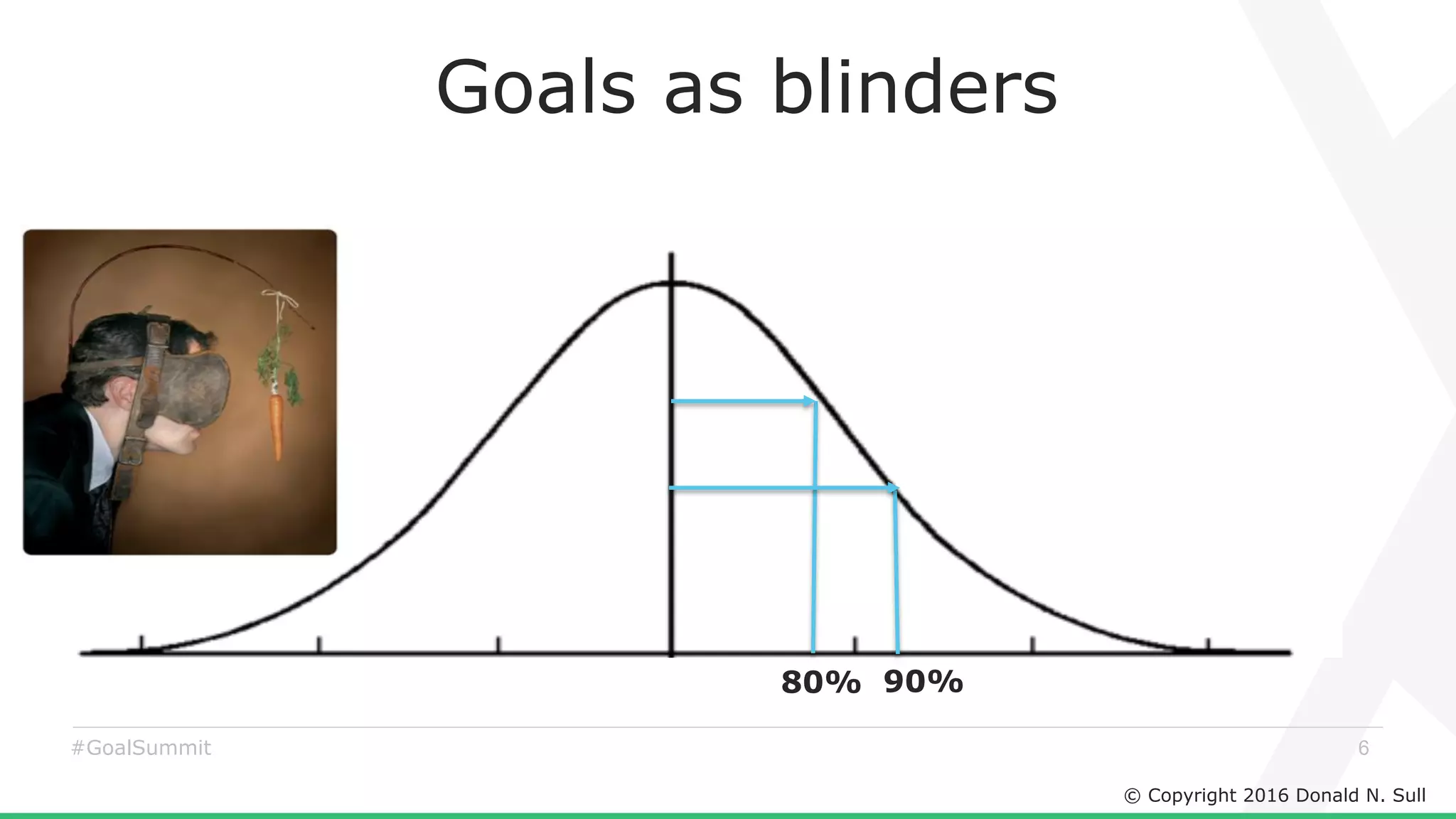
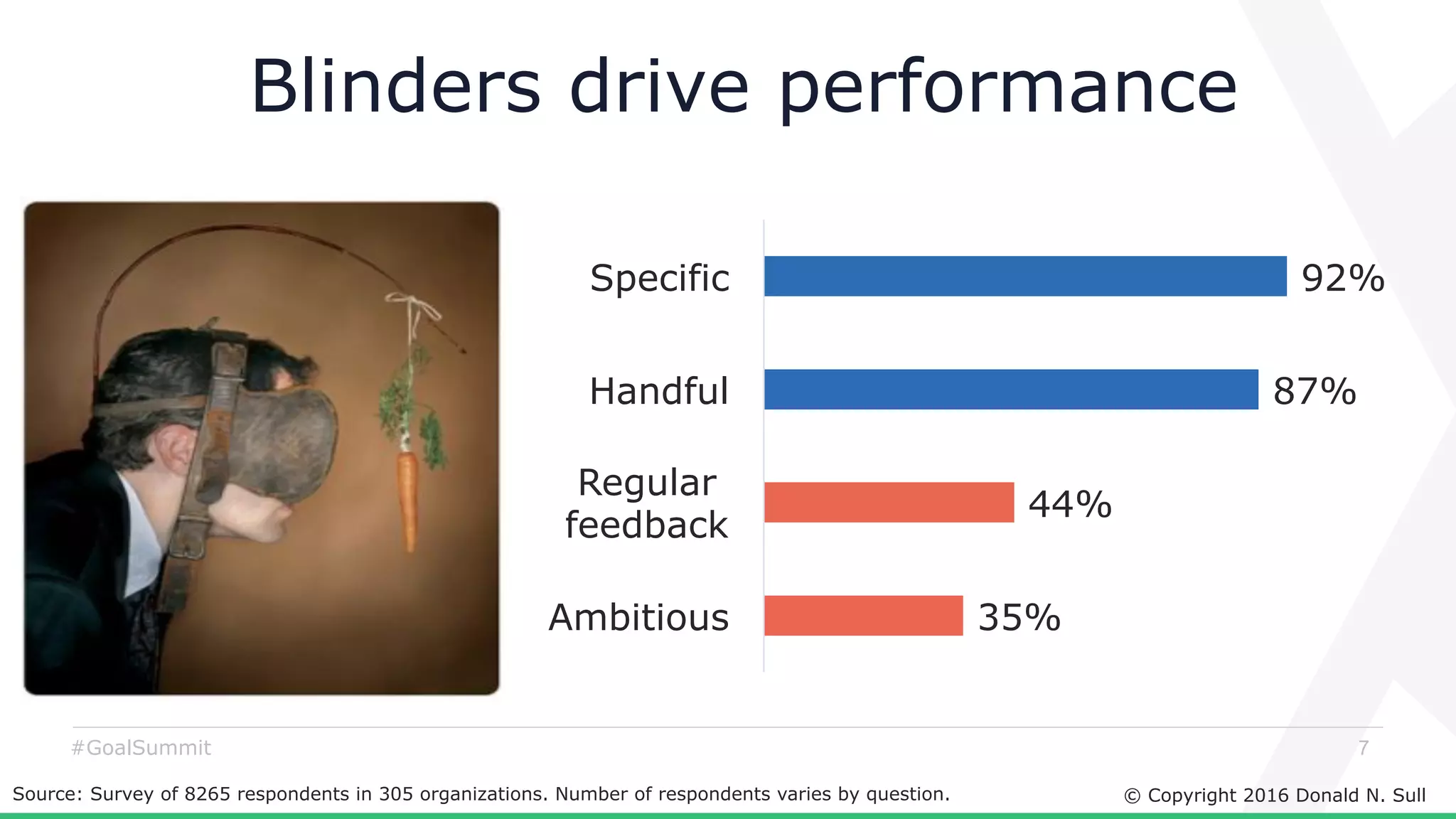
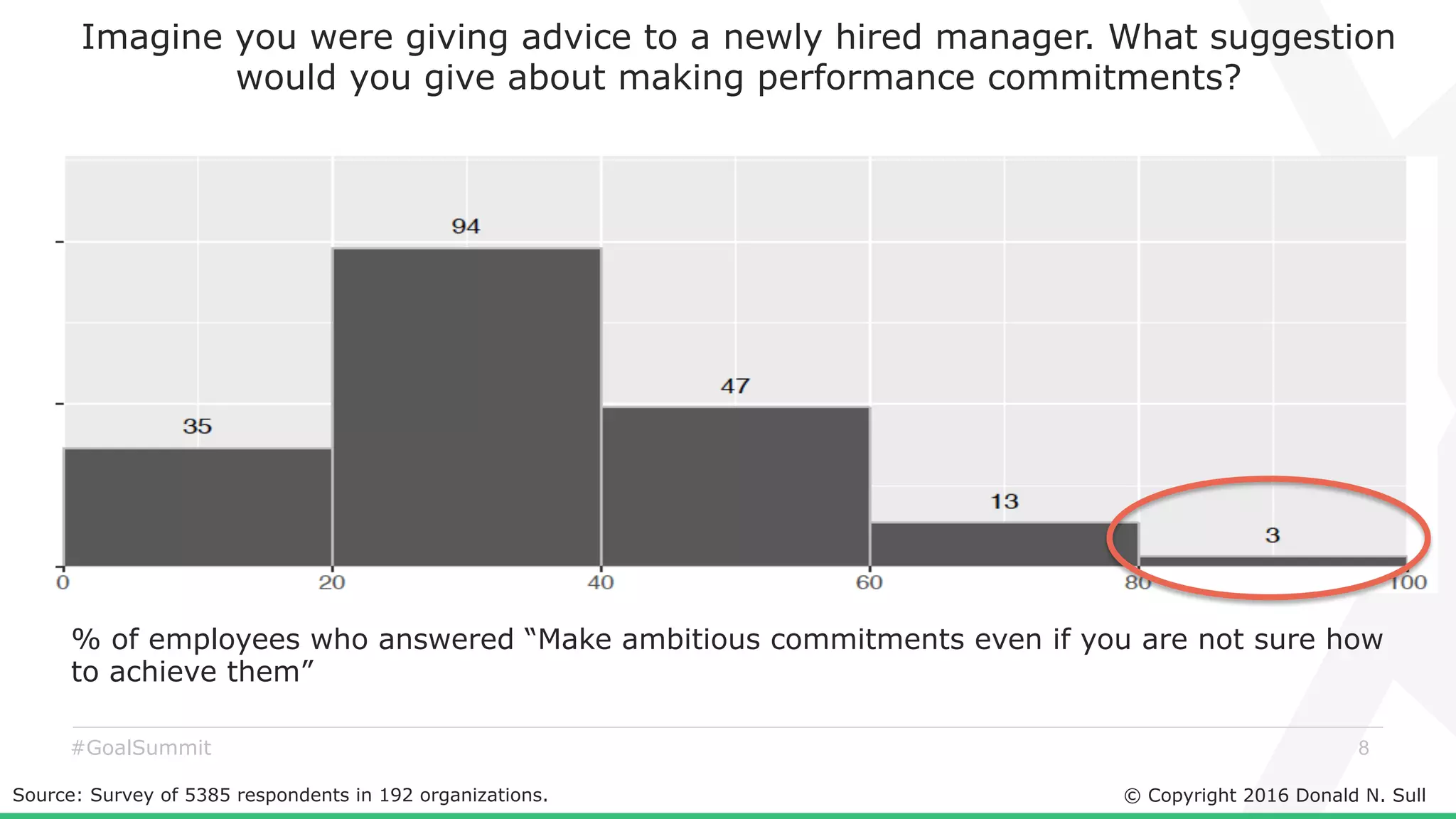
