This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence including:
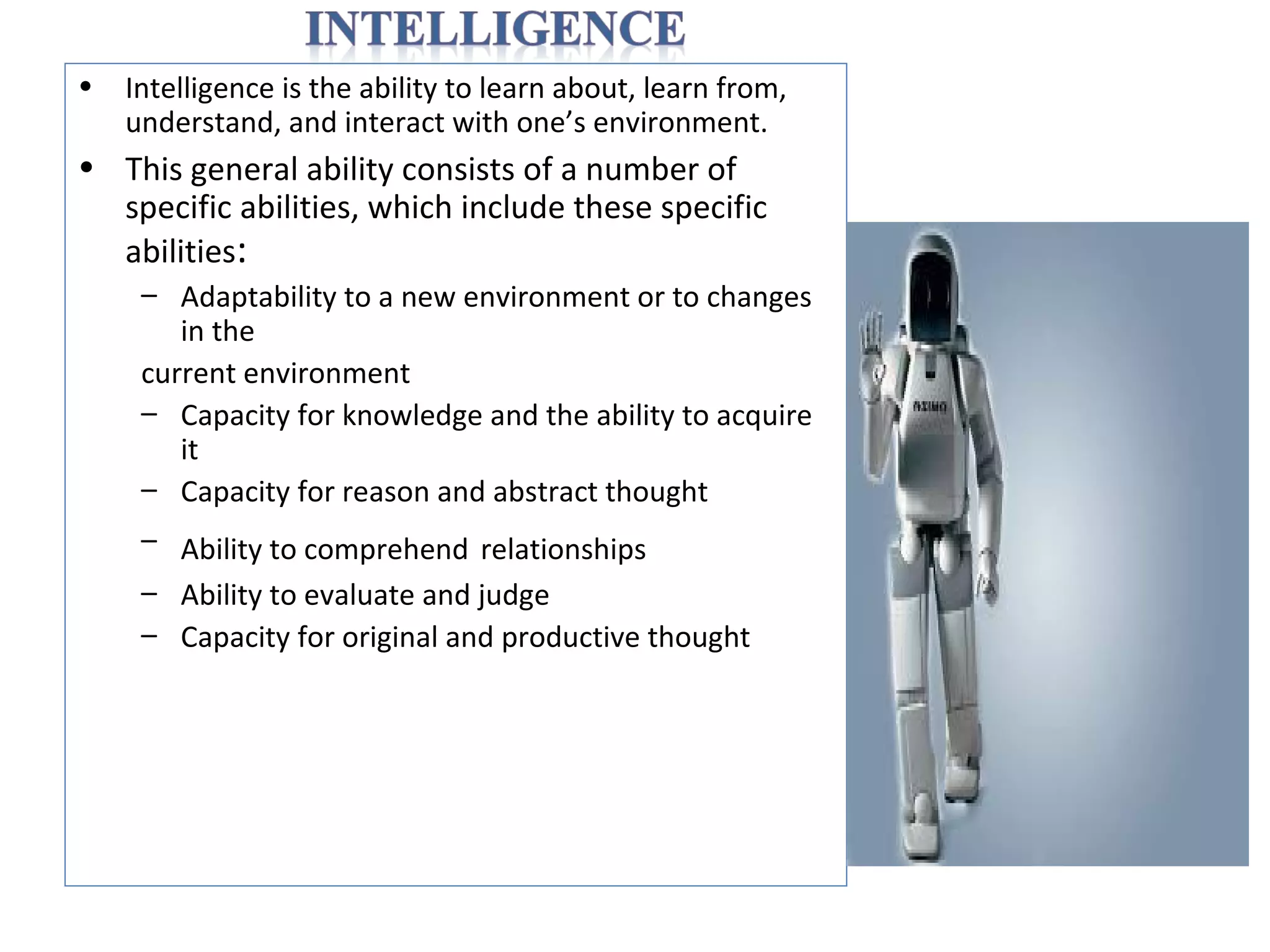
