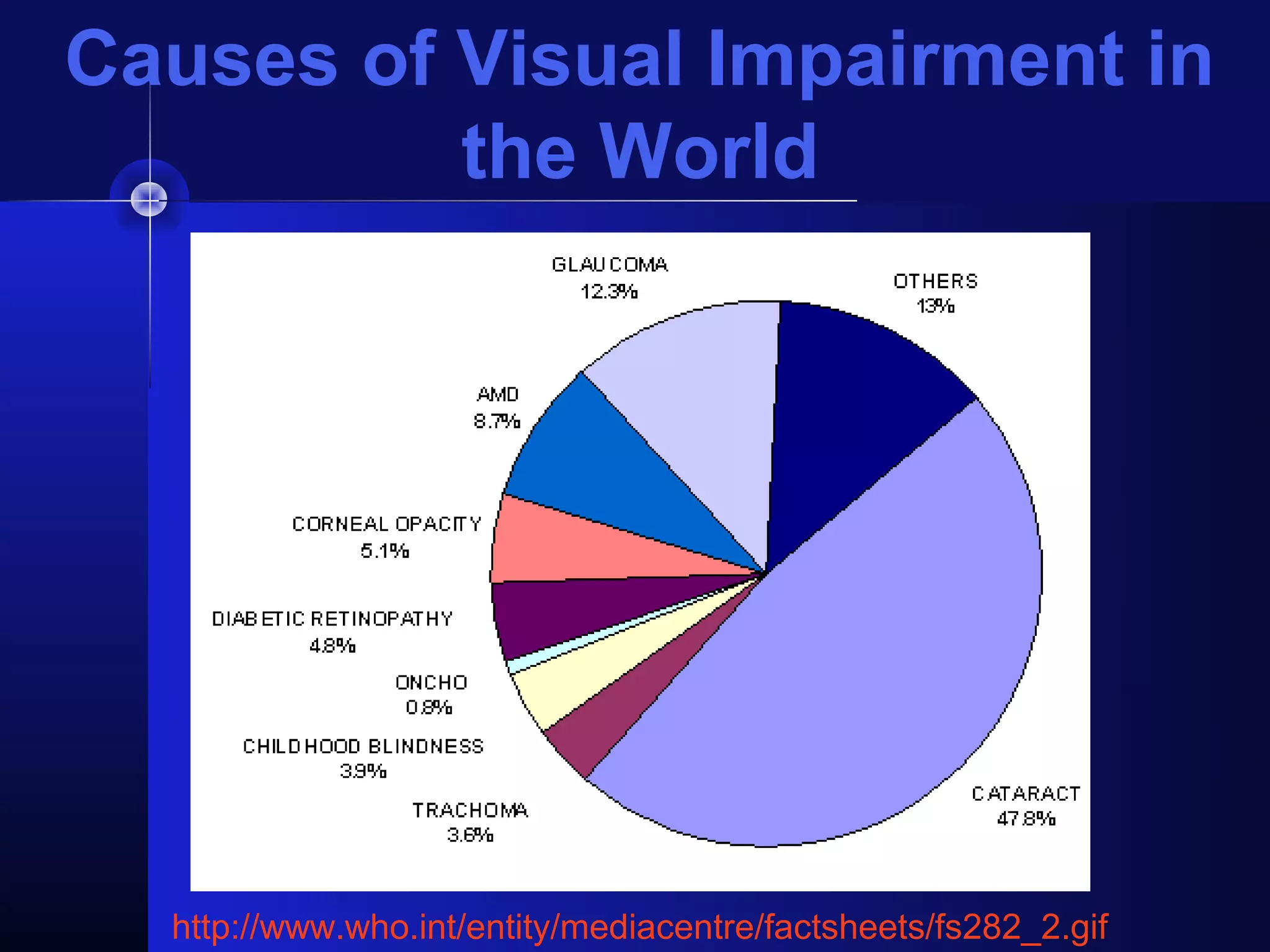
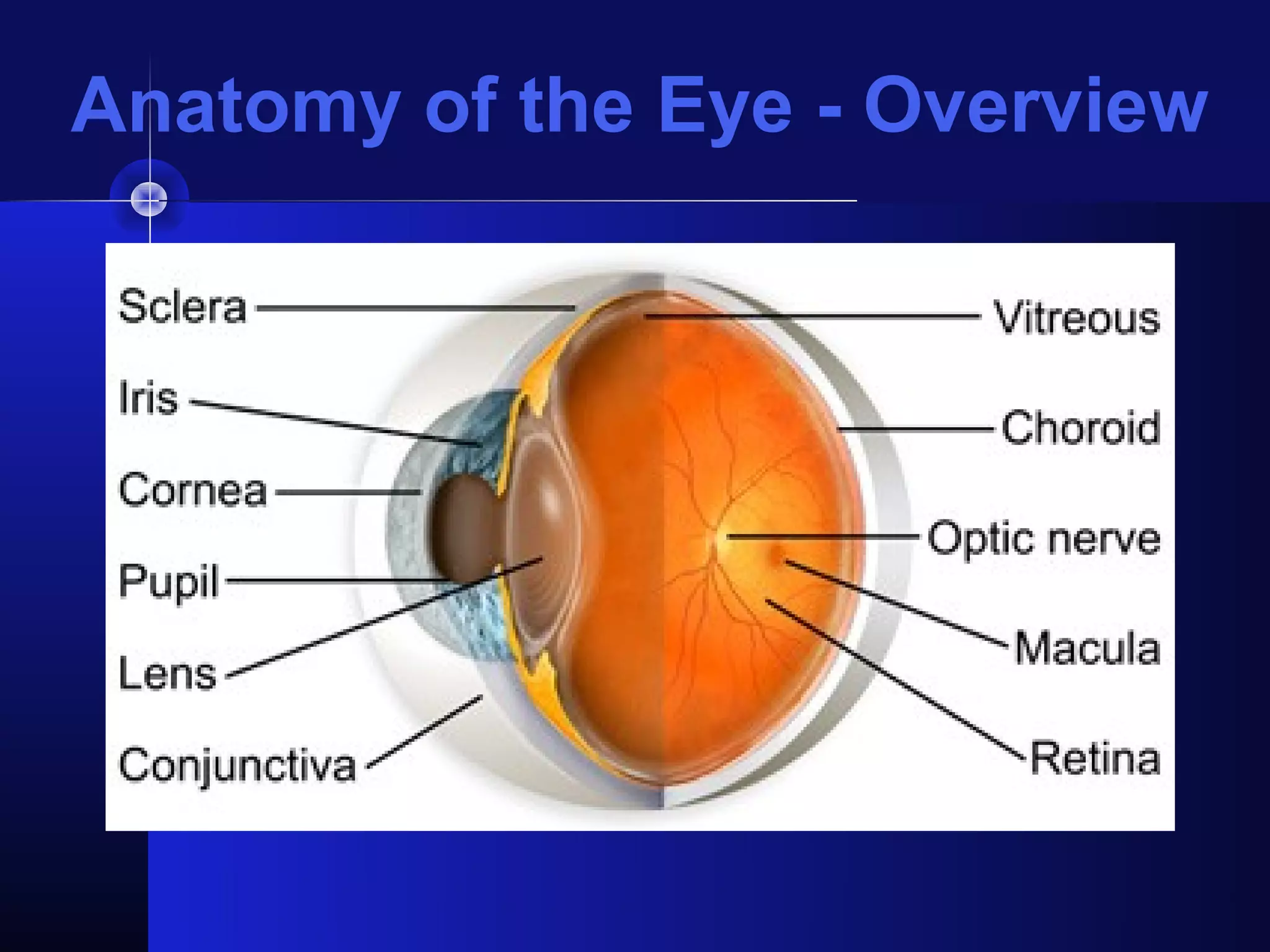
