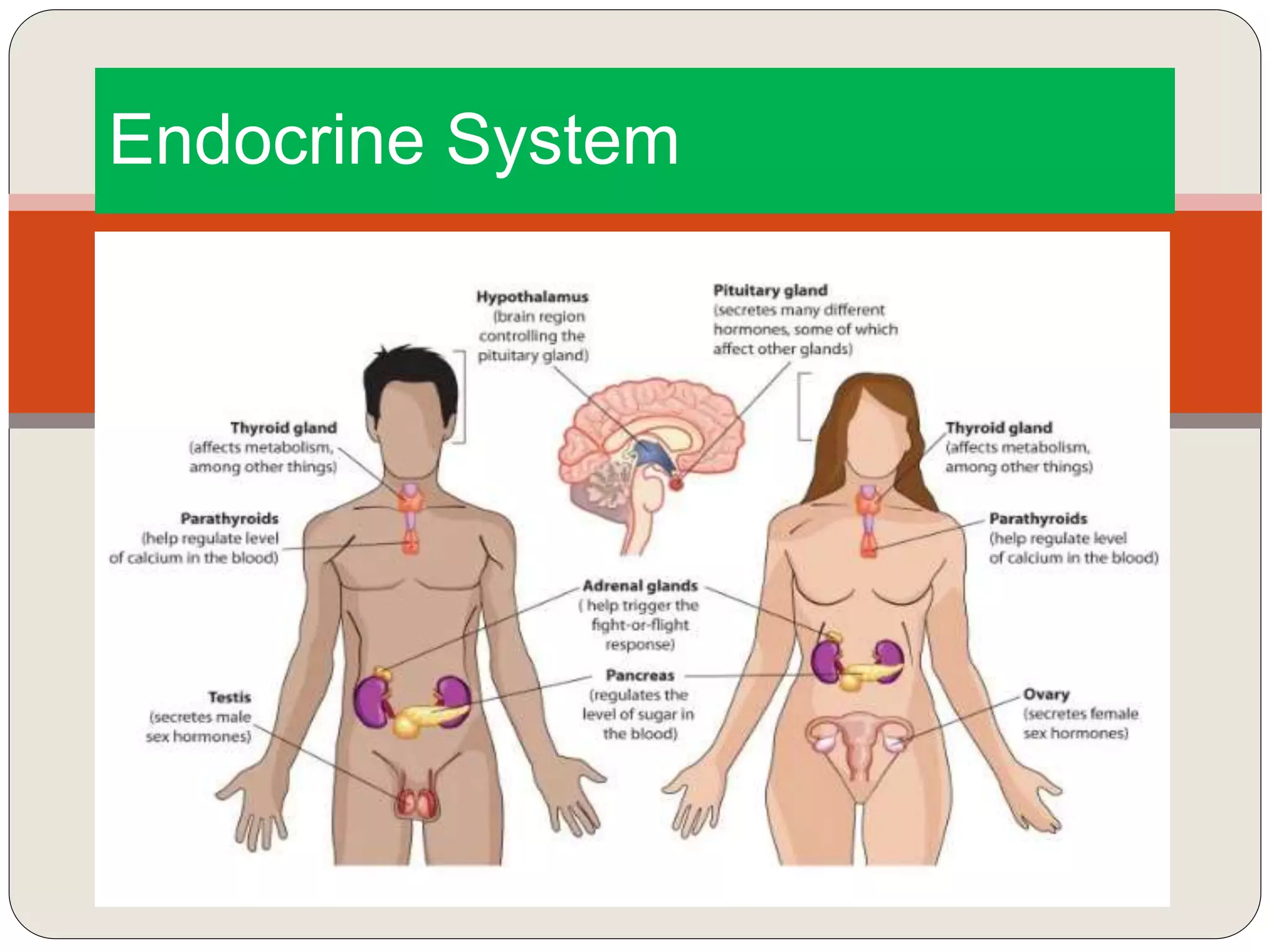
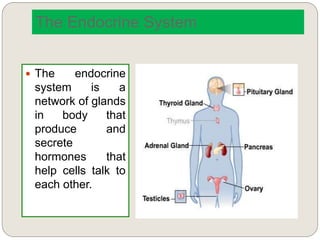
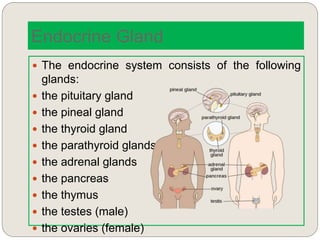
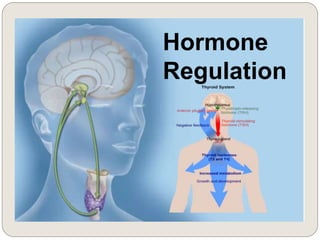
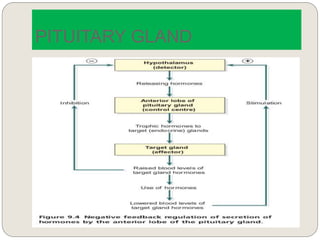
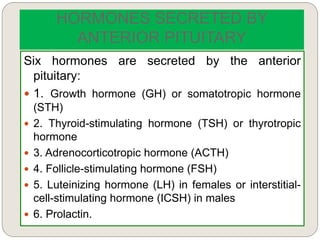
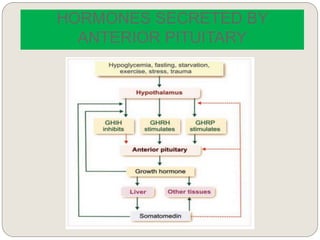
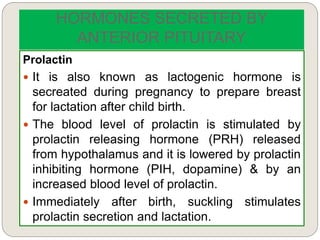
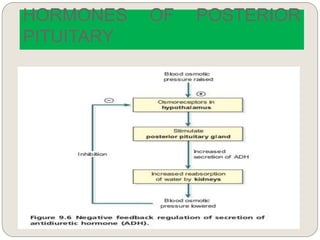
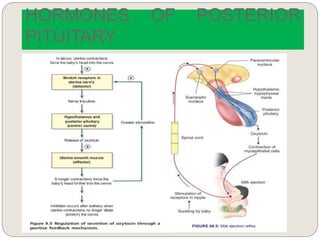
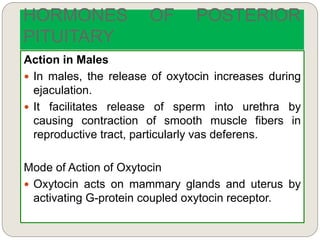
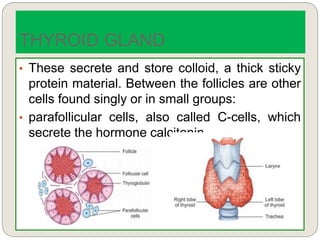
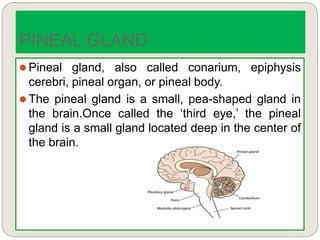
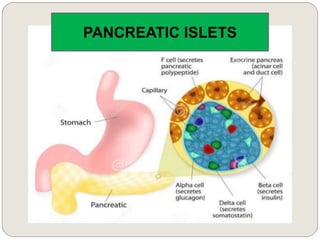
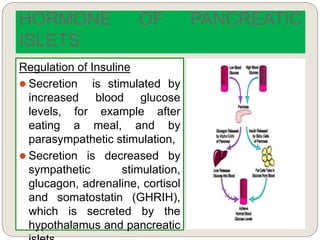
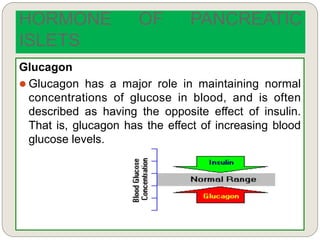
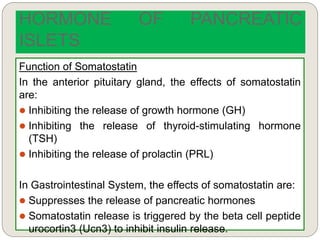
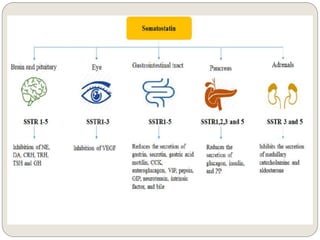
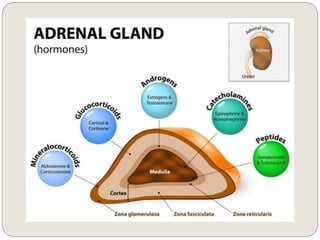
