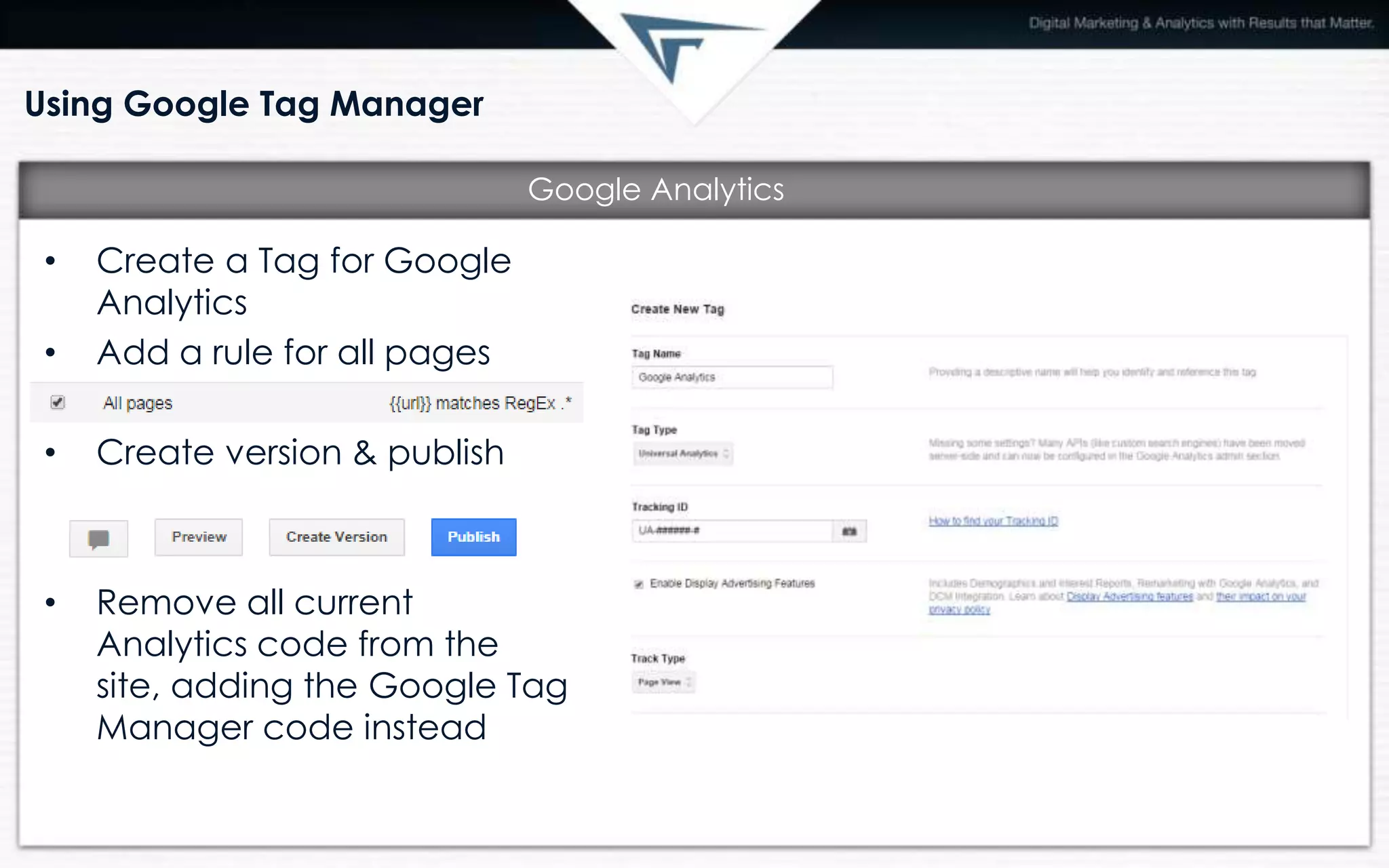
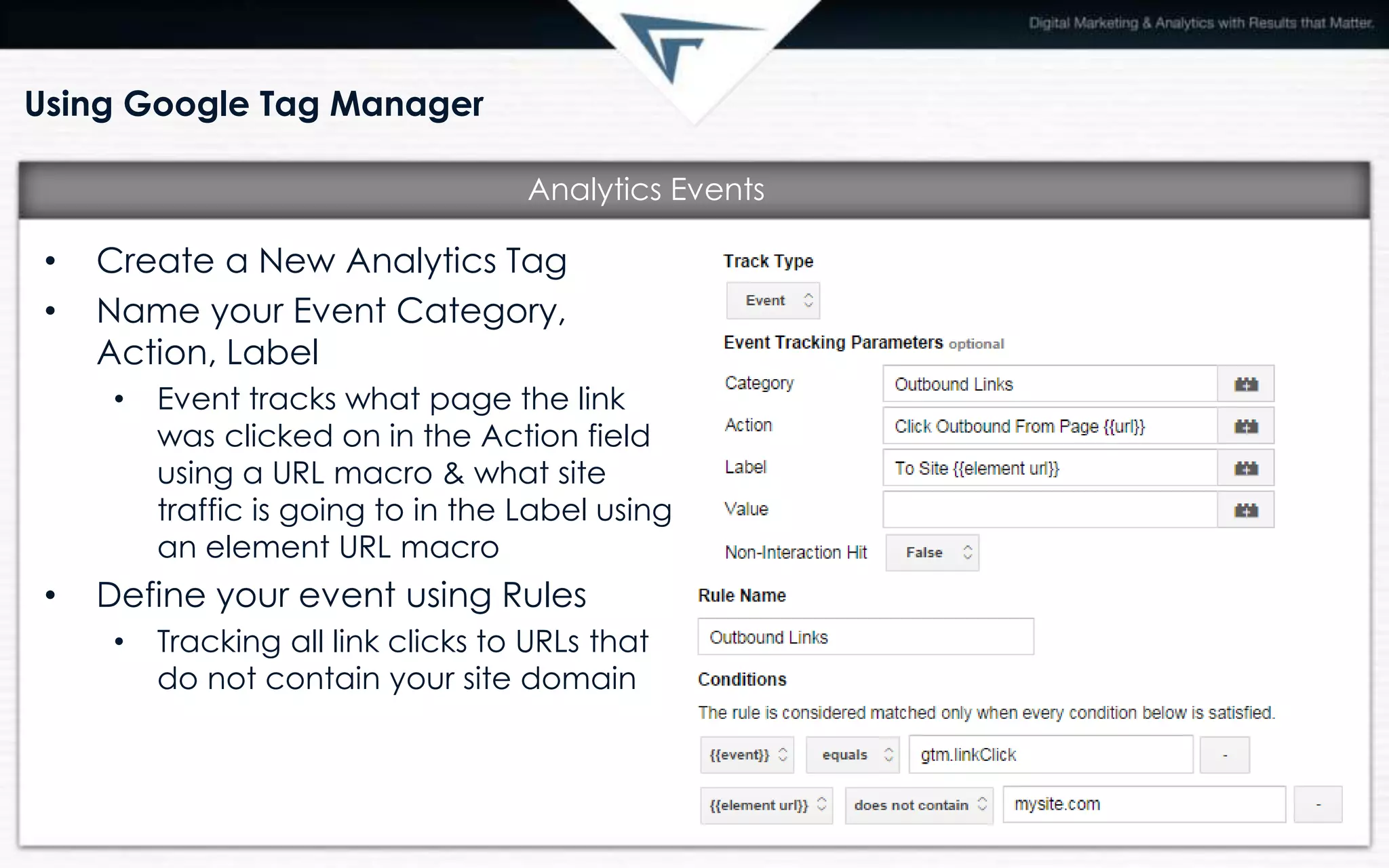
Google Tag Manager is a free Google tool that allows marketers to easily add and update website tags without involving IT. It makes tag implementation and updates faster and more flexible. Once installed, it automatically tracks events like clicks and form submissions. Key benefits include future-proofing websites, speed of updates, flexibility, and built-in debugging. Tags, rules, and macros are used to determine when tags should fire. Common uses include analytics, remarketing, social media tracking, and paid advertising conversion codes.