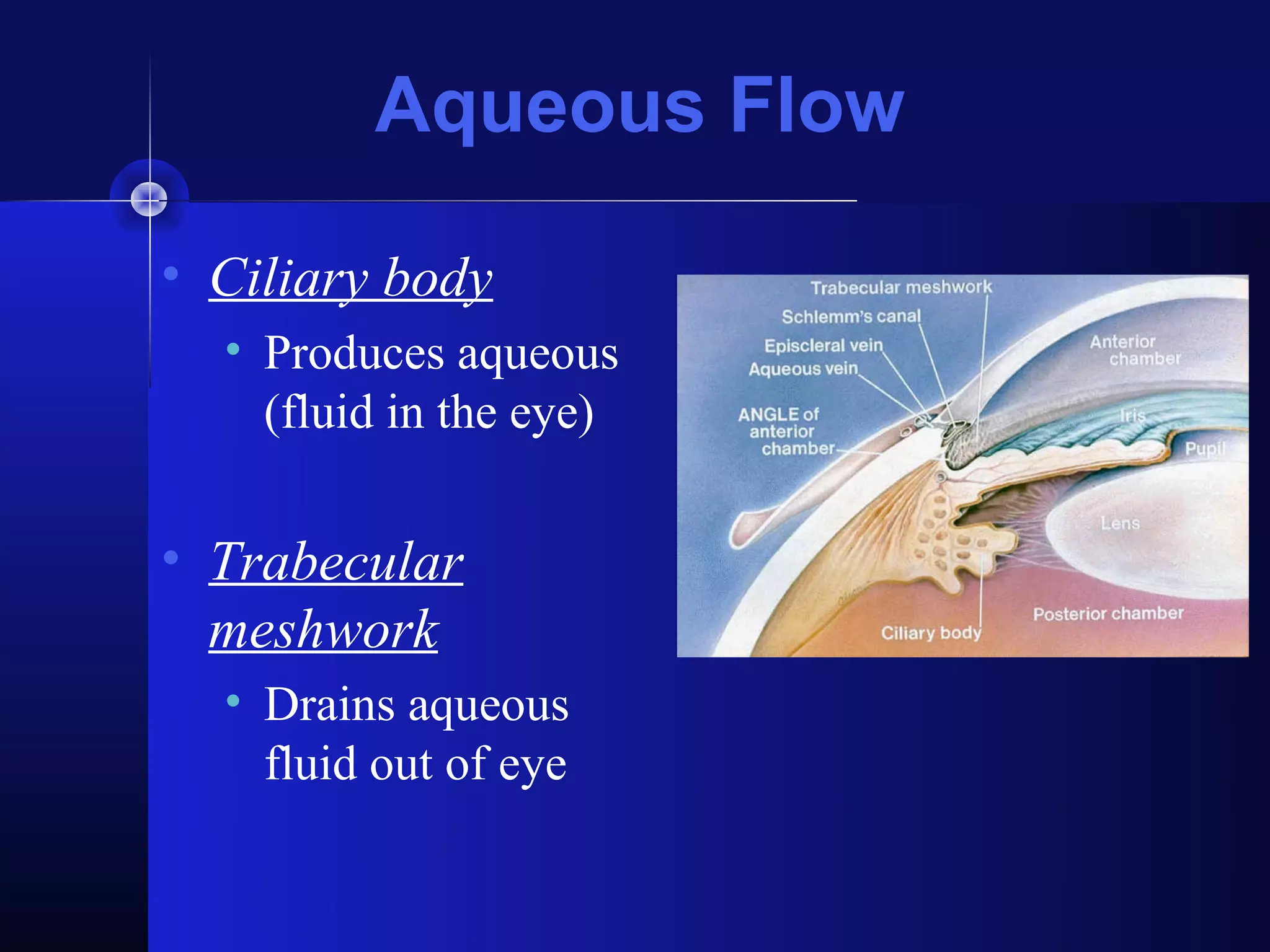
