This document outlines good manufacturing practices (GMPs) for cosmetics manufacturing. It discusses establishing a quality management system and quality assurance programs. Personnel should be adequately trained. Premises, equipment, and production processes should be designed and maintained to minimize risks of contamination. Thorough documentation, quality control testing, and complaint handling are required. The GMPs are intended to assure consistent high quality products that are safe for consumers.




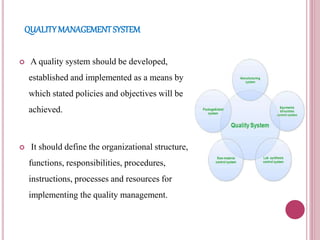
![ Qualityassurance, or QA for short, is the systematic monitoring and
evaluation of the various aspects of a project, service or facility to
maximize the probability that minimum standards of quality are being
attained by the production process. QA cannot absolutely guarantee the
production of quality products [15].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gmp-cosmetics-171130083100/85/Gmp-cosmetics-6-320.jpg)



