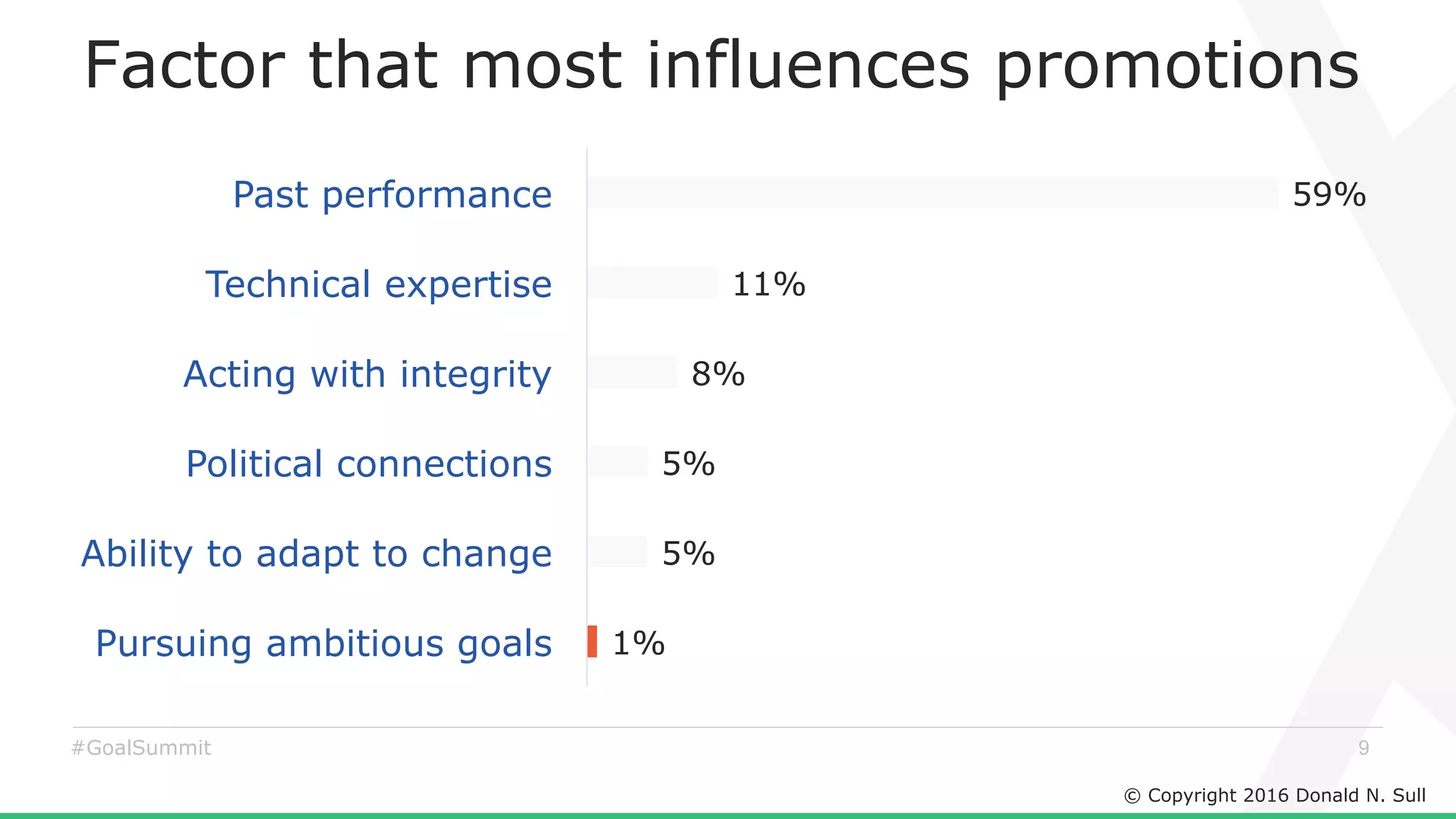
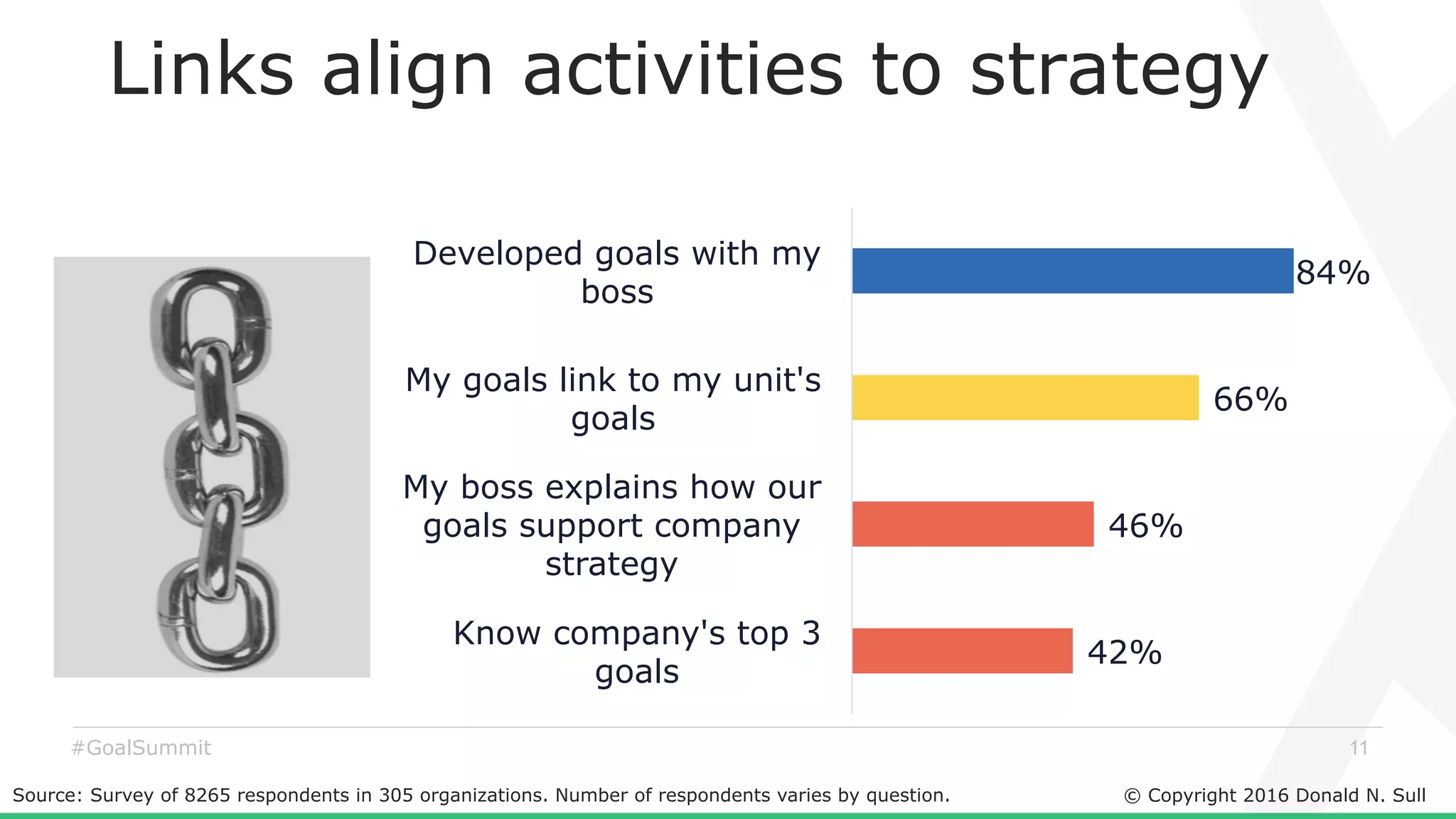
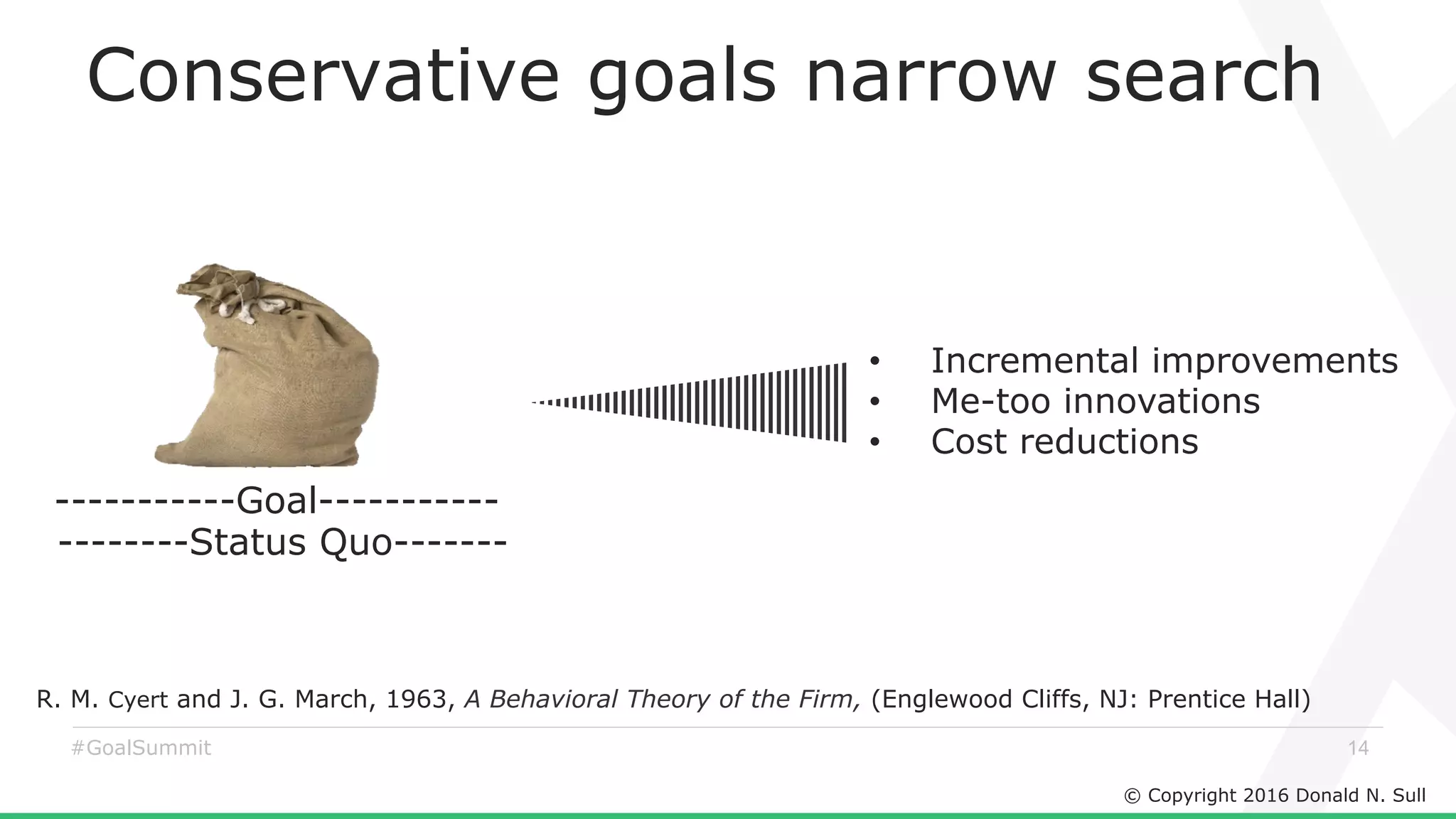