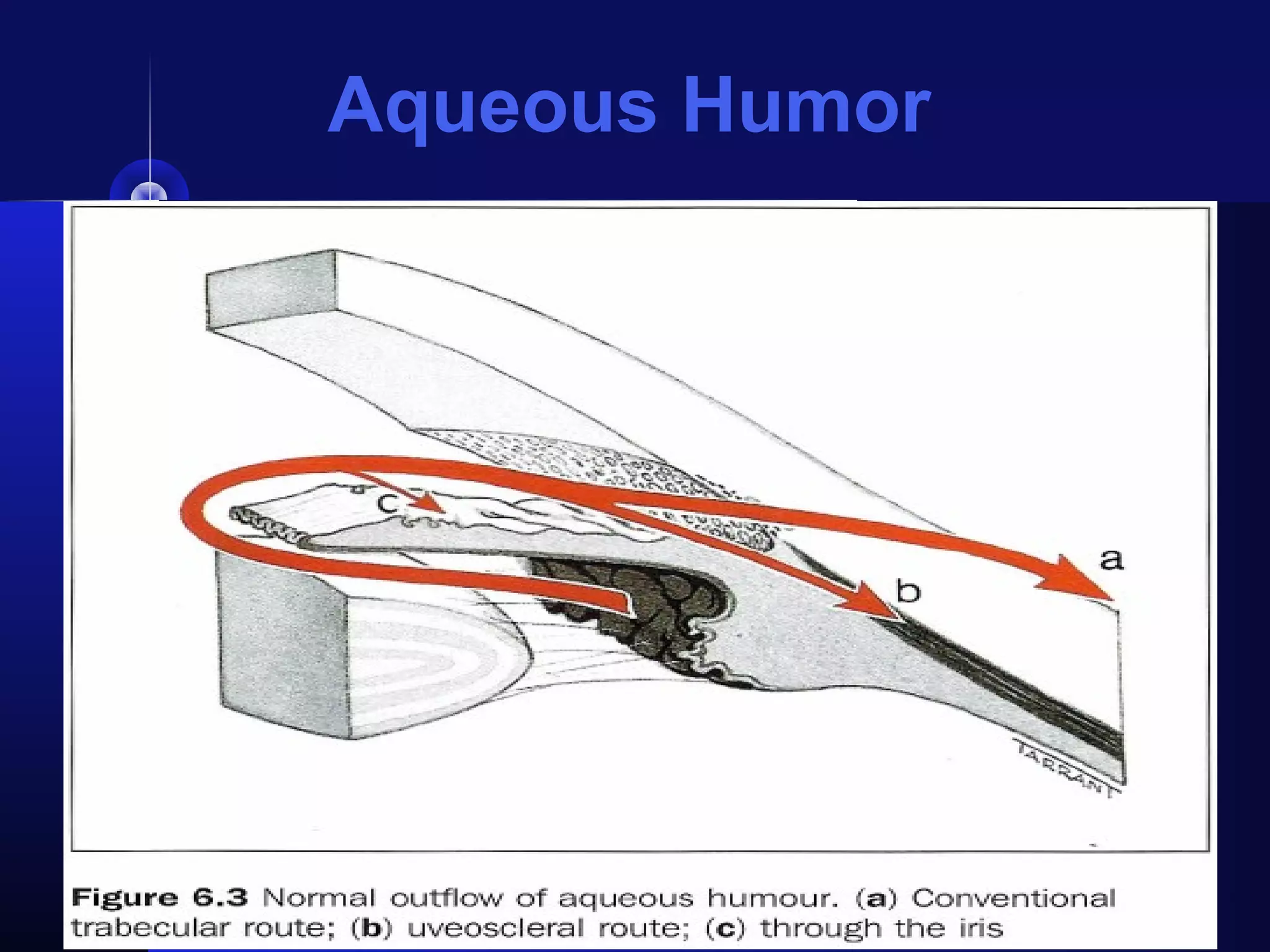
