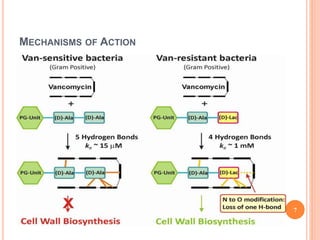
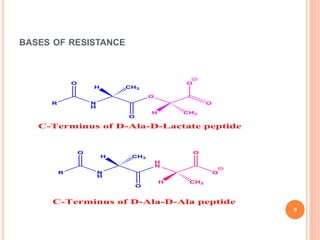
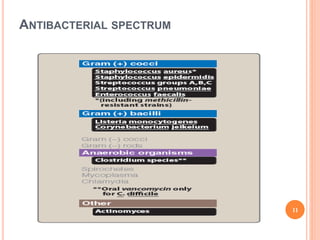
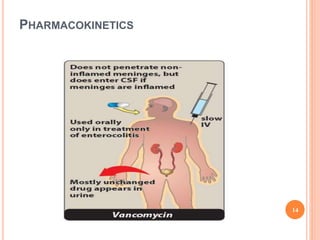
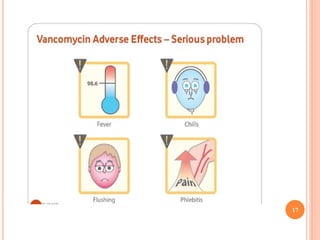
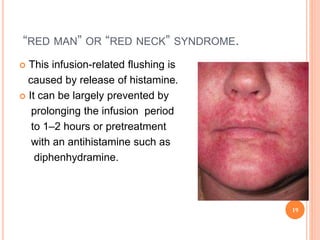
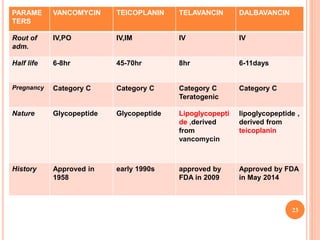
This document outlines information about glycopeptide antibiotics including vancomycin, teicoplanin, telavancin, and dalbavancin. It discusses their mechanisms of action, mechanisms of resistance, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, and adverse reactions. Specifically, it notes that vancomycin inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis, has activity against gram-positive bacteria, and is excreted renally. It is used to treat infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus but can cause adverse reactions like red man syndrome. Teicoplanin and telavancin are similar to vancomycin while dalbavancin has an extremely long half-life allowing