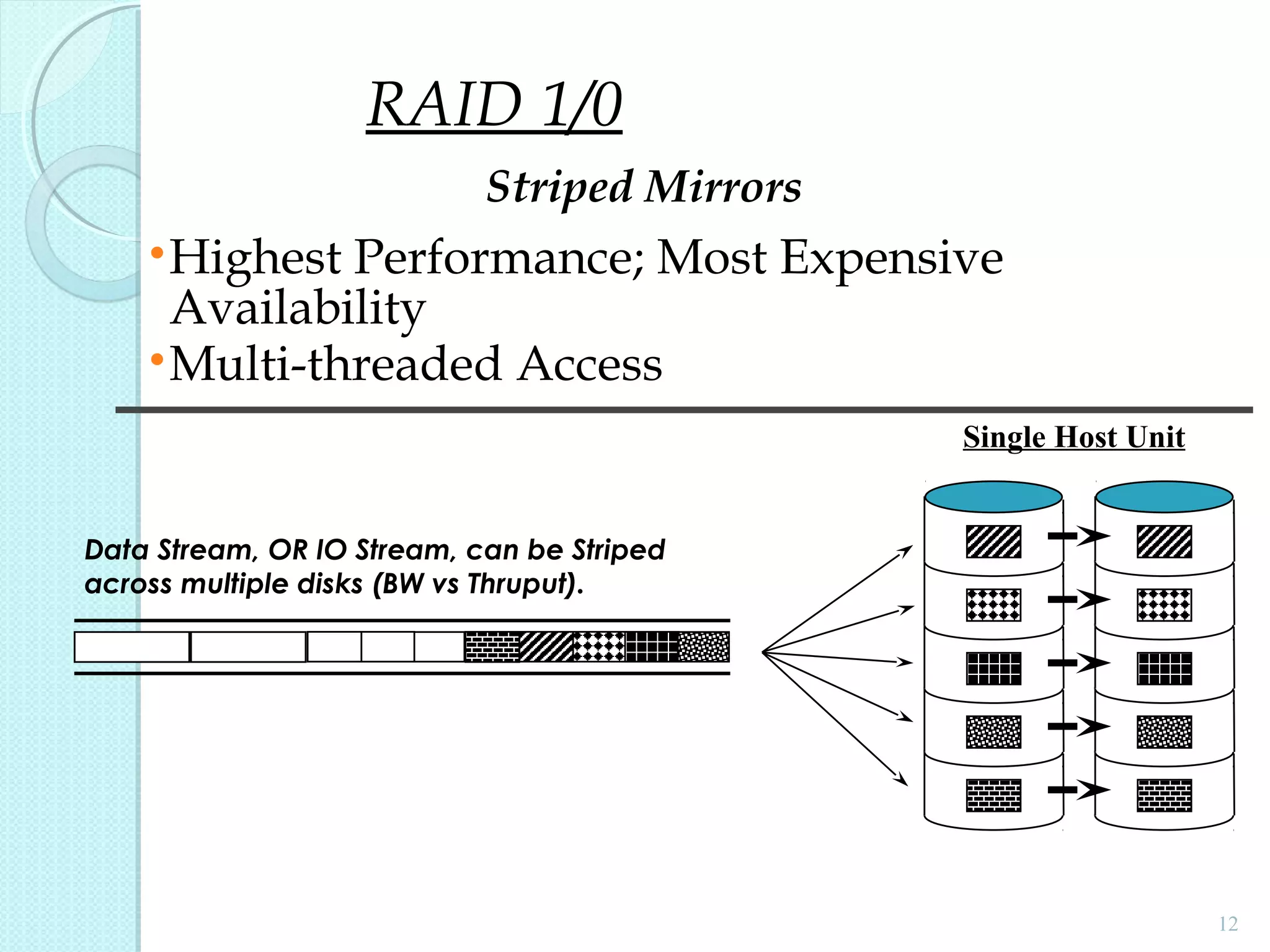
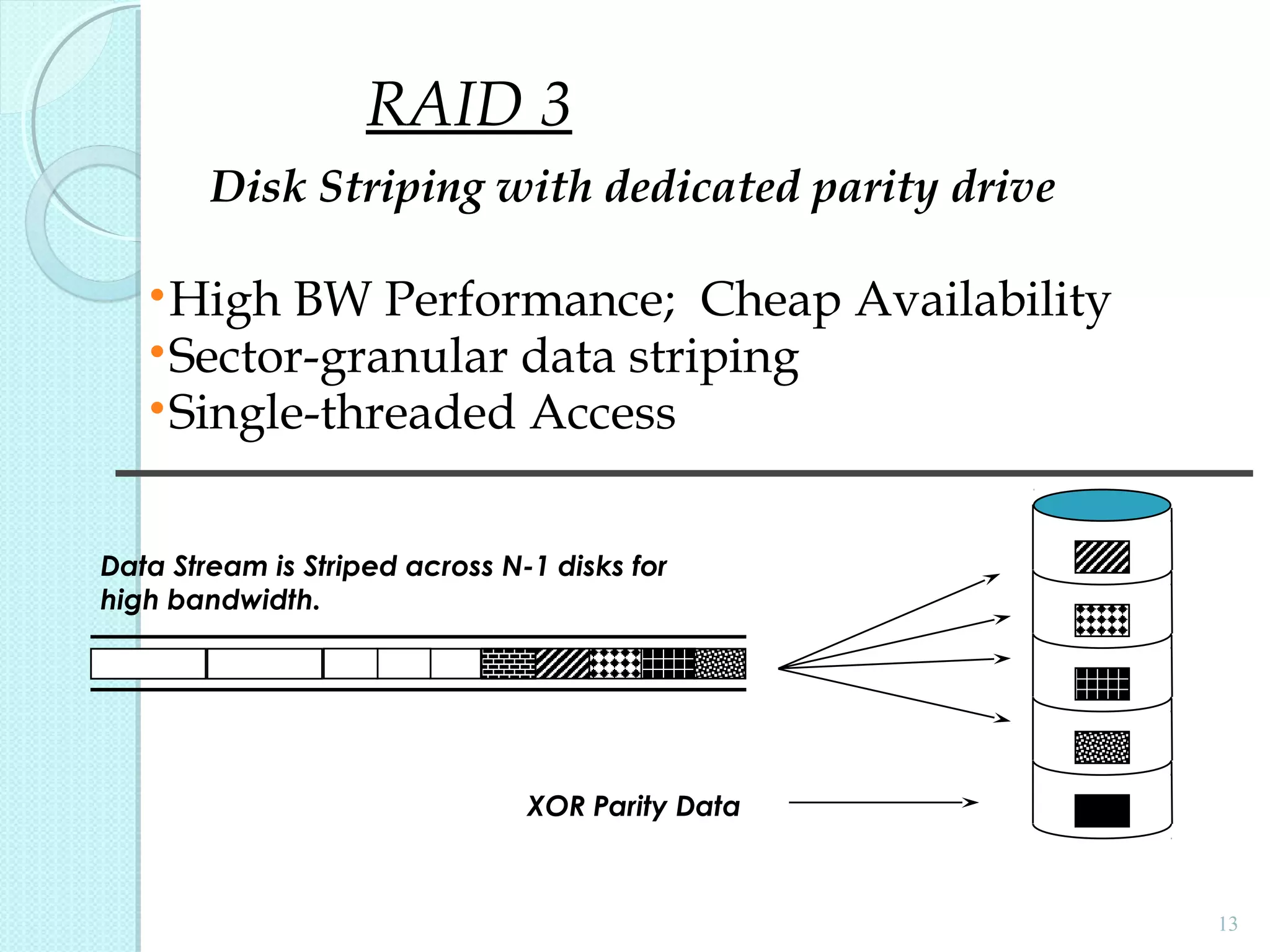
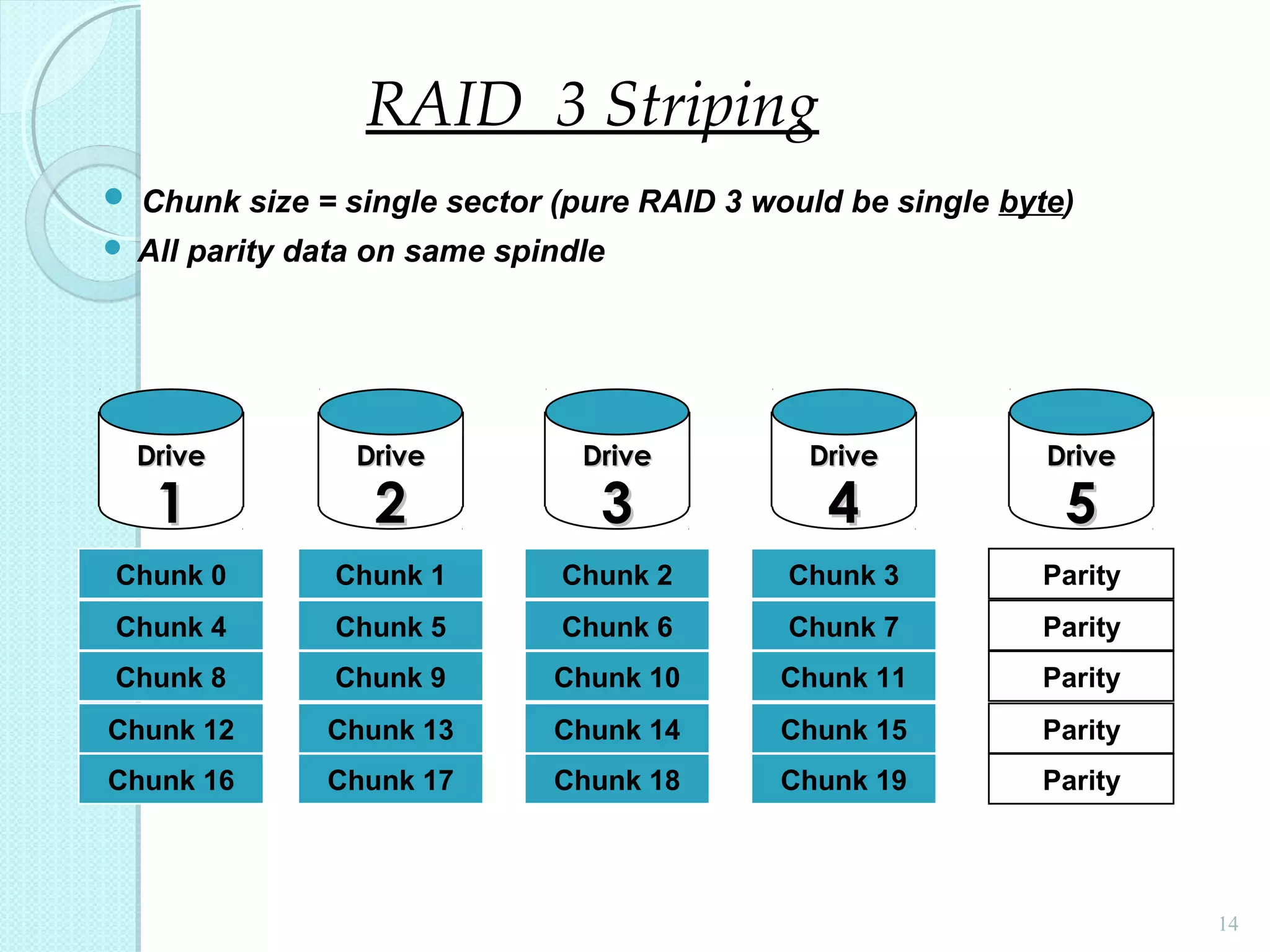