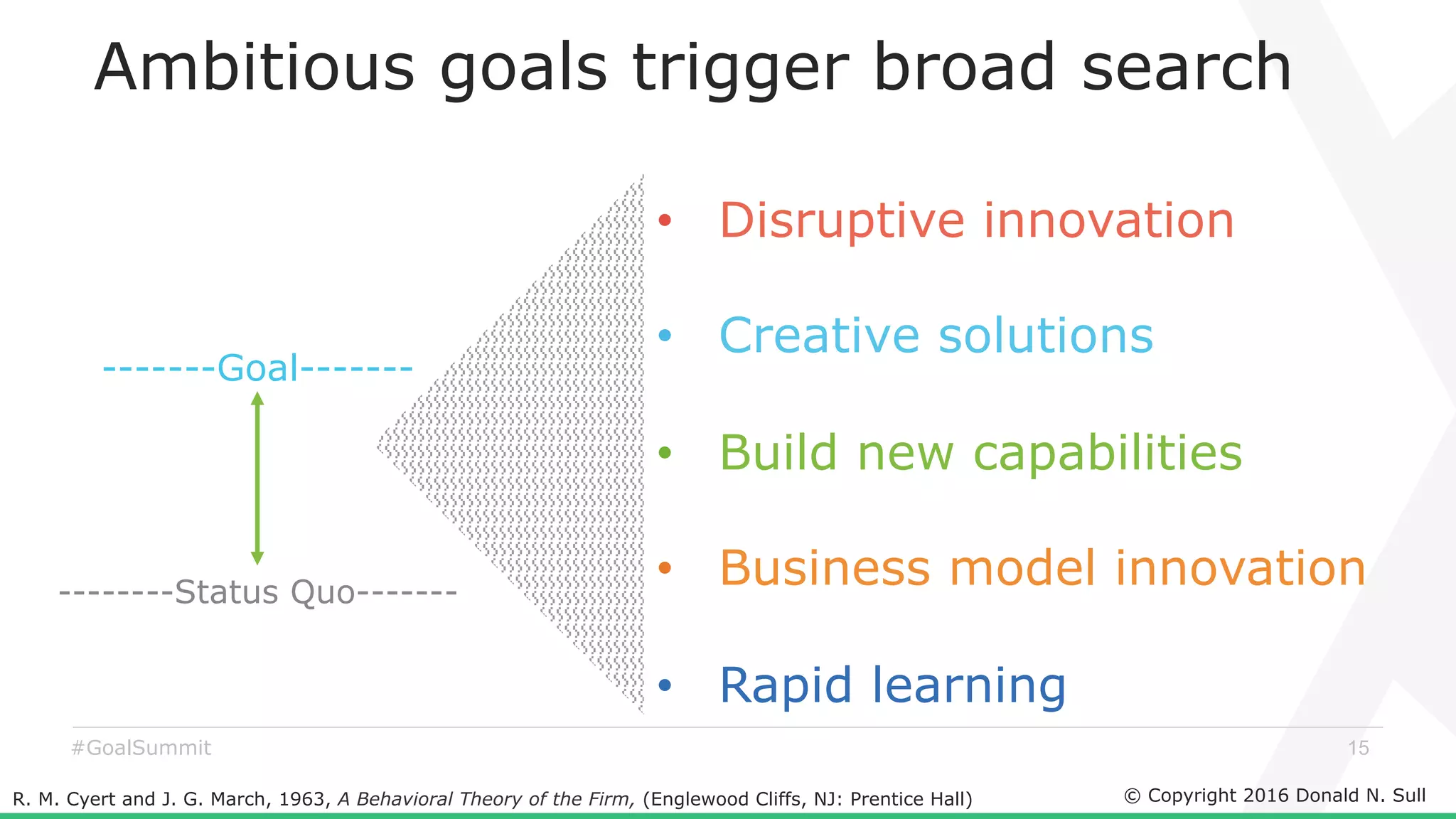
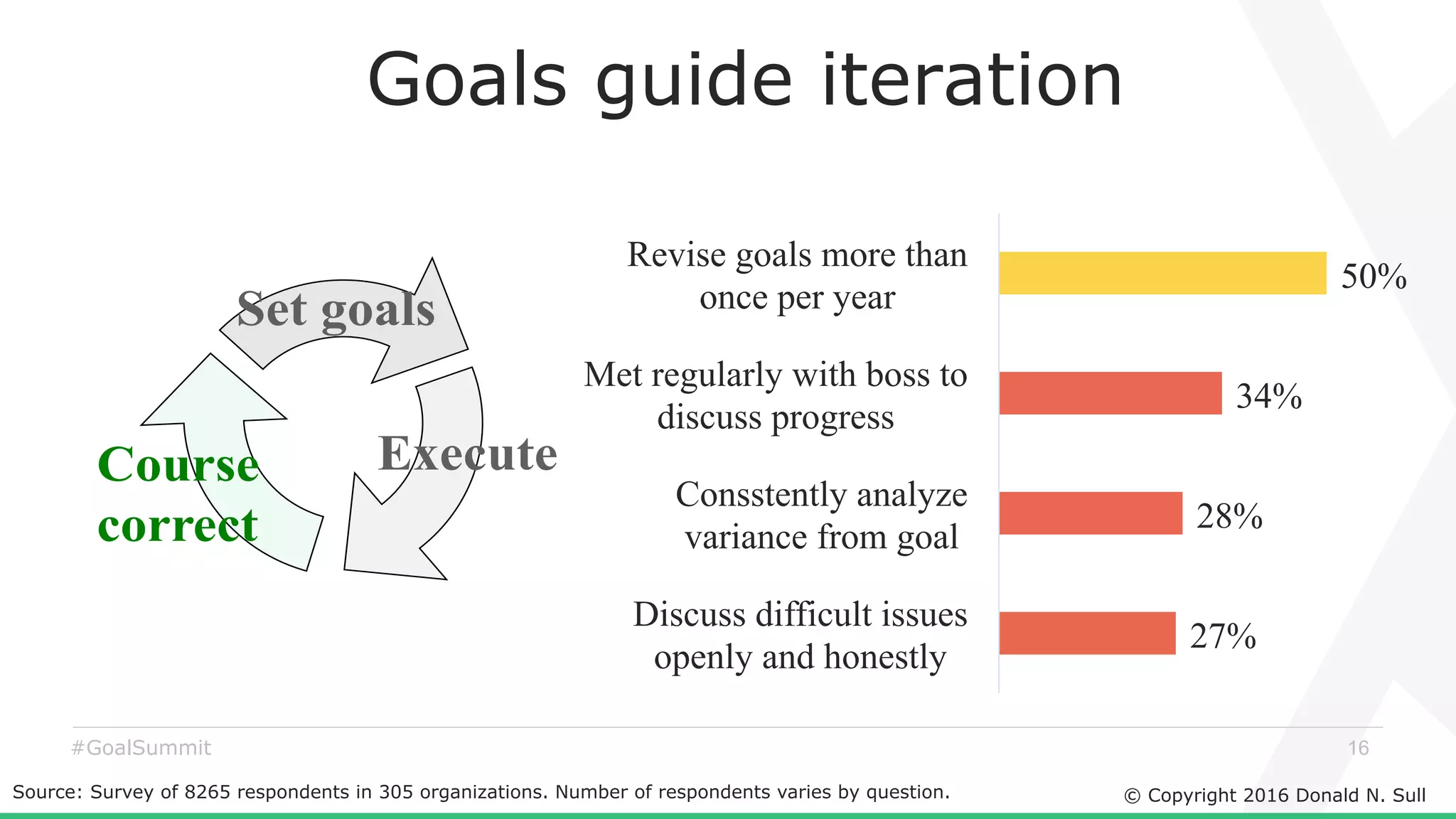
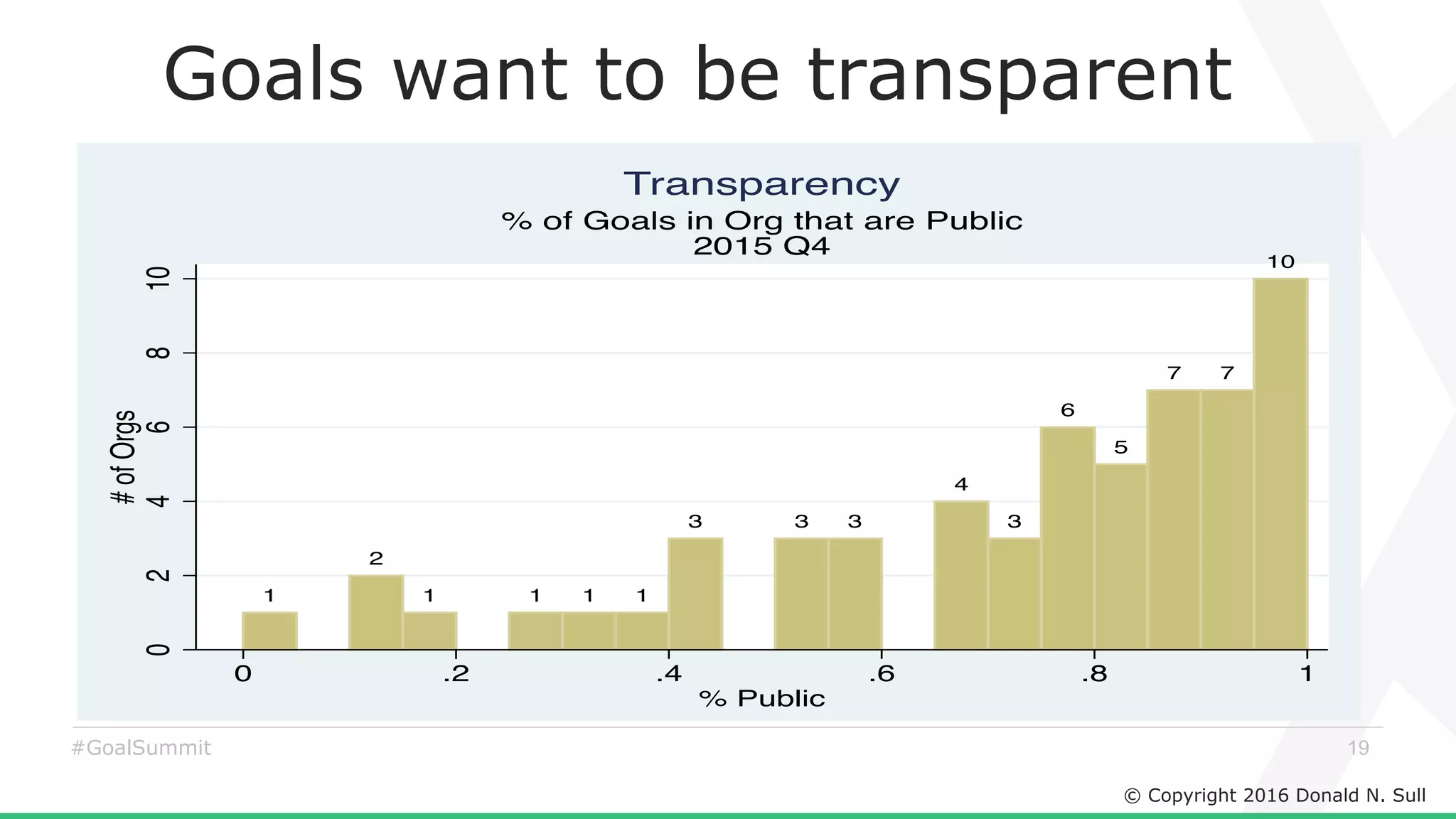