- Defining intelligence and AI, discussing the history and types of AI such as neural networks.
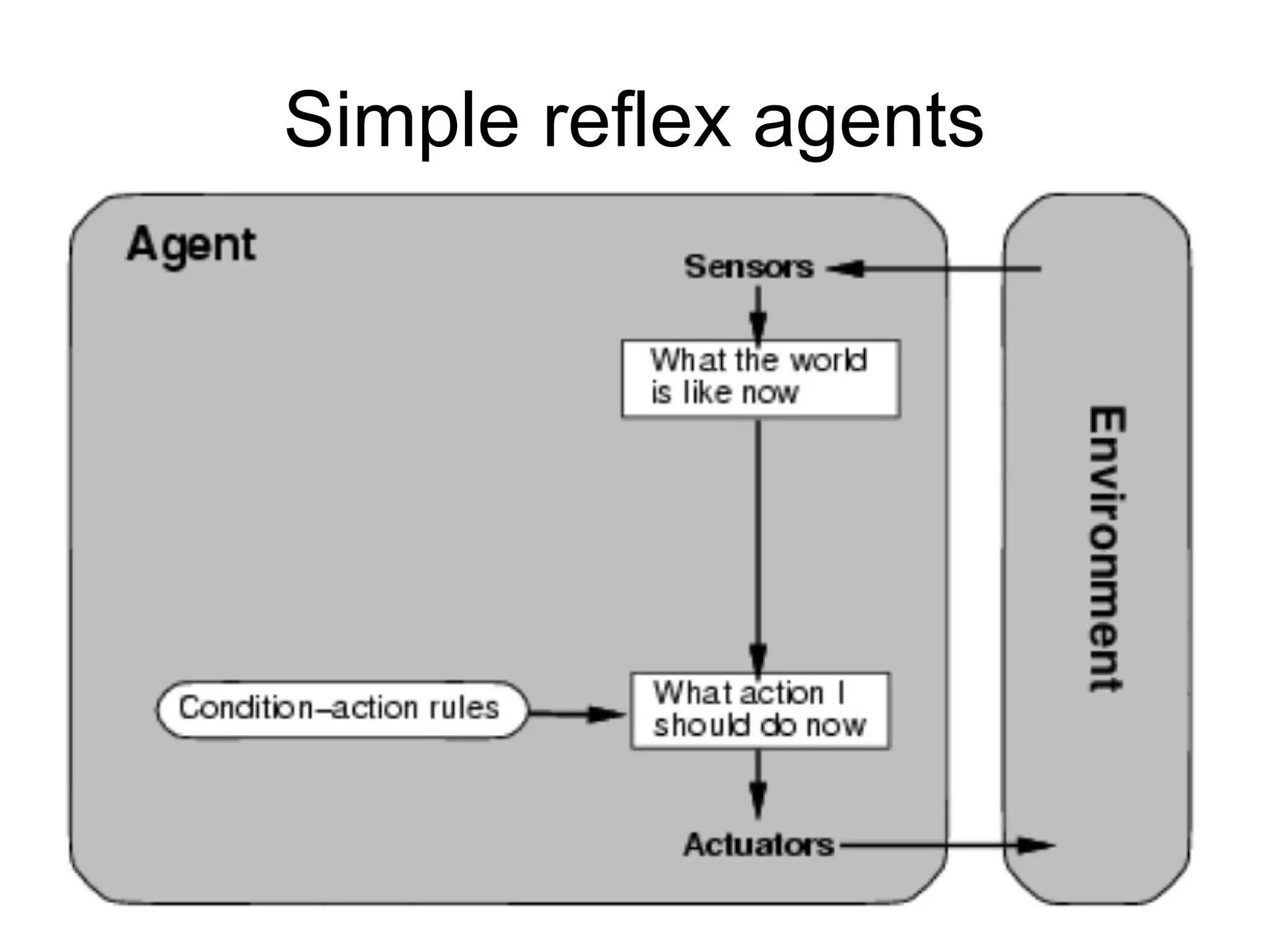