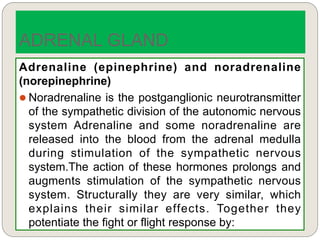
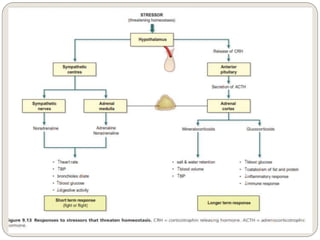
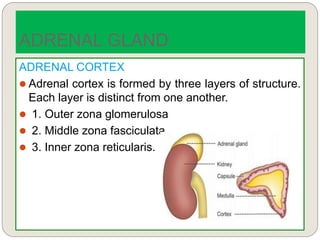
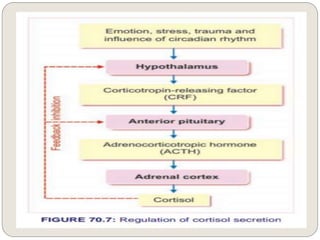
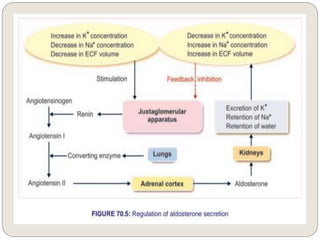
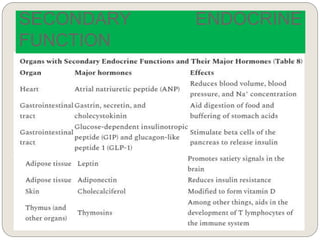
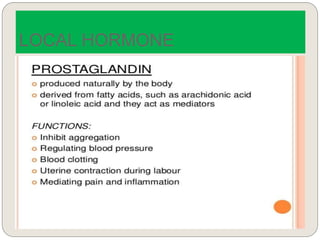
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs and tissues. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The pituitary gland is considered the "master gland" as it controls other endocrine glands by producing hormones that stimulate or inhibit their secretions. Hormones travel through the bloodstream to target cells, regulating critical functions like growth, metabolism, mood, fertility, and fluid and mineral balance. Negative feedback loops help maintain optimal hormone levels within a narrow range.