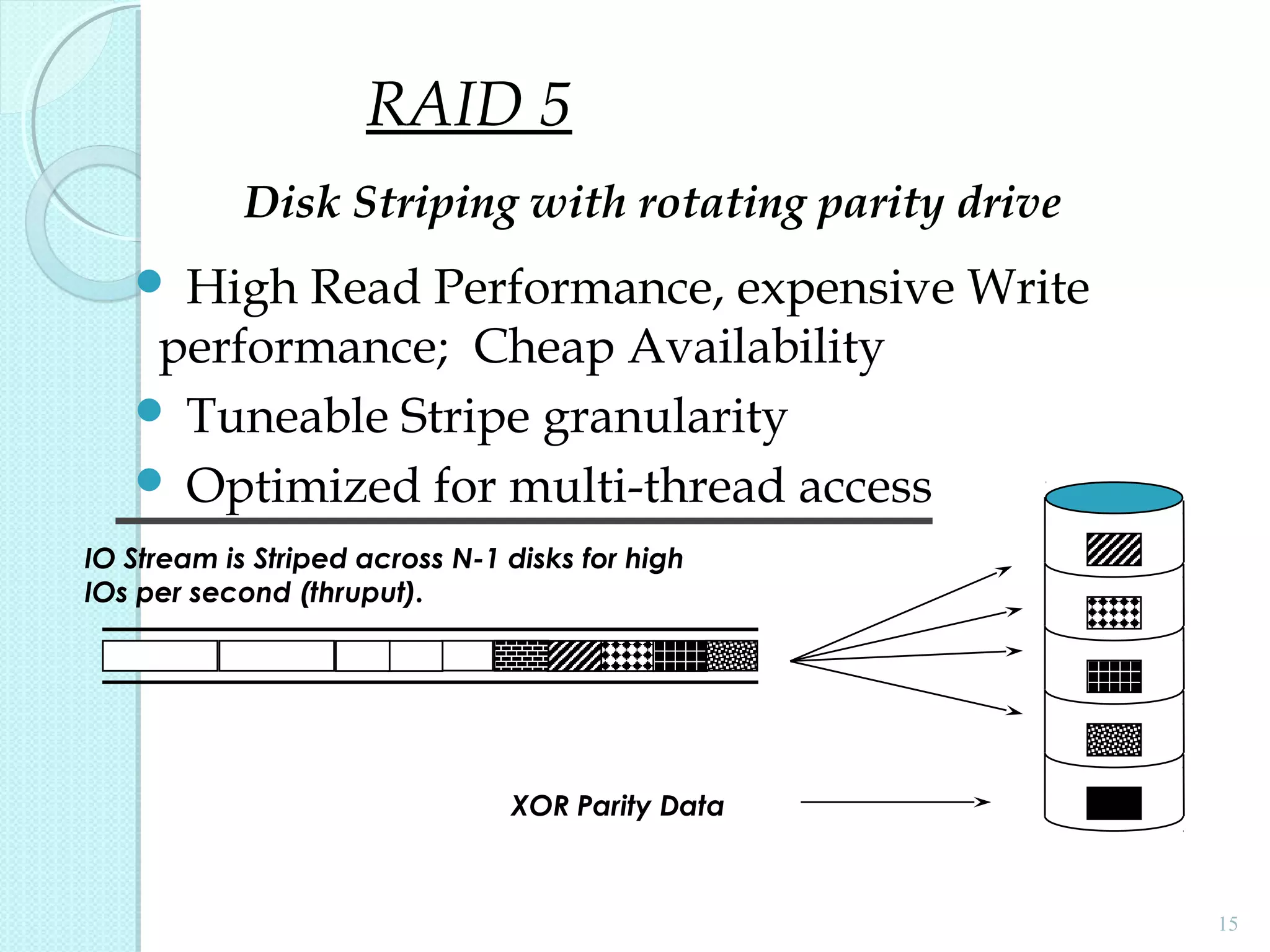
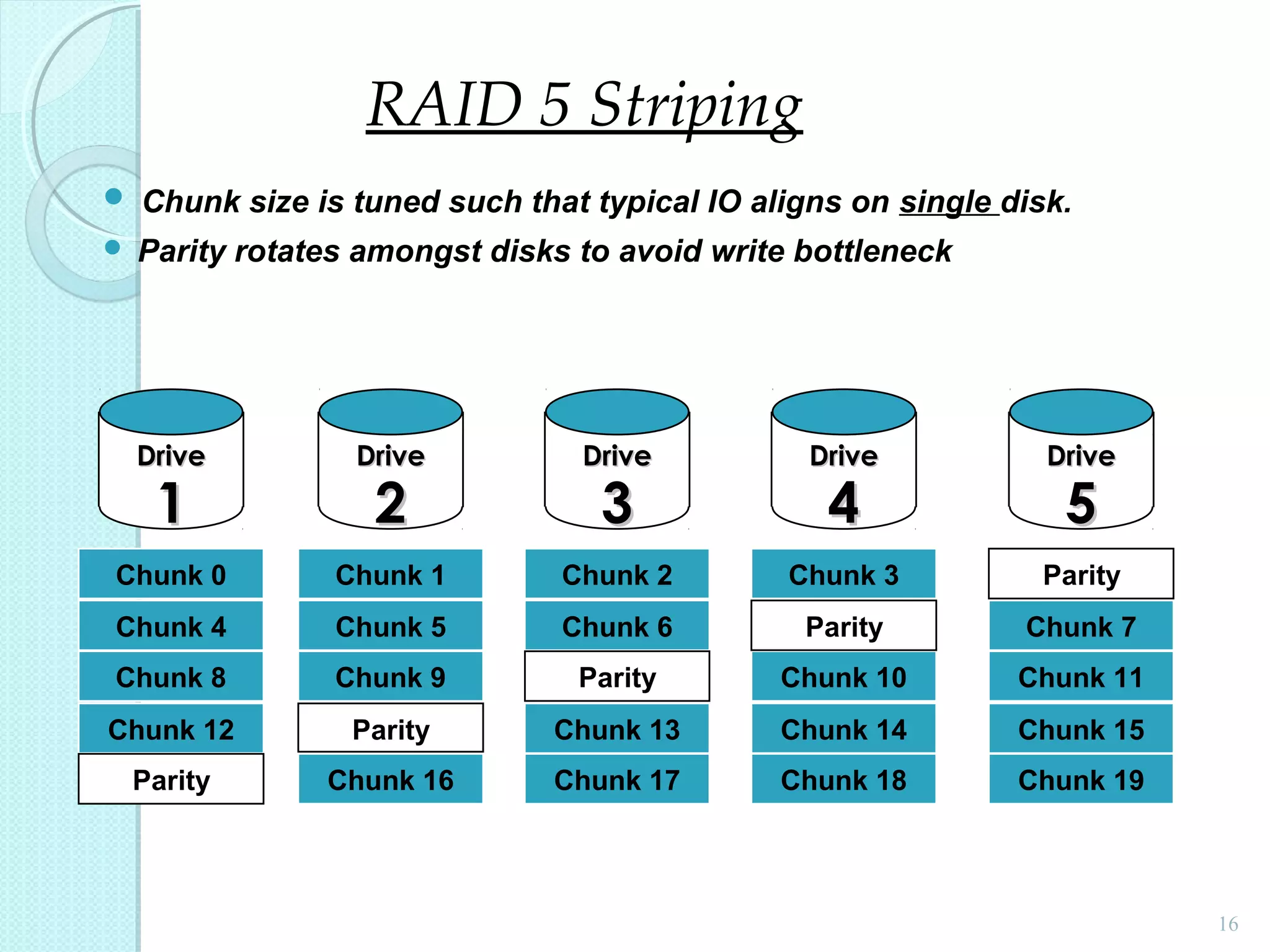
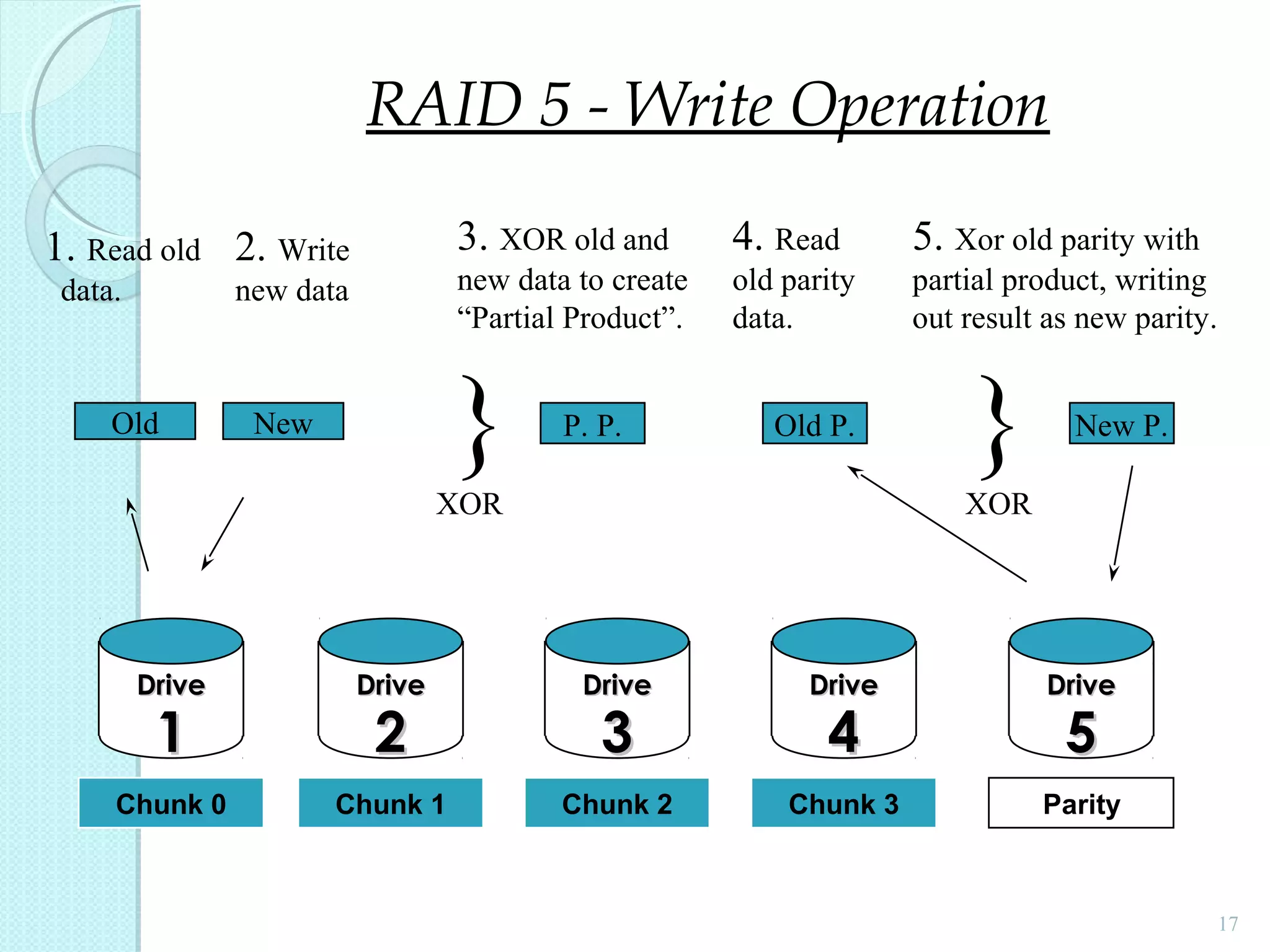
The document provides an overview of Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) technology, emphasizing its role in enhancing data performance and availability through parallelism and redundancy. It outlines various RAID levels (0, 1, 3, 5, and 10) and their unique tradeoffs in terms of performance, availability, and cost. Overall, RAID addresses the growing performance gap between CPU and I/O operations, ensuring both high throughput and data reliability.