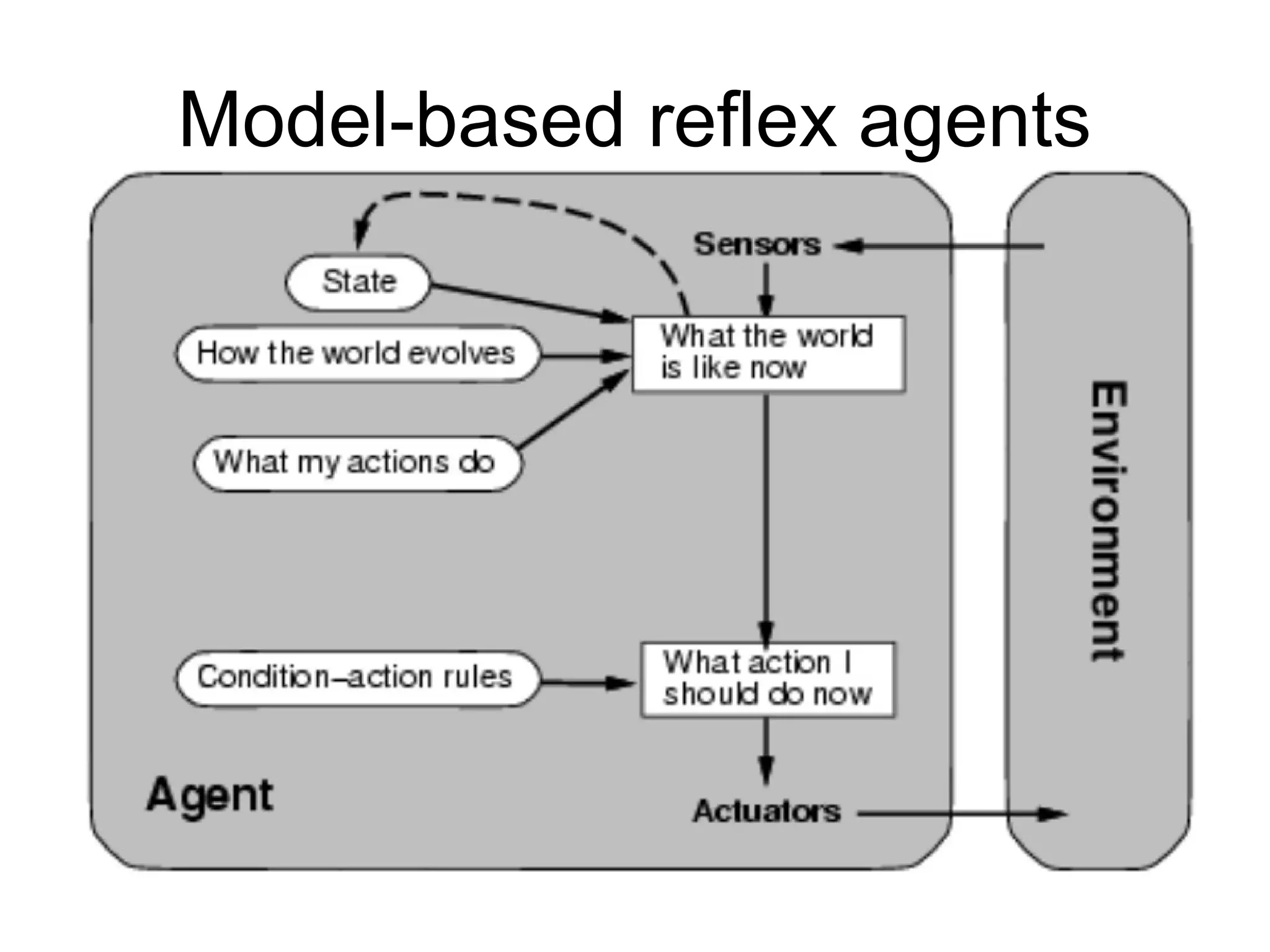
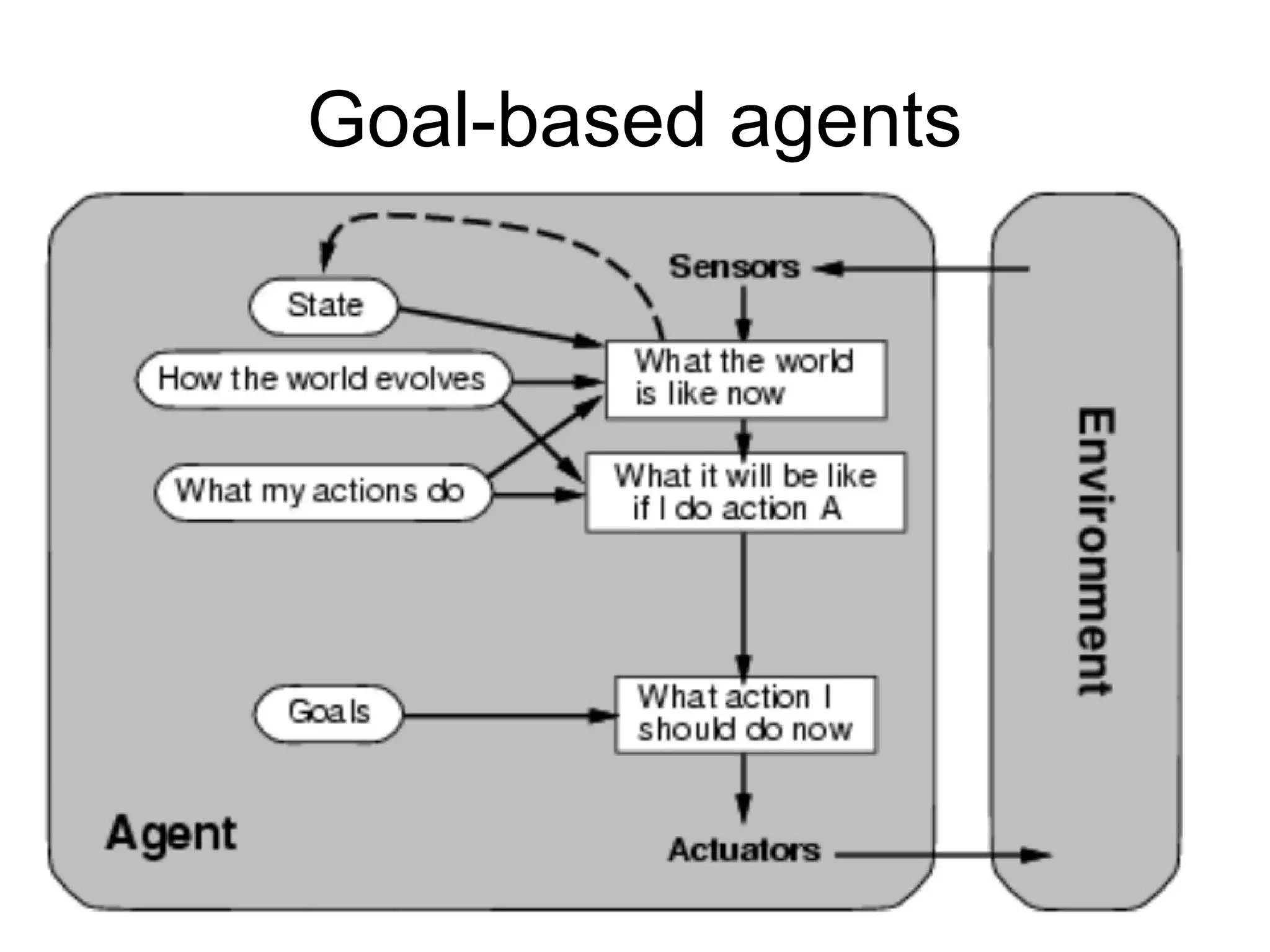
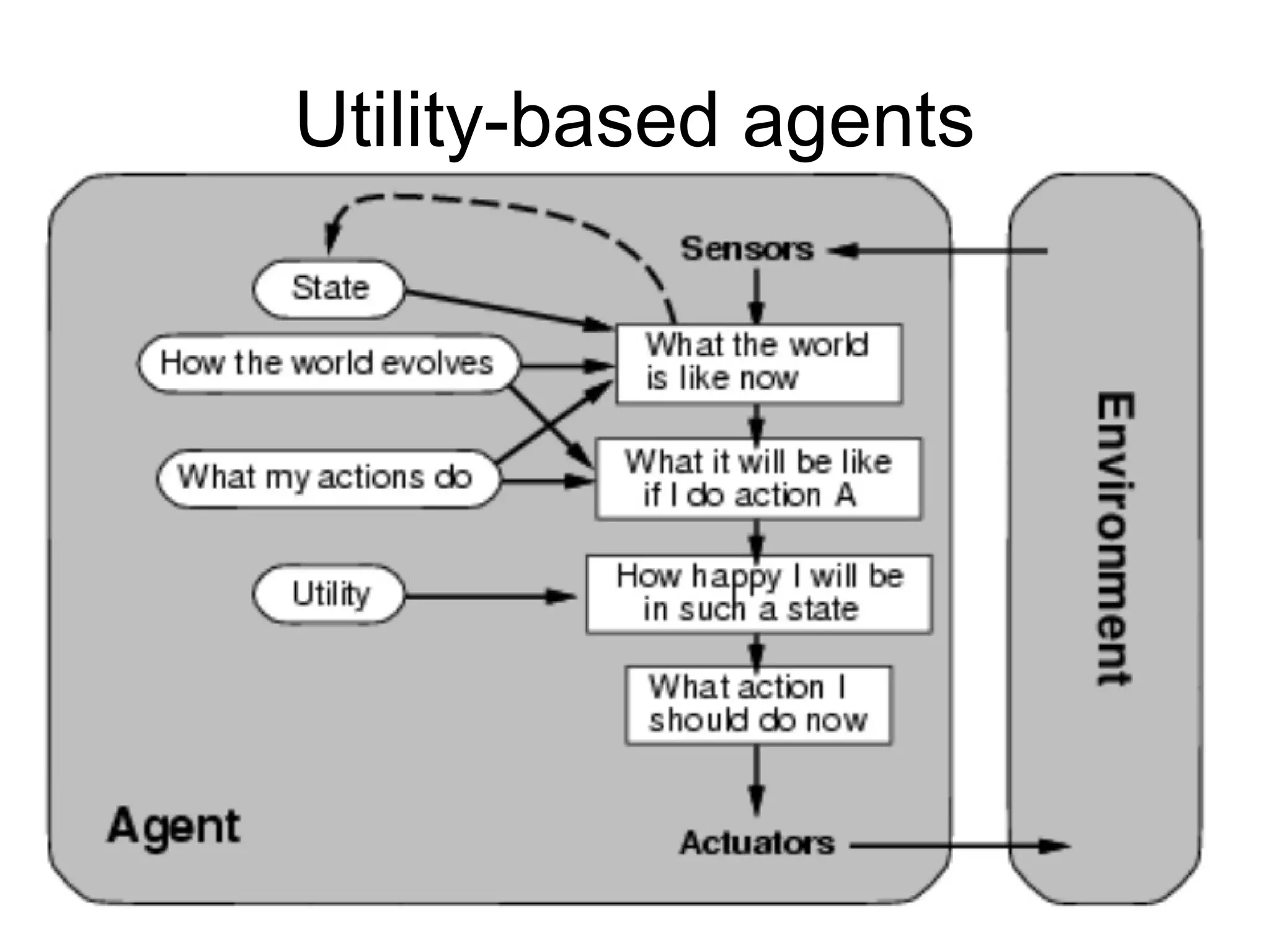
