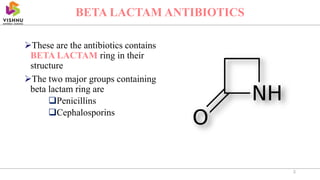
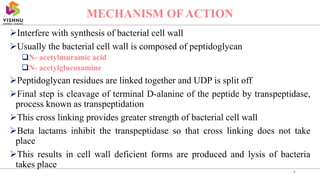
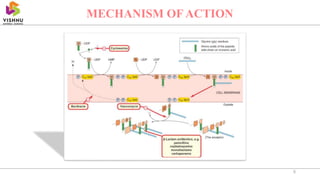
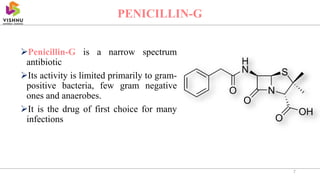
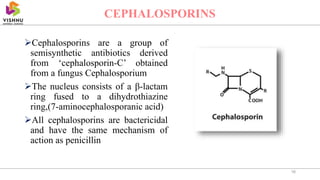
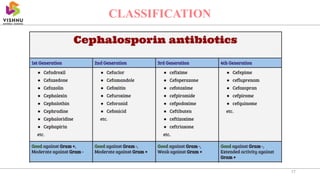
This document summarizes beta lactam antibiotics, which contain a beta lactam ring in their structure. The two major groups are penicillins and cephalosporins. Penicillin was the first antibiotic discovered in 1928 and was the first to be used clinically to treat infections. Beta lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting the transpeptidase enzyme involved in bacterial cell wall synthesis, resulting in cell lysis. While effective, they can cause adverse effects like hypersensitivity reactions and toxicity. Semisynthetic derivatives were created to improve properties like oral efficacy, spectrum of activity, and resistance to degradation.