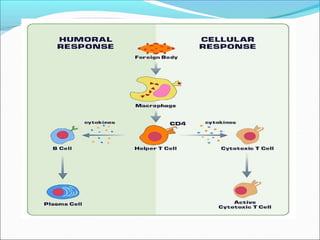
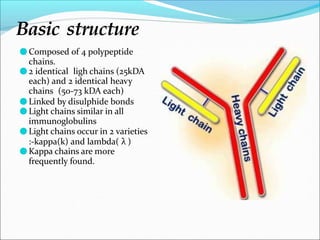
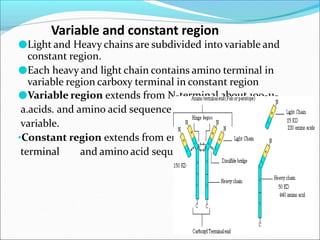
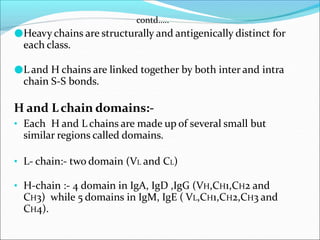
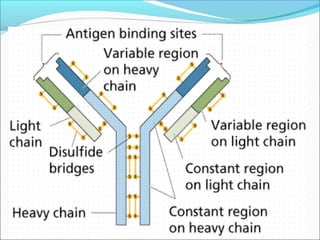
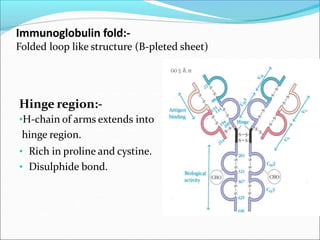
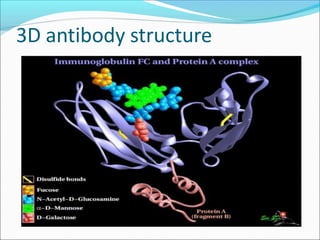
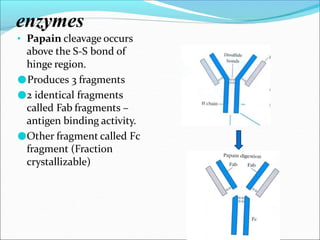
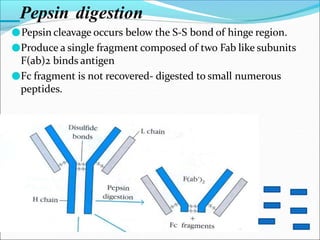
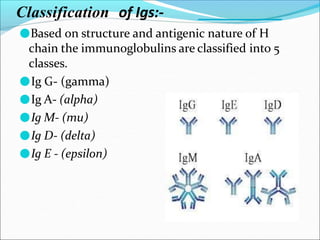
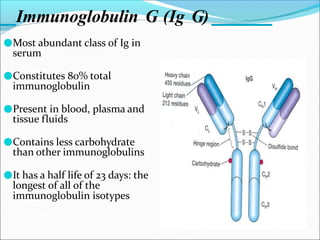
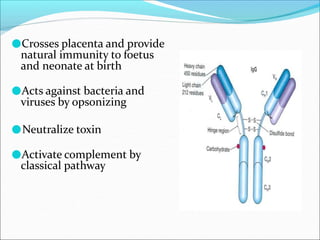
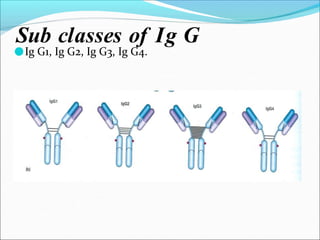
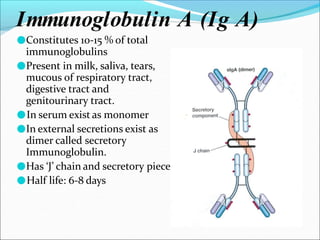
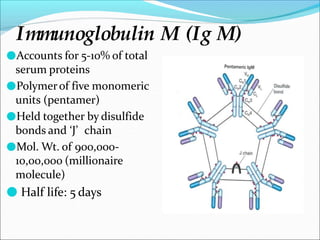
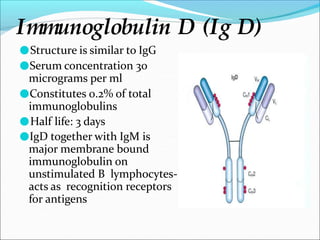
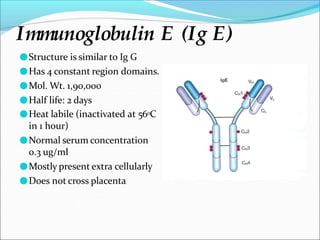
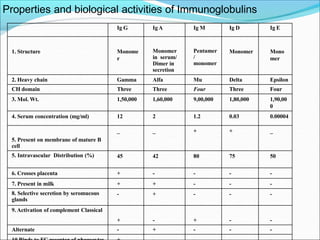
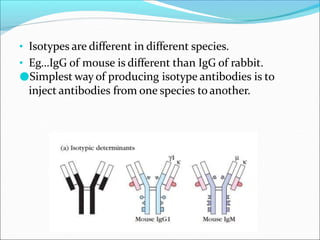
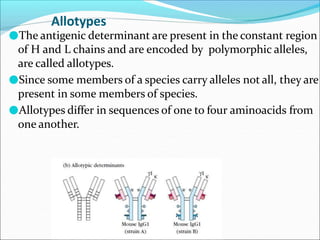
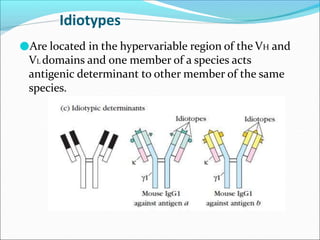
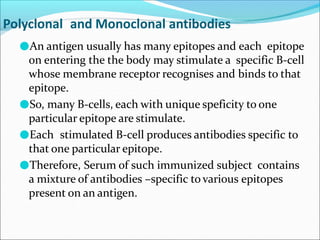
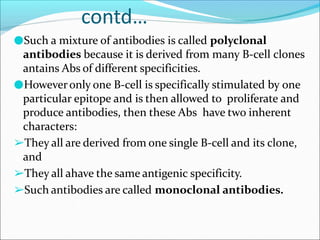
Antibodies, also called immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells that recognize and bind to antigens. They have two identical light chains and two identical heavy chains connected by disulfide bonds. The variable regions at the tips of the Y allow antibodies to bind to specific antigens, while the constant regions define the antibody's class. There are five antibody classes (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE) that have different structures and functions such as activating complement or binding to mast cells. Monoclonal antibodies are derived from a single clone and have identical specificity, unlike polyclonal antibodies from multiple clones.