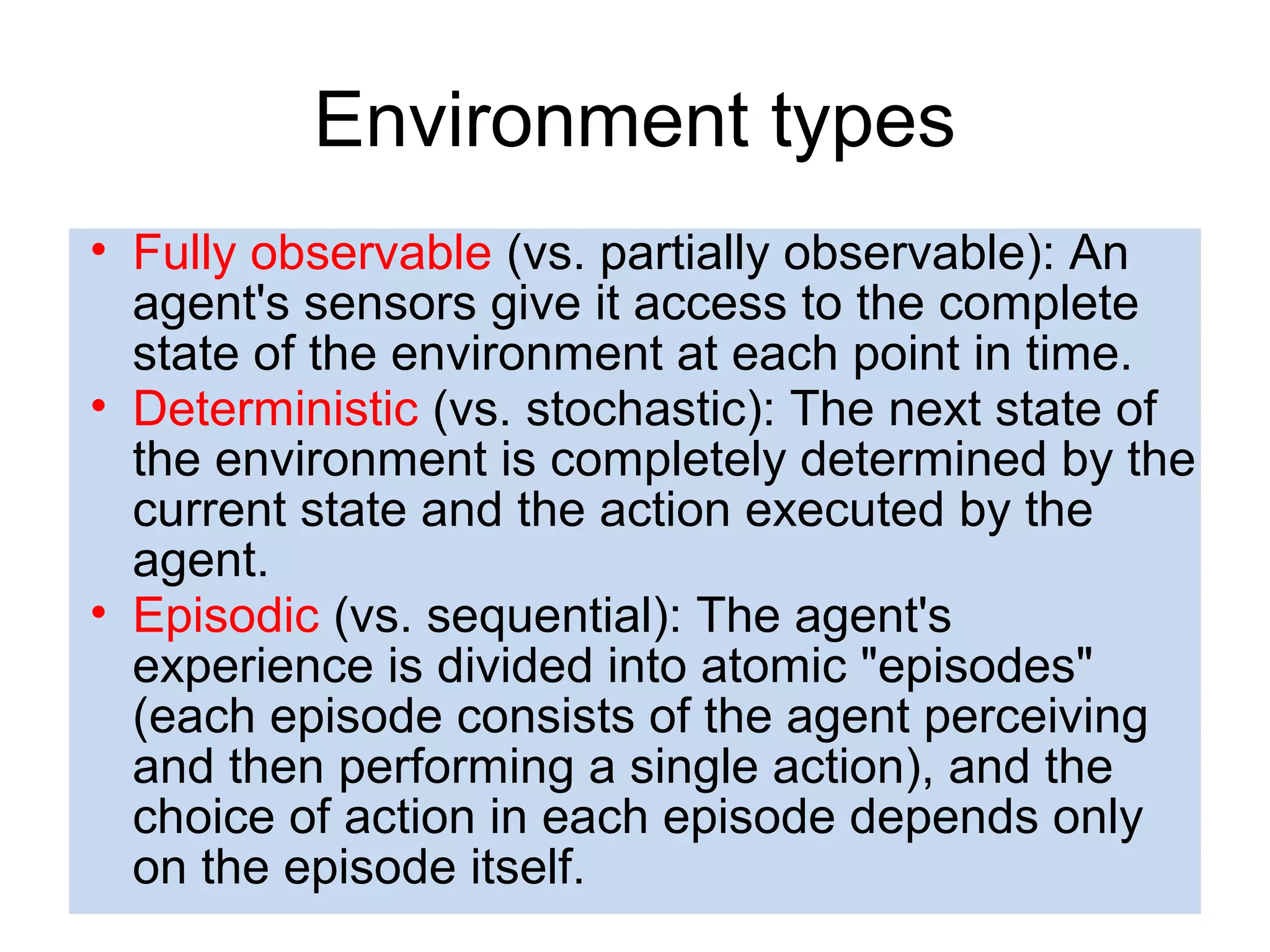
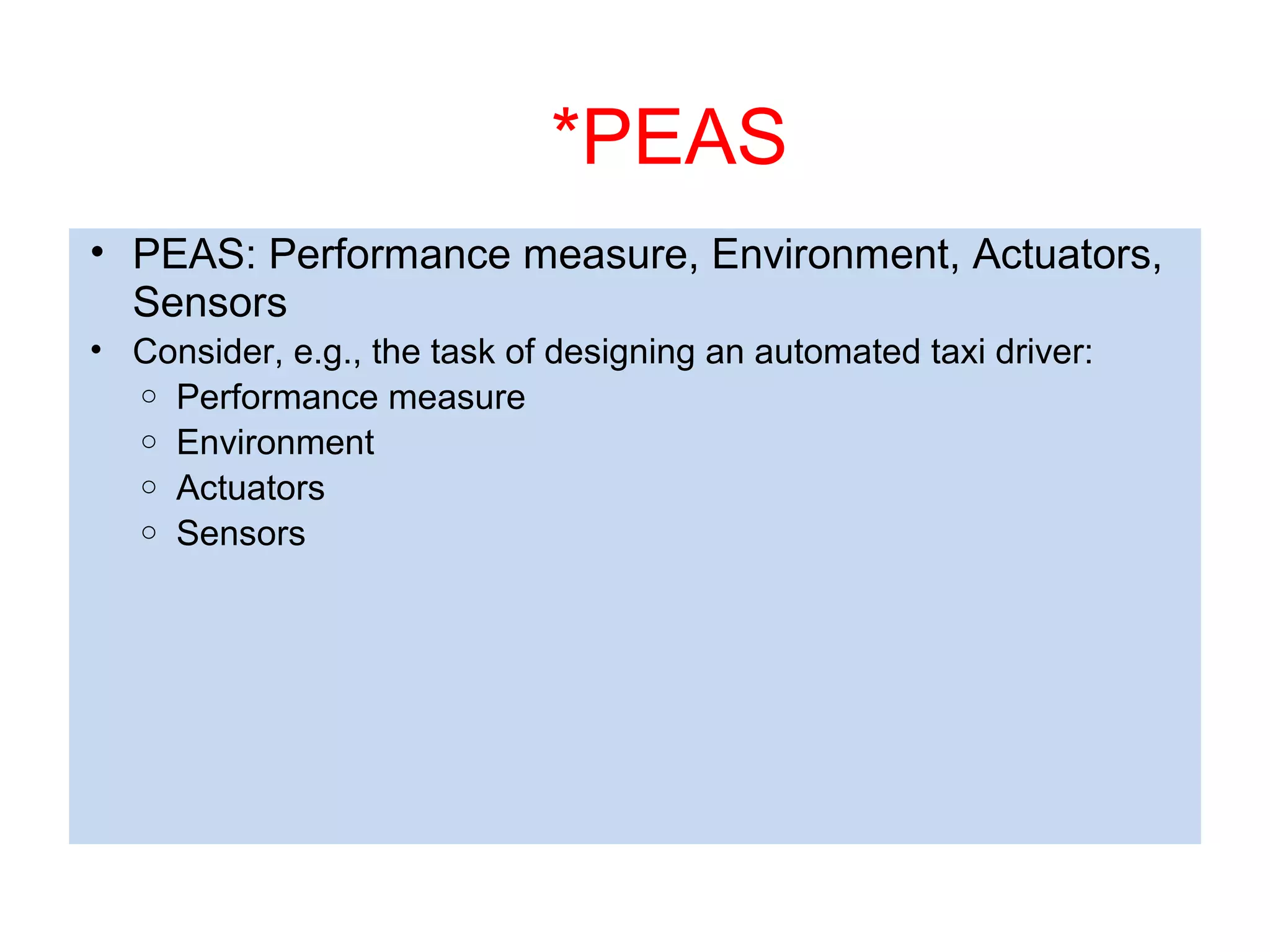
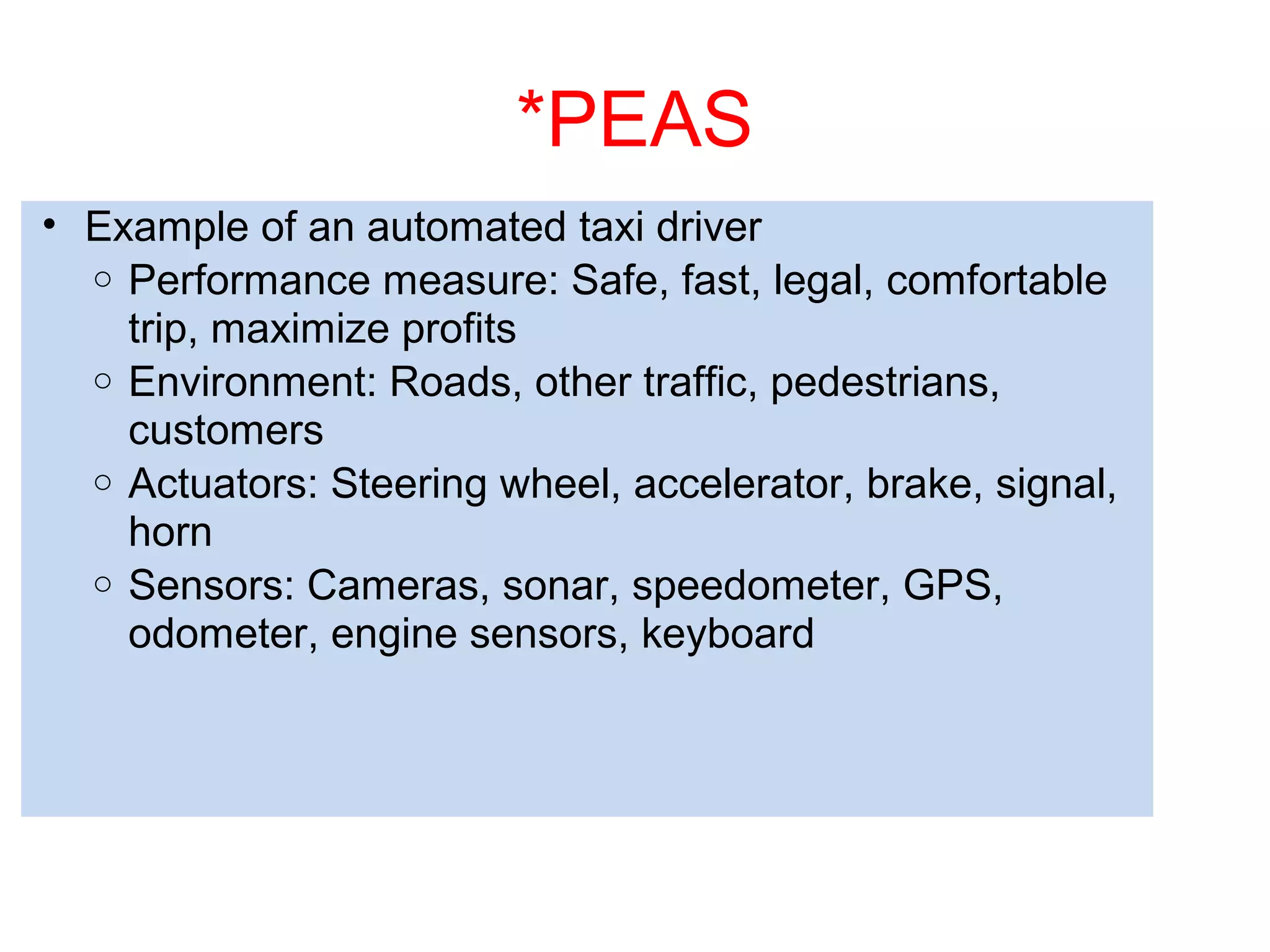