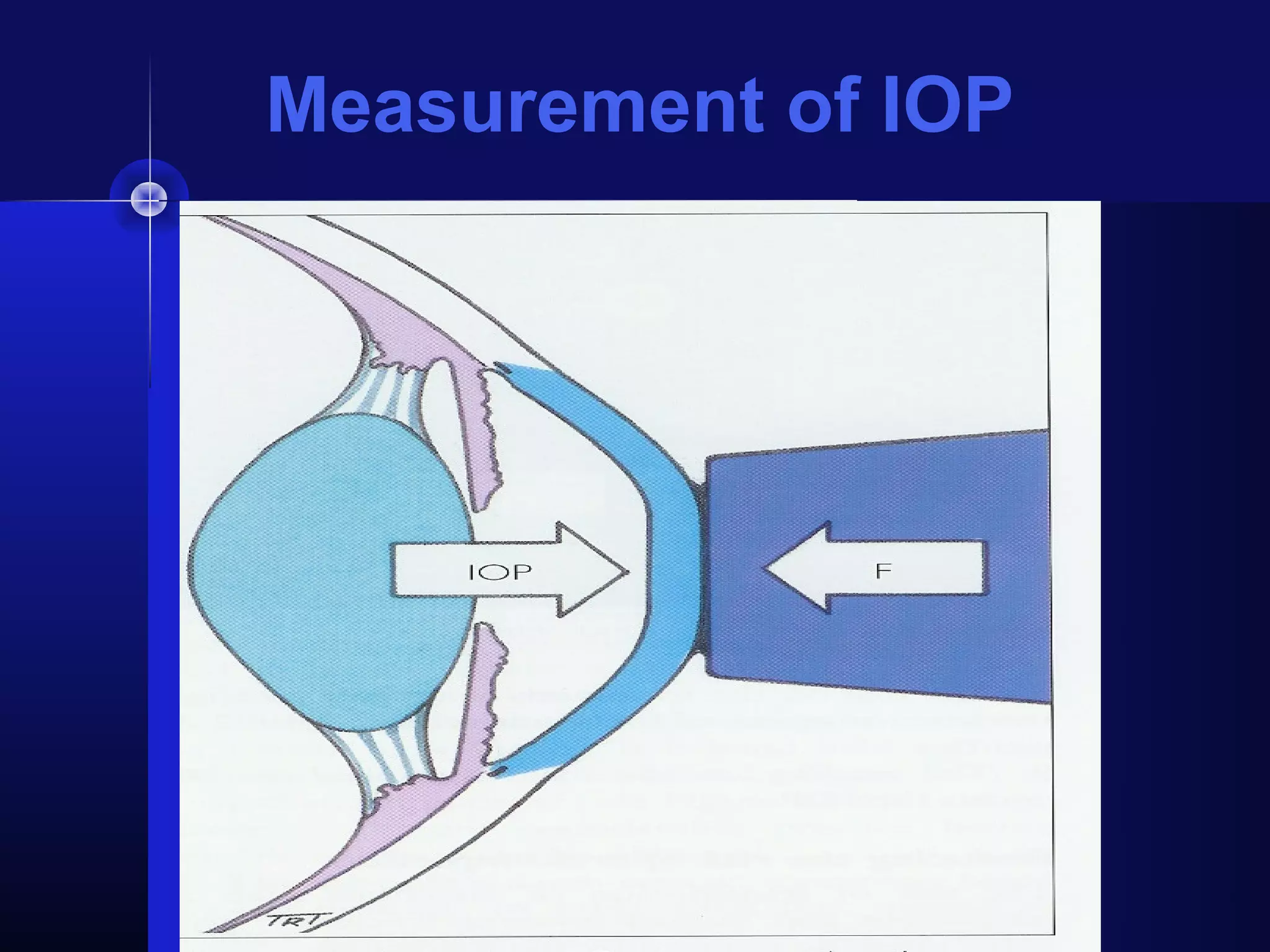
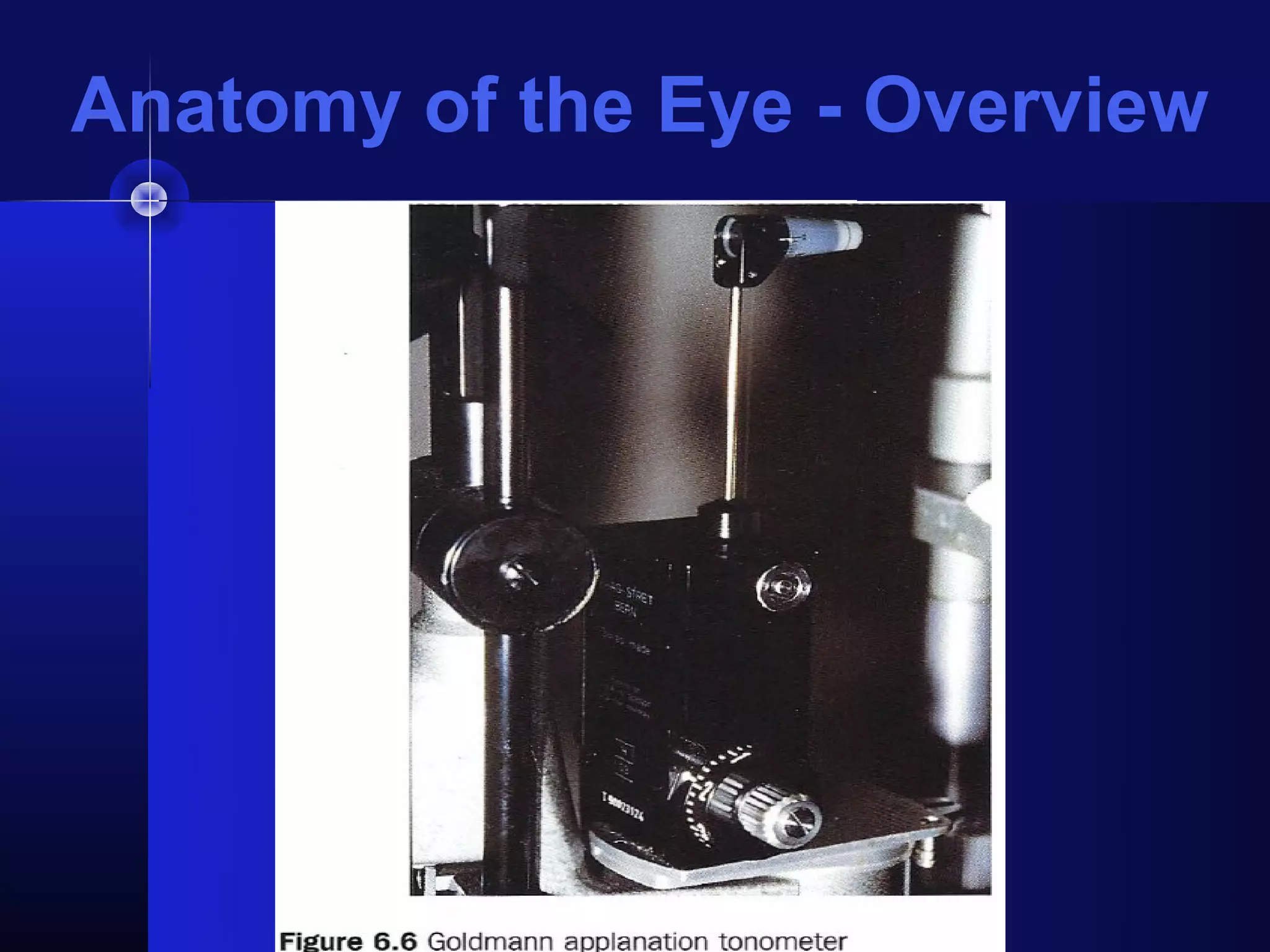
