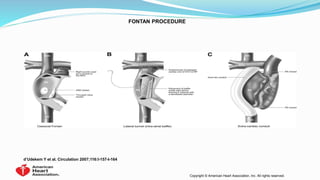
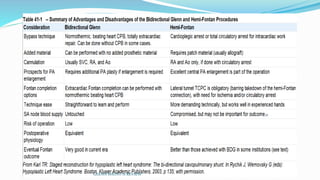
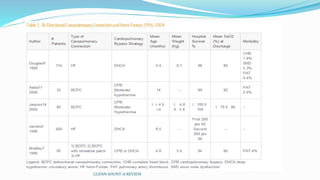
1) Cavopulmonary connections like the Glenn shunt divert systemic venous return directly to the pulmonary circulation, improving oxygen saturation for patients with single ventricle physiology.
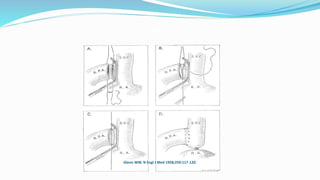
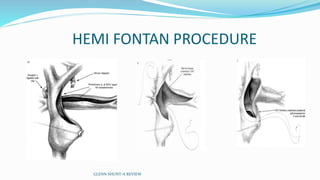
2) The Glenn shunt involves anastomosis of the superior vena cava to the right pulmonary artery, reducing the volume load on the single ventricle.
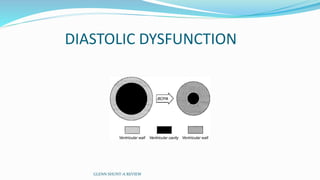
3) Immediate postoperative issues include managing ventilation, elevated cavopulmonary pressures, hypertension/bradycardia, low cardiac output, and cyanosis which may result from pulmonary or systemic venous desaturation or decreased pulmonary blood flow.





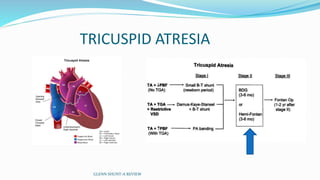

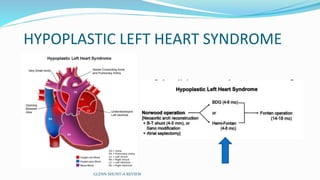



![ Glenn.
unidirectional (classic) and bidirectional superior cavopulmonary
anastomoses and inferior cavopulmonary anastomosis (inferior
vena cava [IVC]-to-PA connection).
Interim palliation with a BDG shunt - standard of care in infancy (4
to 9 months of age).
GLENN SHUNT-A REVIEW](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glenshunt-180722052620/85/Glen-shunt-BDG-12-320.jpg)