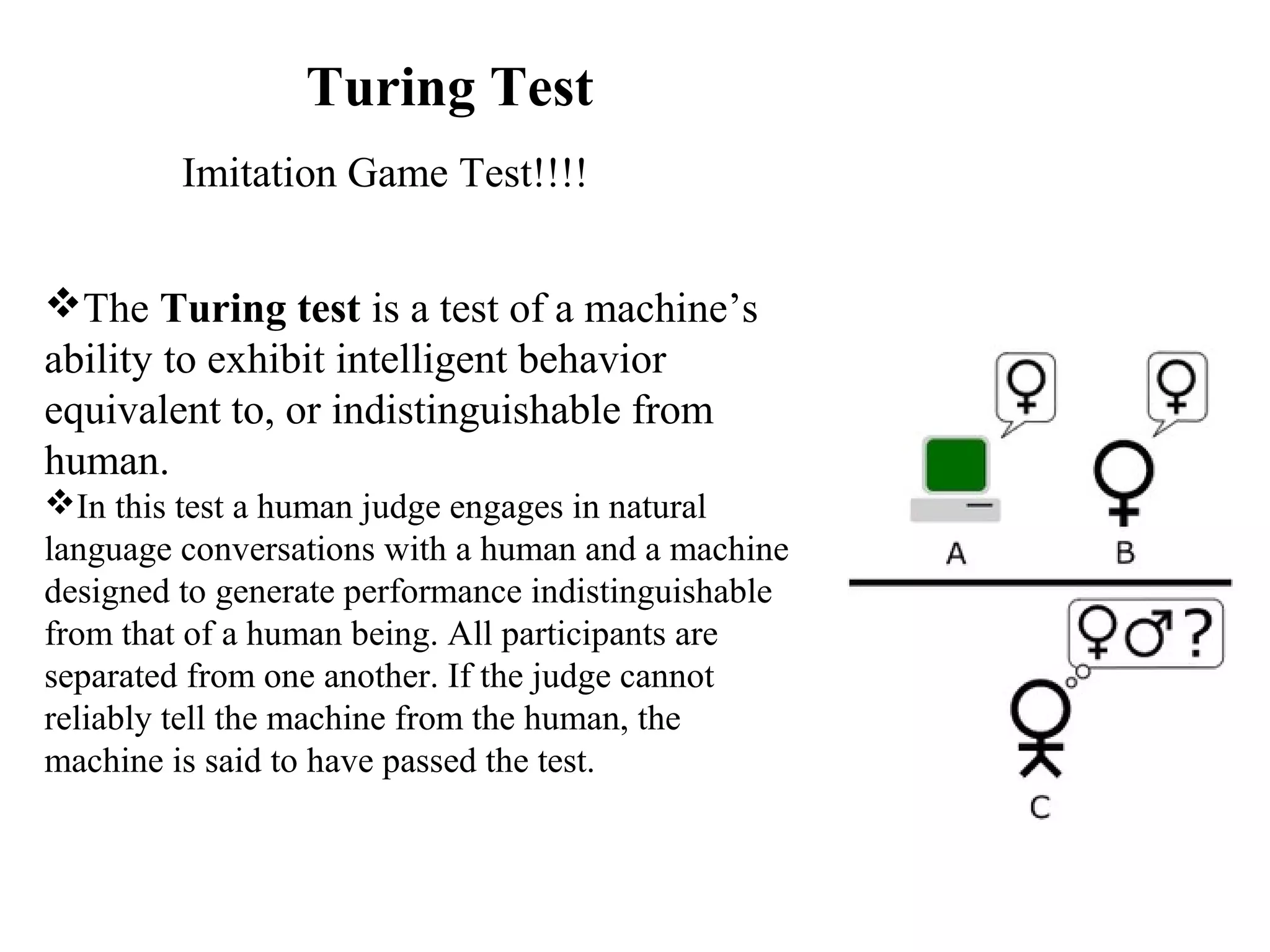
- Explaining the Turing test and different types of intelligent agents and their environments.