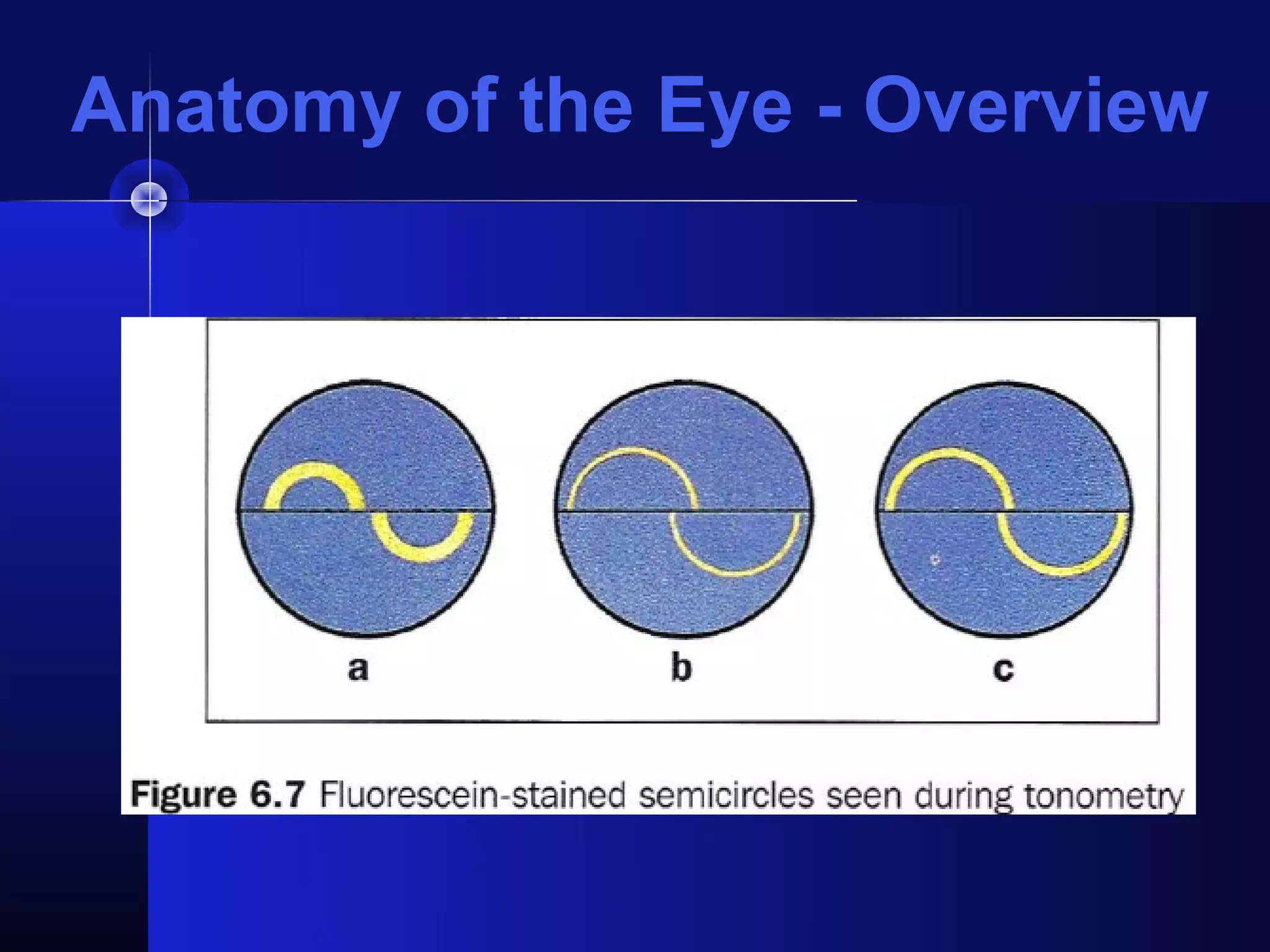
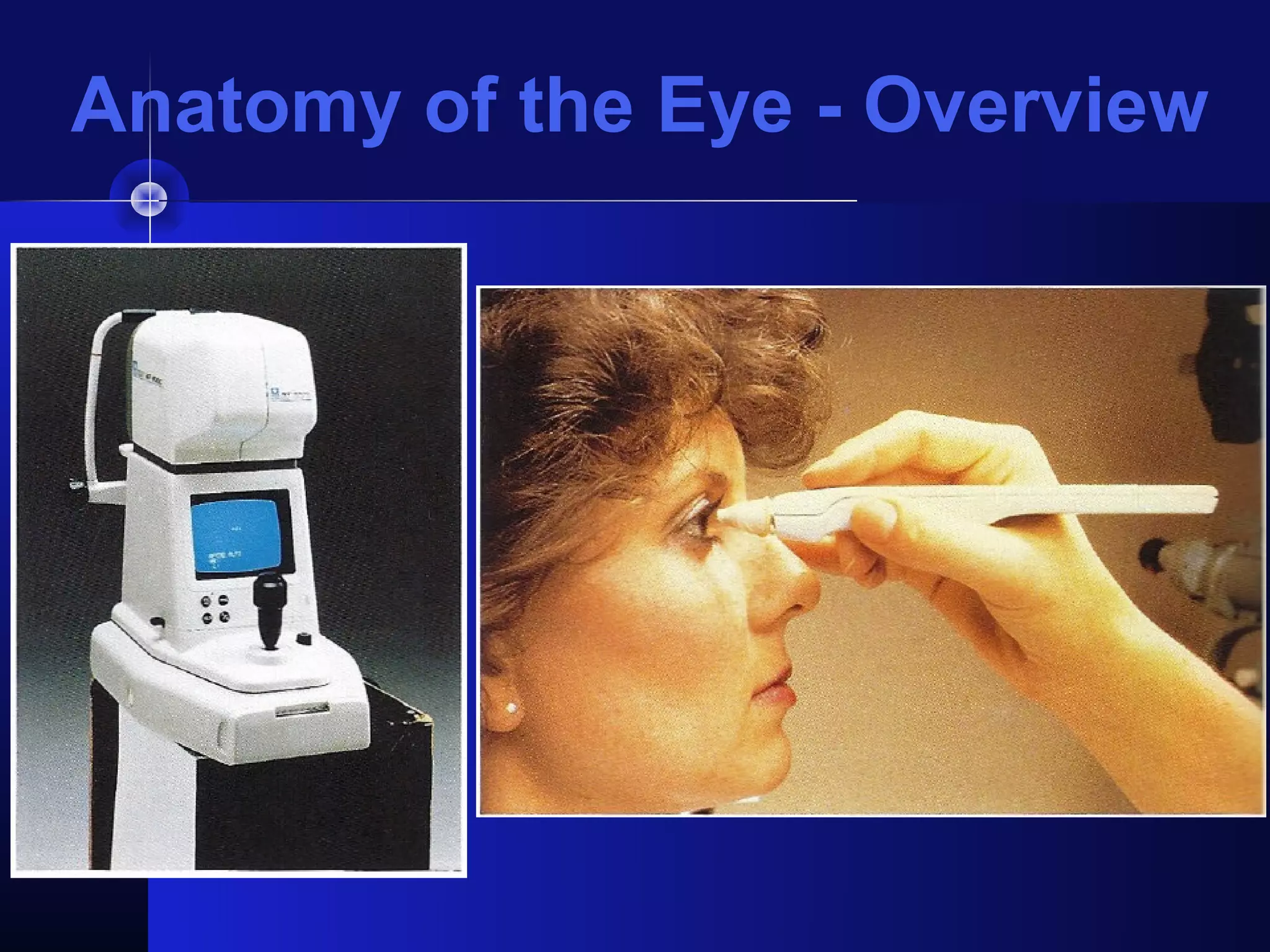
