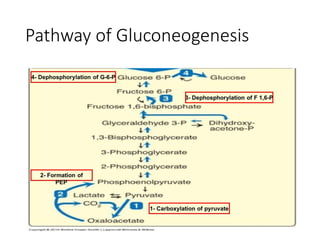
Gluconeogenesis is a process by which non-carbohydrate substrates like lactate, glycerol, and certain amino acids are converted into glucose, mainly in the liver and kidneys. It is required to maintain blood glucose levels during periods of fasting or low carbohydrate intake. The pathway involves a series of enzymatic reactions that largely reverse the steps of glycolysis to produce glucose-6-phosphate, which is then converted into glucose and released into the bloodstream. Gluconeogenesis is regulated by hormones like glucagon and requires energy in the form of ATP.