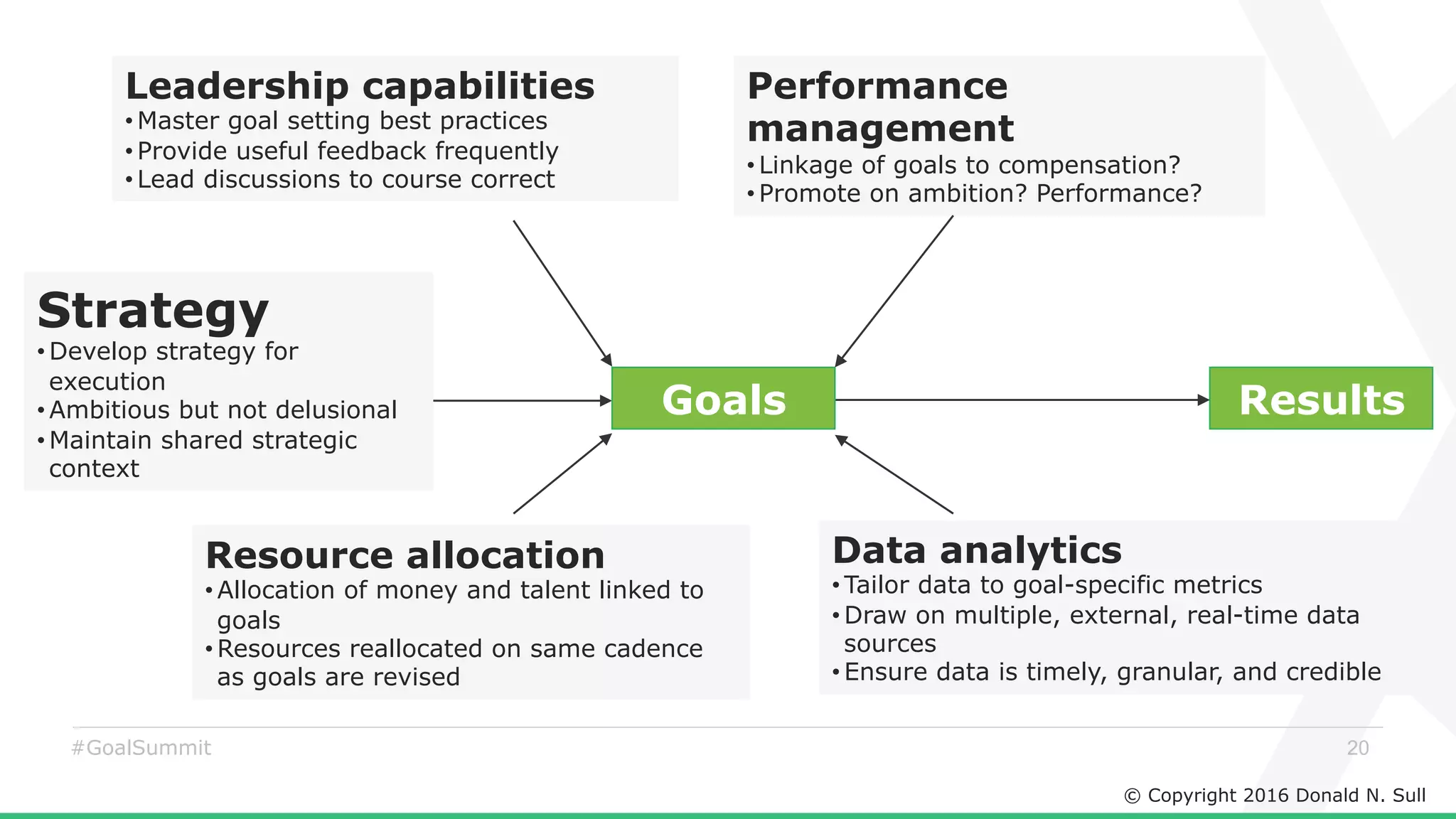
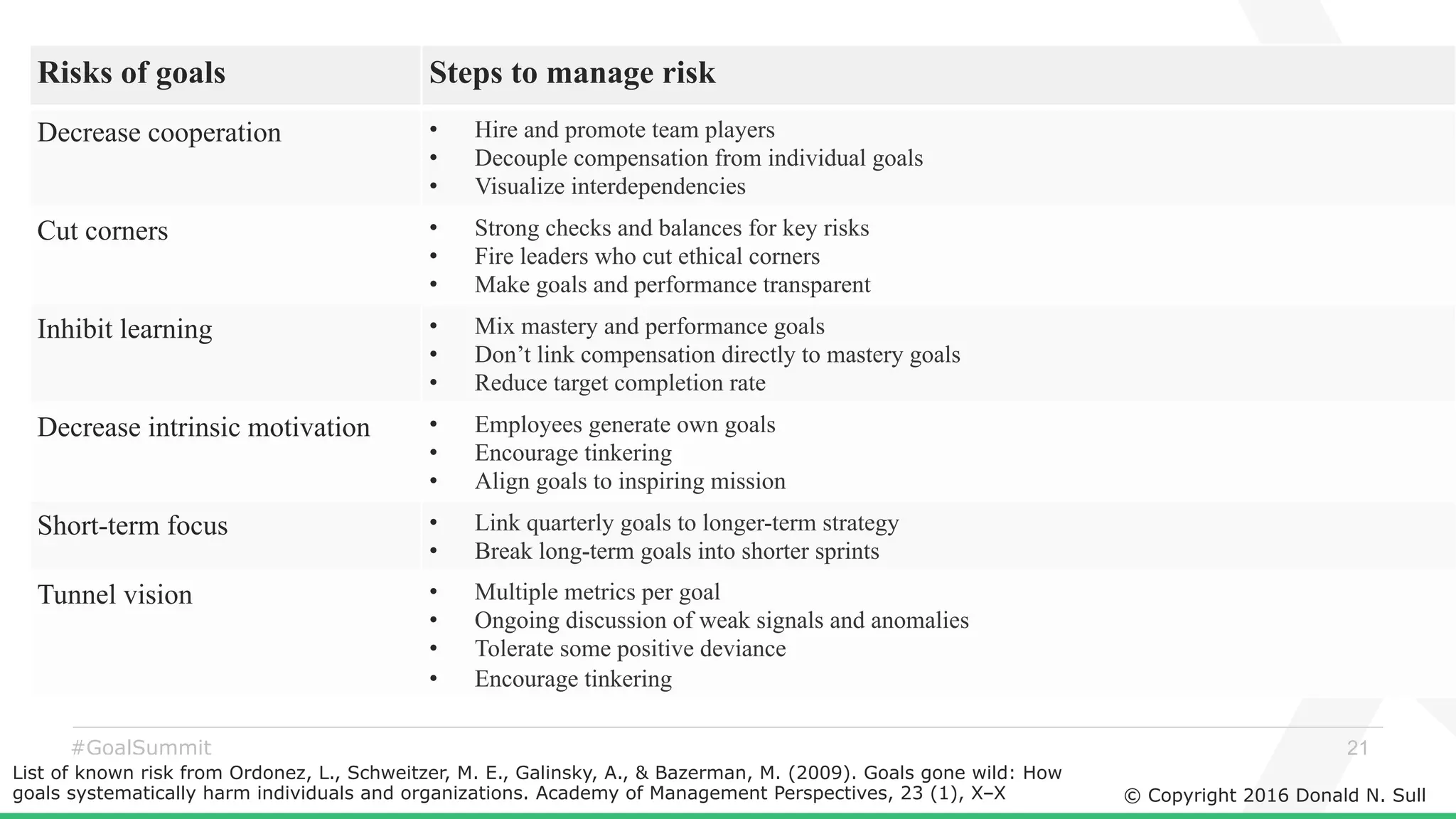
The document discusses the critical role of goals in linking strategy to execution within organizations, highlighting common obstacles such as lack of performance culture and agility. It emphasizes how goals can drive performance by acting as blinders, links to align activities, bold hypotheses to encourage innovation, and signals for coordination among teams. Strategies for effective goal setting and management are suggested, along with risks associated with goal strategies and ways to mitigate them.