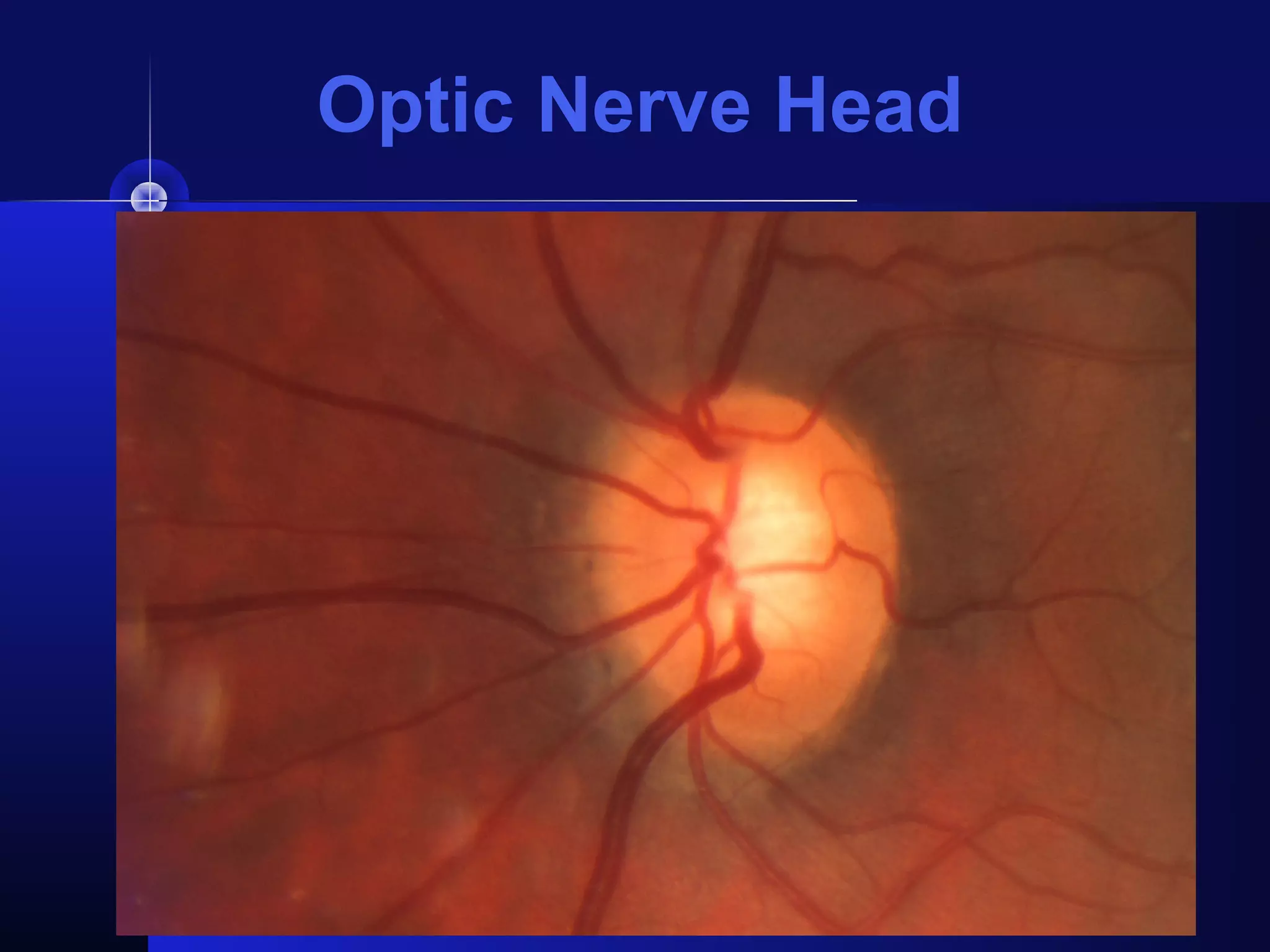