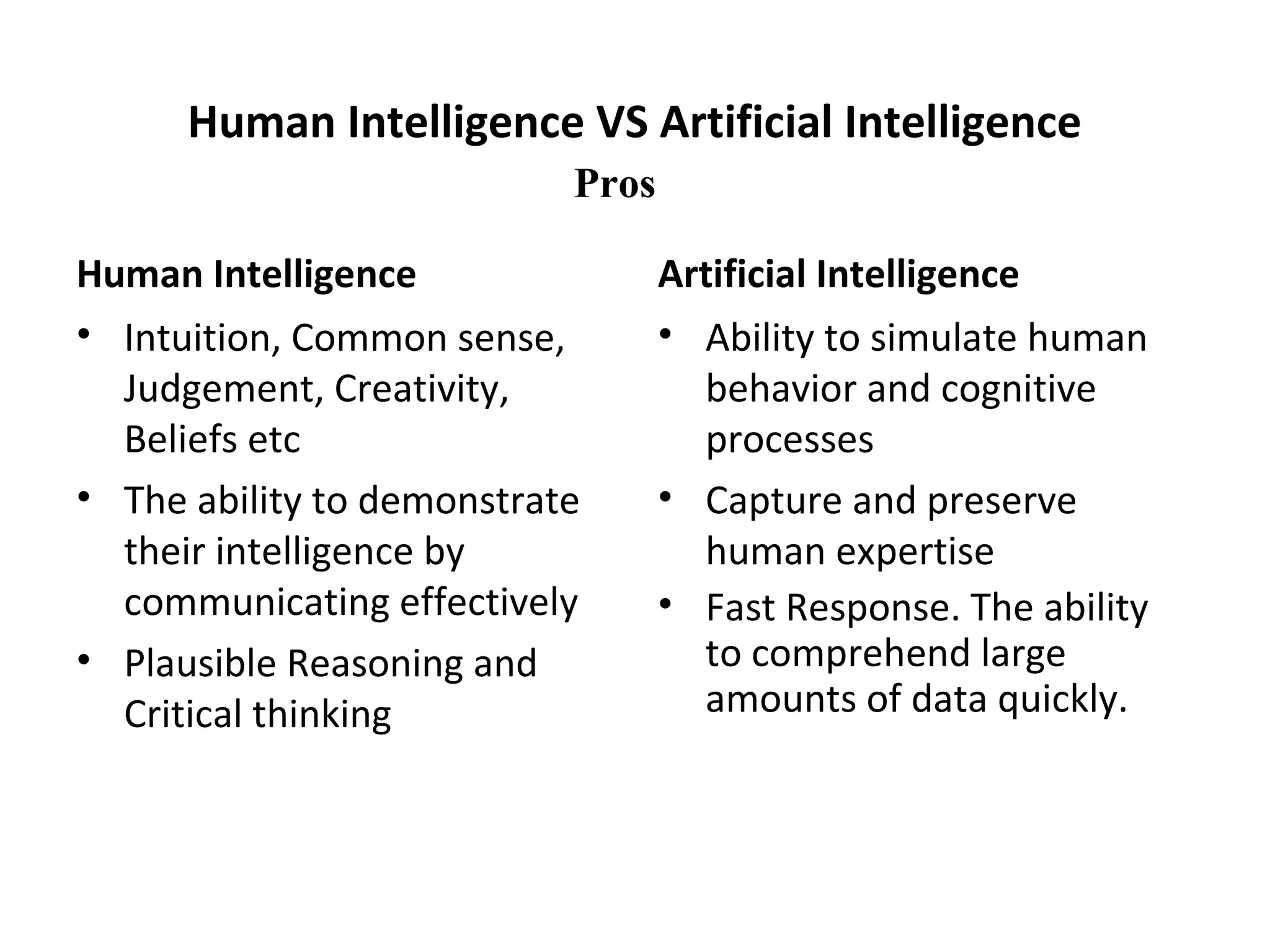
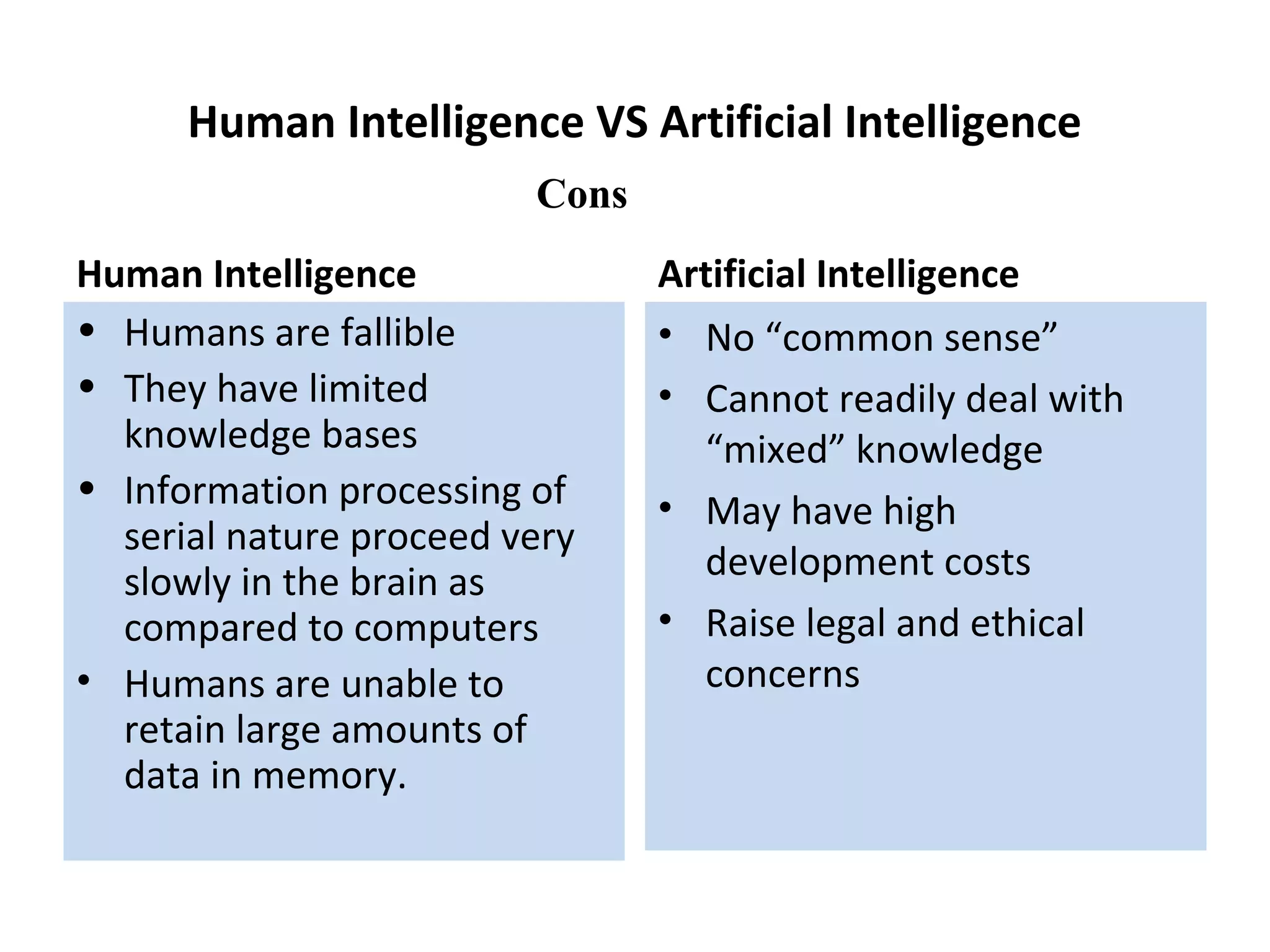
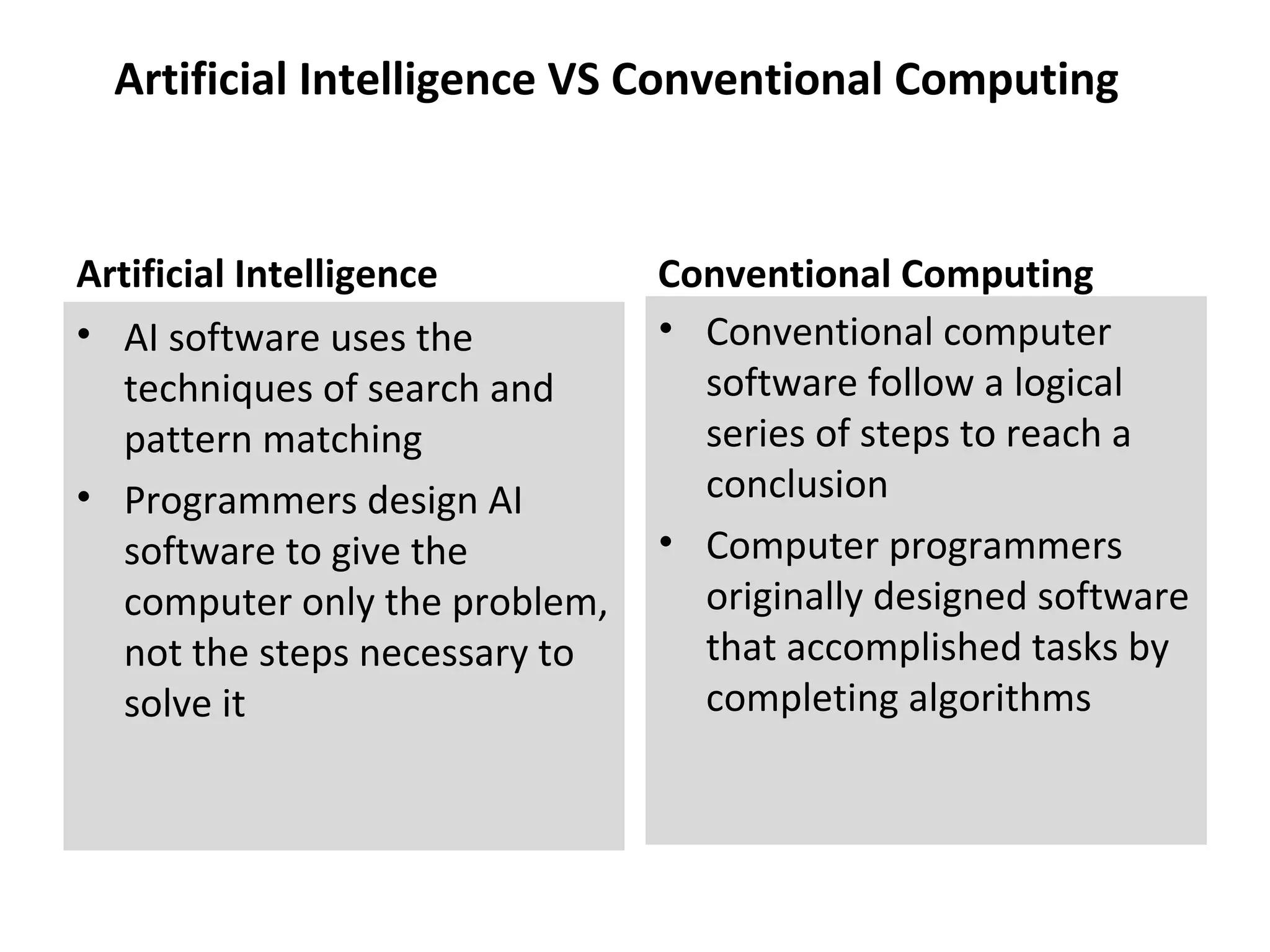
- Comparing human and AI in terms of