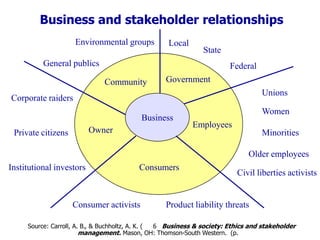
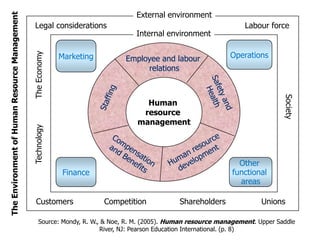
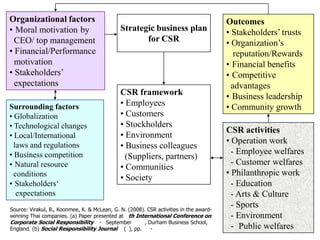
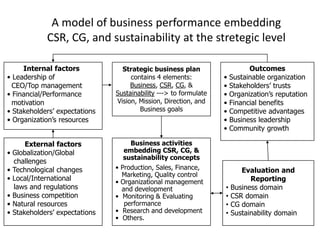
The document discusses a model of organizational performance that integrates corporate social responsibility (CSR), corporate governance (CG), and sustainability at a strategic level to address global challenges and promote sustainable development. It highlights the importance of considering the interests of various stakeholders in business practices and examines the impact of socio-economic factors such as capitalism and consumerism on future global challenges. Additionally, it outlines a research framework and potential future studies on performance indicators related to these integrated practices.


![Key words: Global challenges
• … any major trend, shock, or development that
has the potential for serious global impacts
(OCHA-PDSB, 2010, p. 4)
Source: Geldorf, K. (2010, January). Global challenges and their impact on international
humanitarian action. Retrieved, 20 October 2013, from
https://docs.unocha.org/sites/dms/Documents/Global_Challenges_Policy_Brief_Jan10.pdf
[UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA)- Policy Development and
Studies Branch (PDSB)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grf2013-presentation-131120081012-phpapp01/85/Global-Challenges-Sustainable-Development-And-Their-Implications-For-Organization-Performance-3-320.jpg)