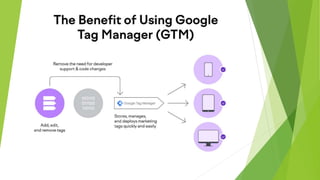
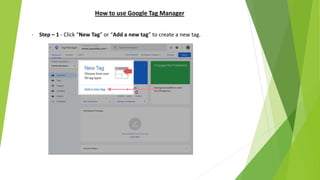
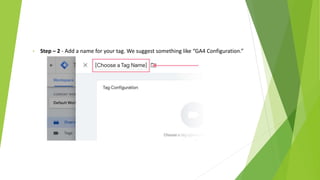
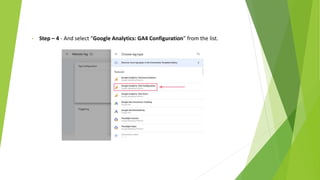
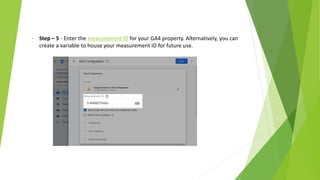
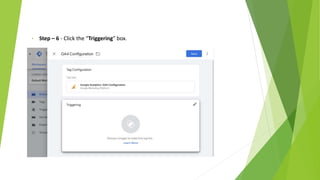
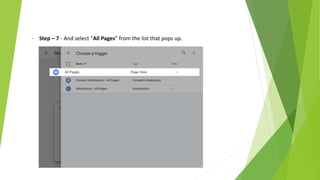
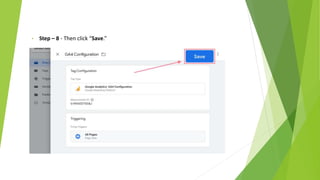
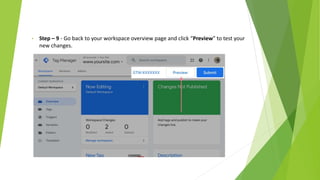
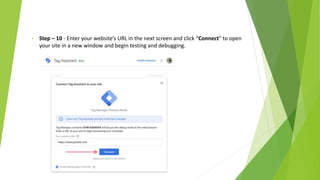
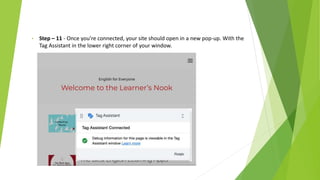
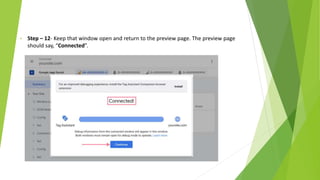
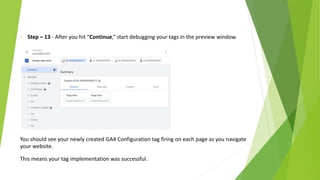
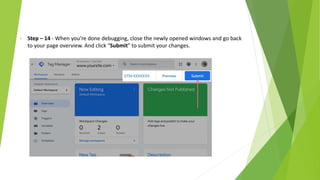
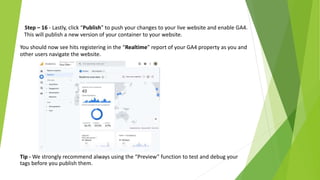
Google Tag Manager is a tag management system that allows users to easily create, maintain, and deploy tracking codes on websites. It offers benefits like reduced reliance on developers, testing and debugging capabilities, user permission control, and easy configuration of popular tools. Google Tag Manager can be used to track a wide variety of user behaviors and events, such as link clicks, form submissions, conversions, and more. Setting up tags in Google Tag Manager involves creating a new tag, configuring it, setting triggers, testing in preview mode, and then publishing changes.