capabilities and limitations.
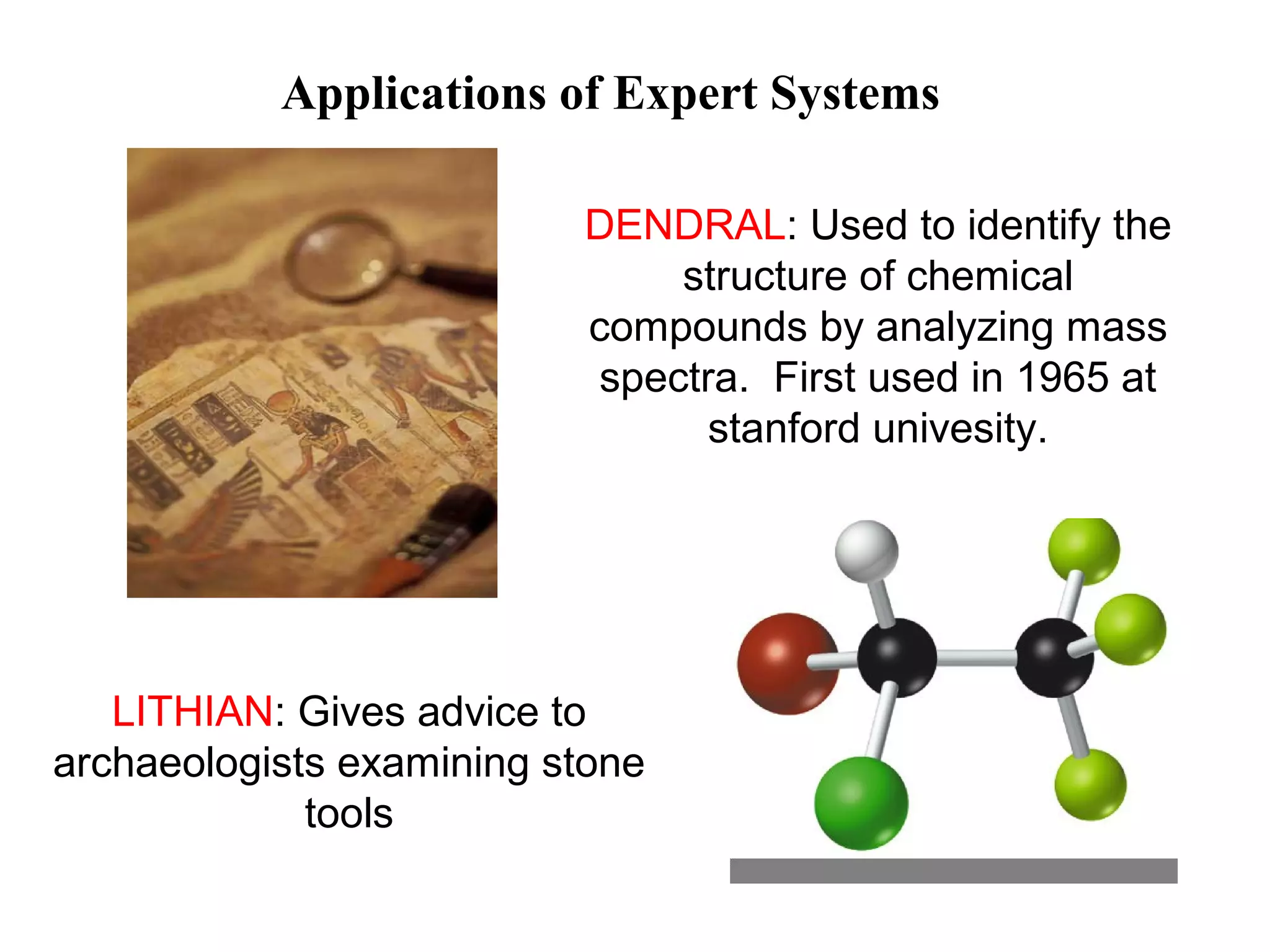
- Discussing applications of expert systems and how AI learns and resembles the human mind.