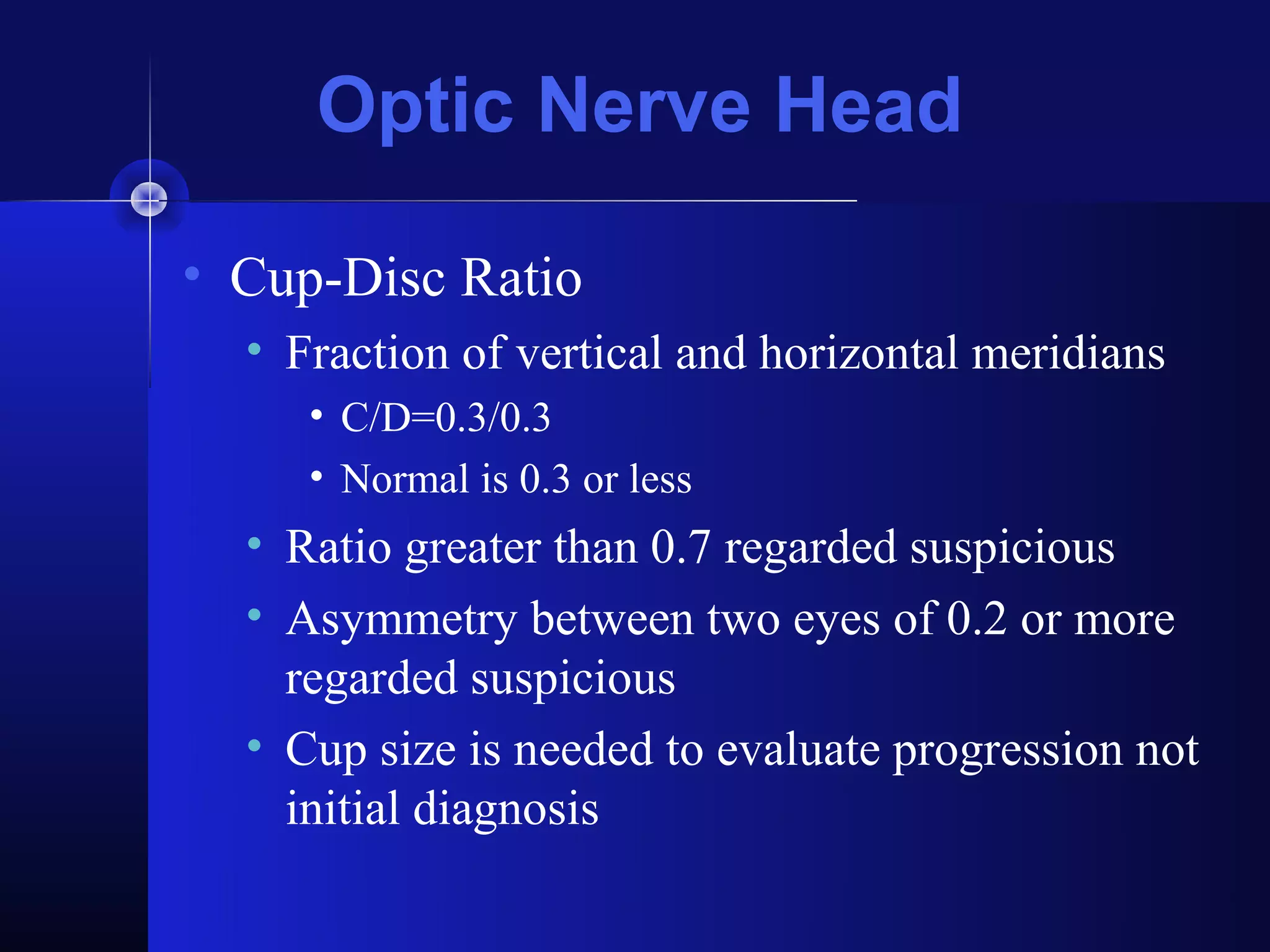
