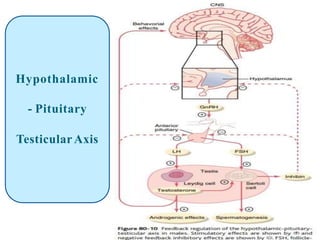
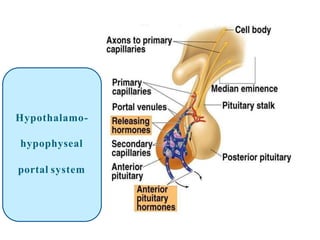
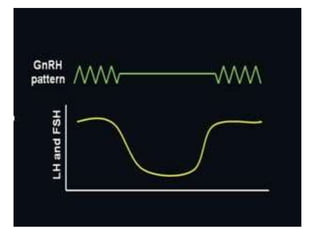
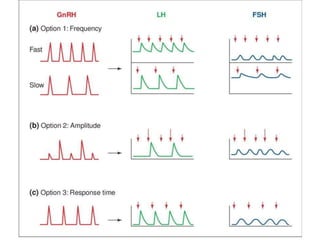
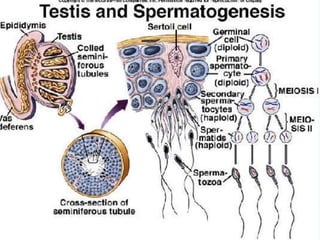
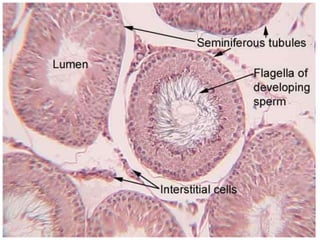
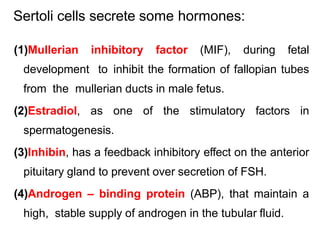
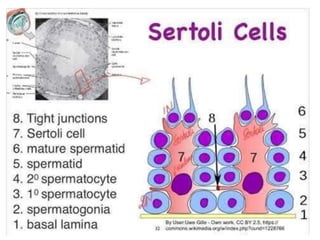
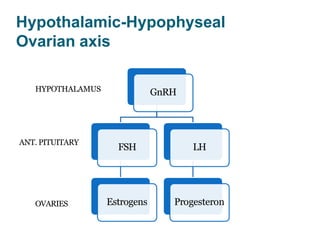
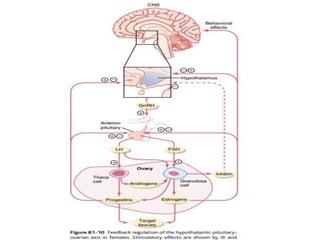
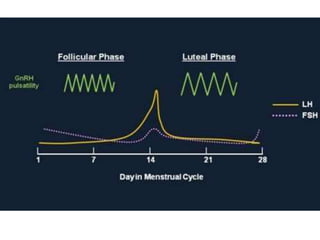
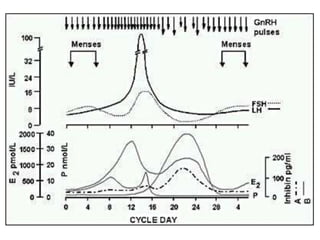
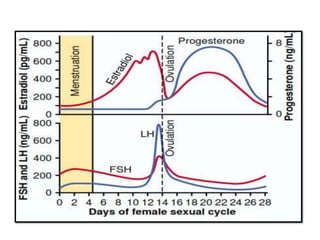
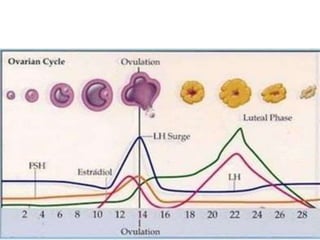
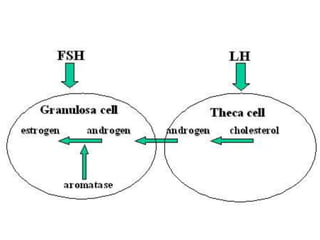
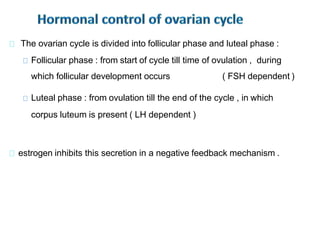
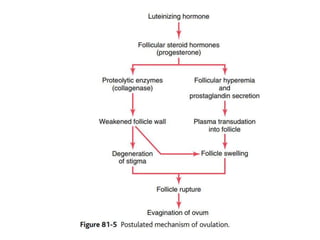
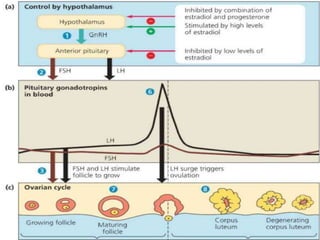
By the end of the lecture, students should be able to: define key terms like gametogenesis; understand the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and how it controls spermatogenesis and oogenesis; and recall feedback mechanisms. Gametogenesis refers to the development of eggs and sperm, including spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females. The hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonads interact via hormones to regulate these processes. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulates follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone production, which then control the release of sex hormones that regulate gamete production and maturation.