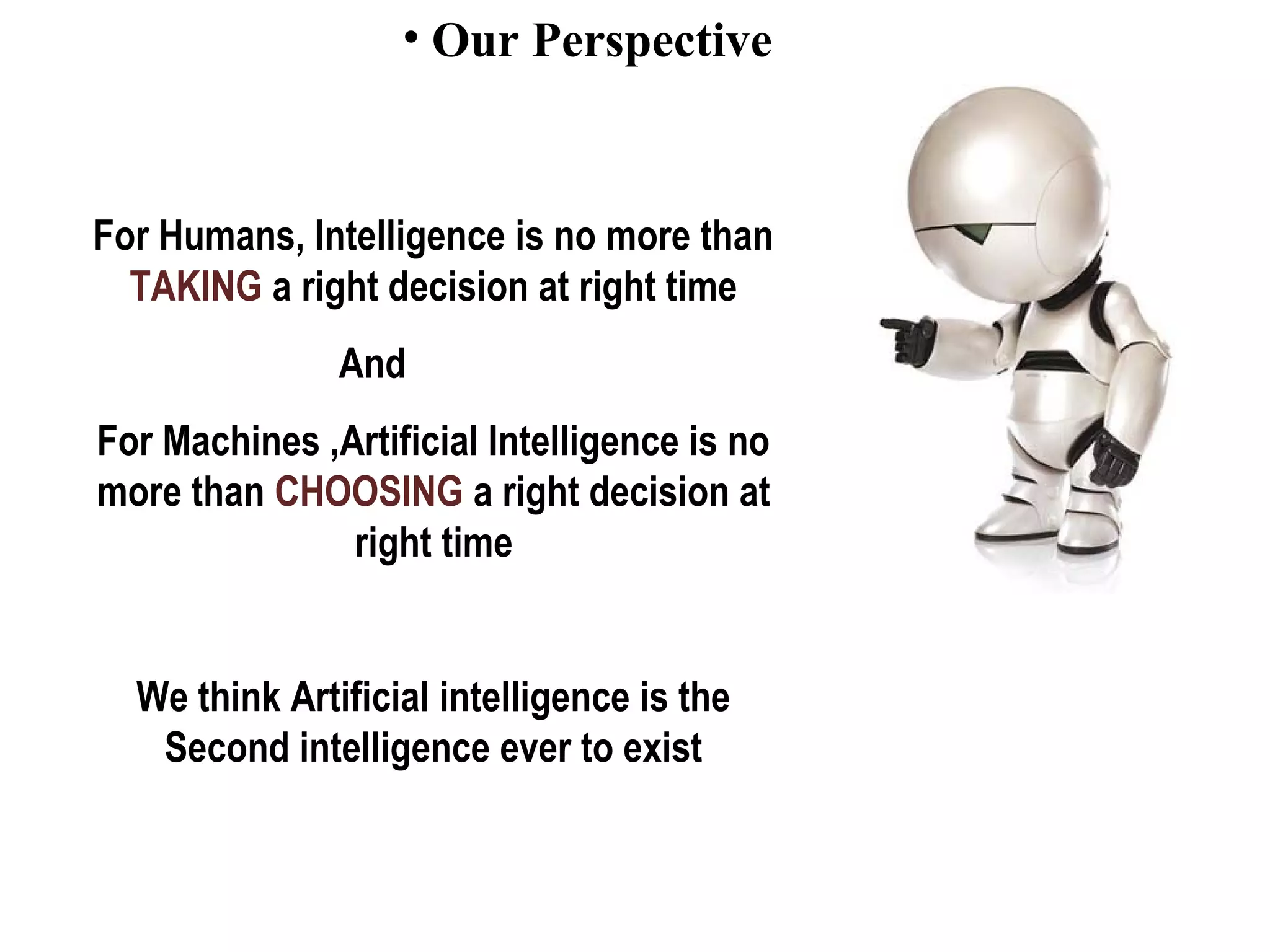
- Concluding that AI is an attempt to build computational models of intelligence.




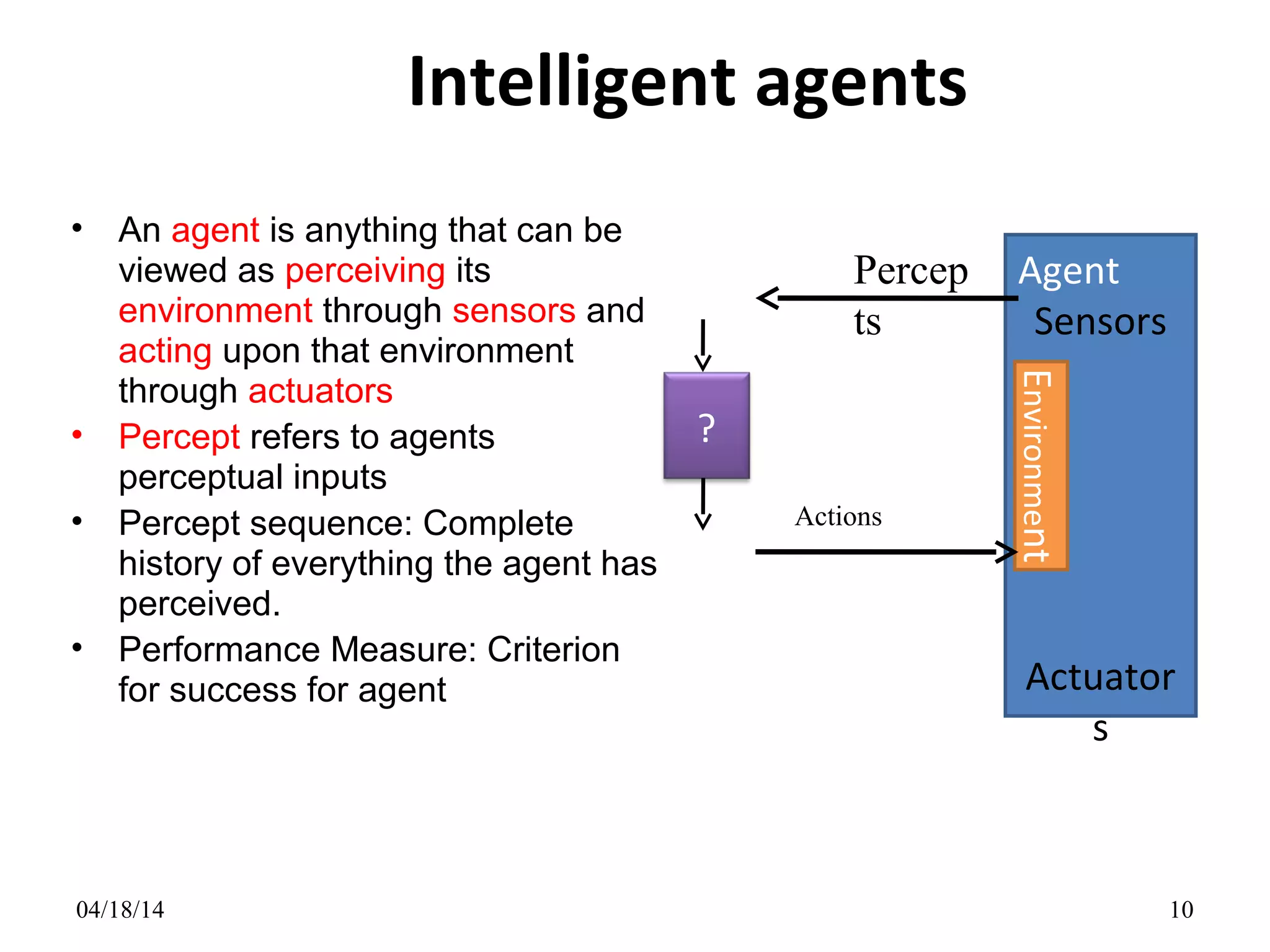
![• The agent function maps from percept
histories to actions:
[f: P* A]
Agents and environments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialintelligenceself-140418143731-phpapp01/75/Artificial-Intelligence-Introduction-11-2048.jpg)