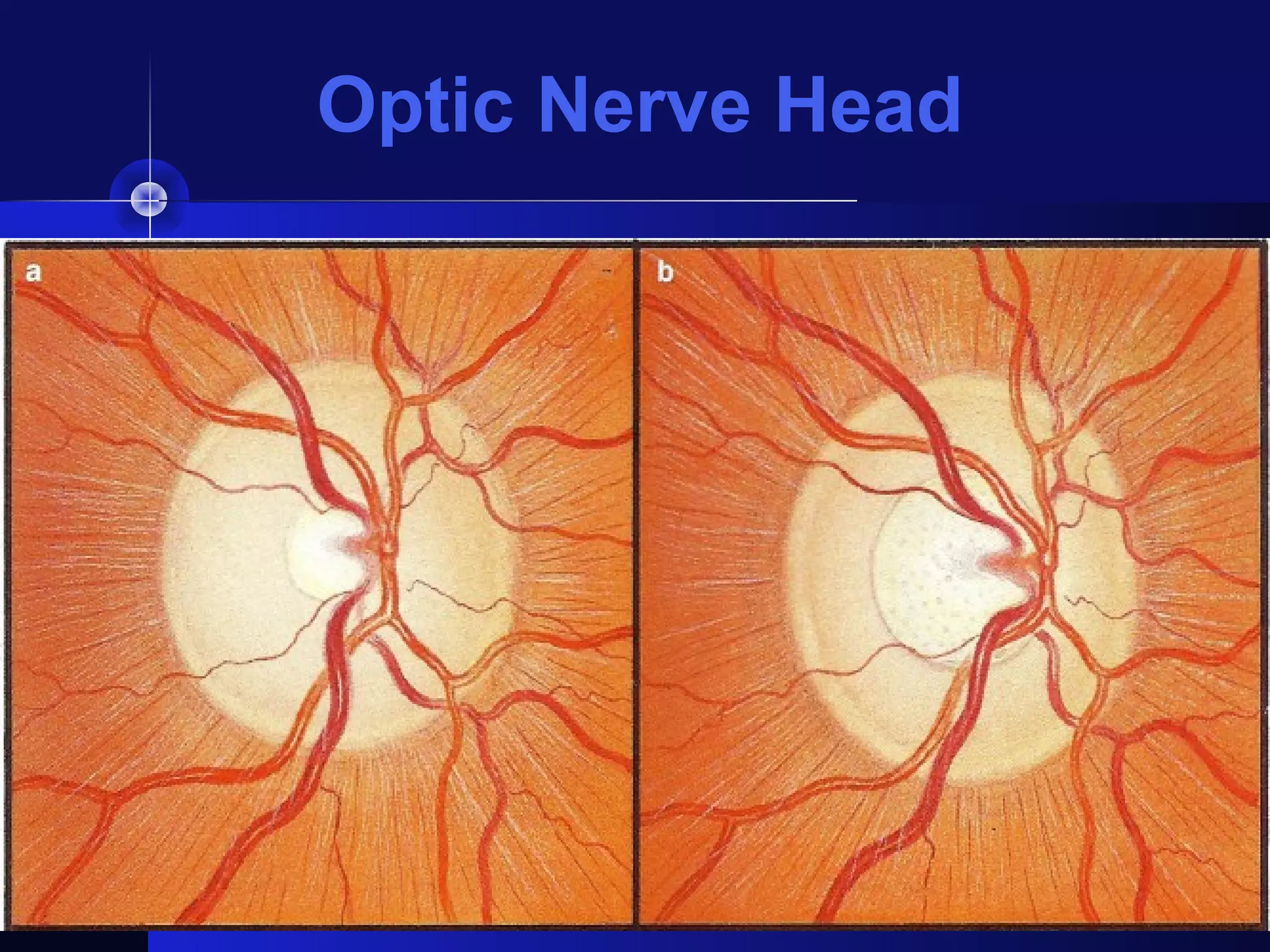
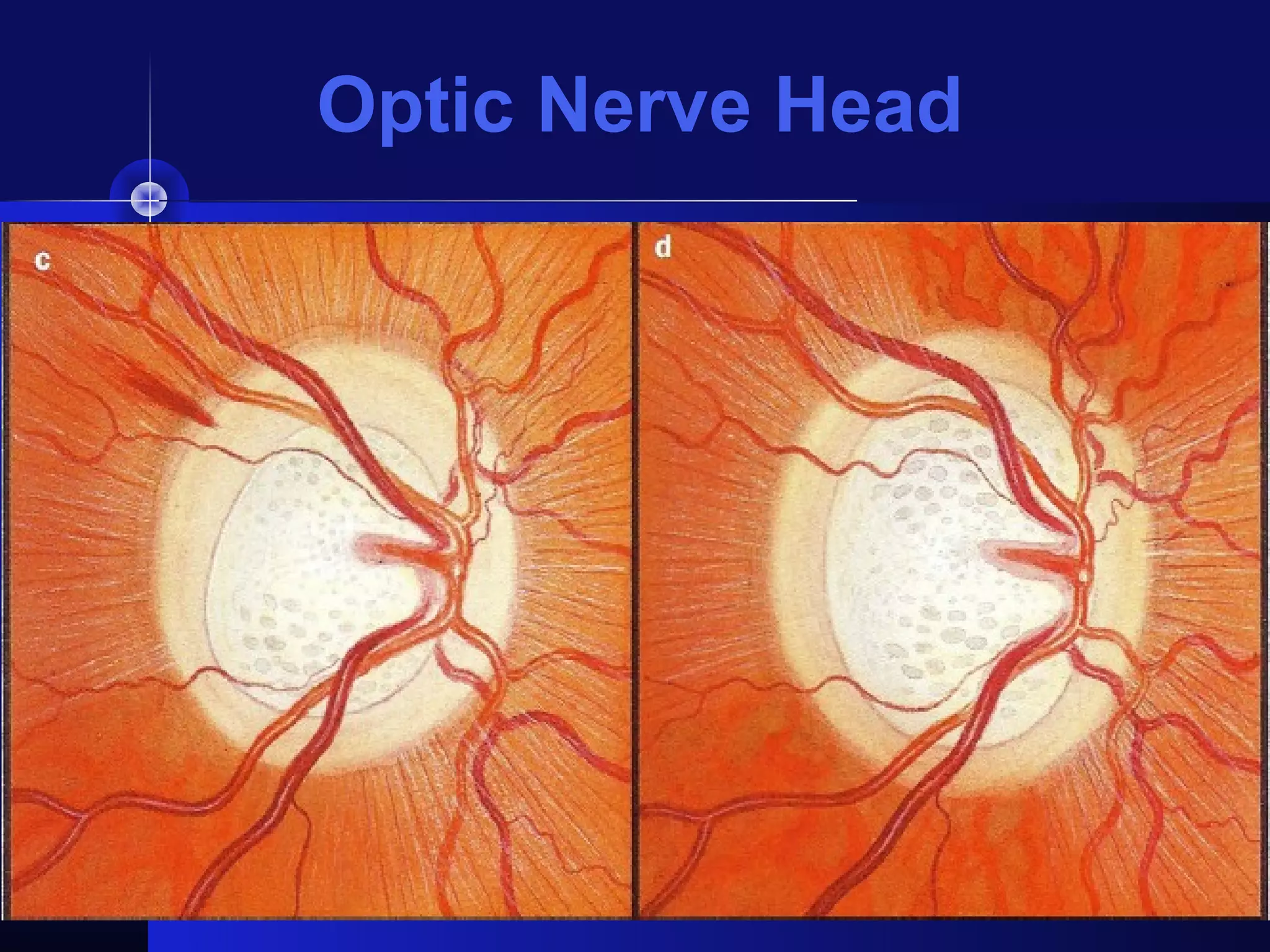
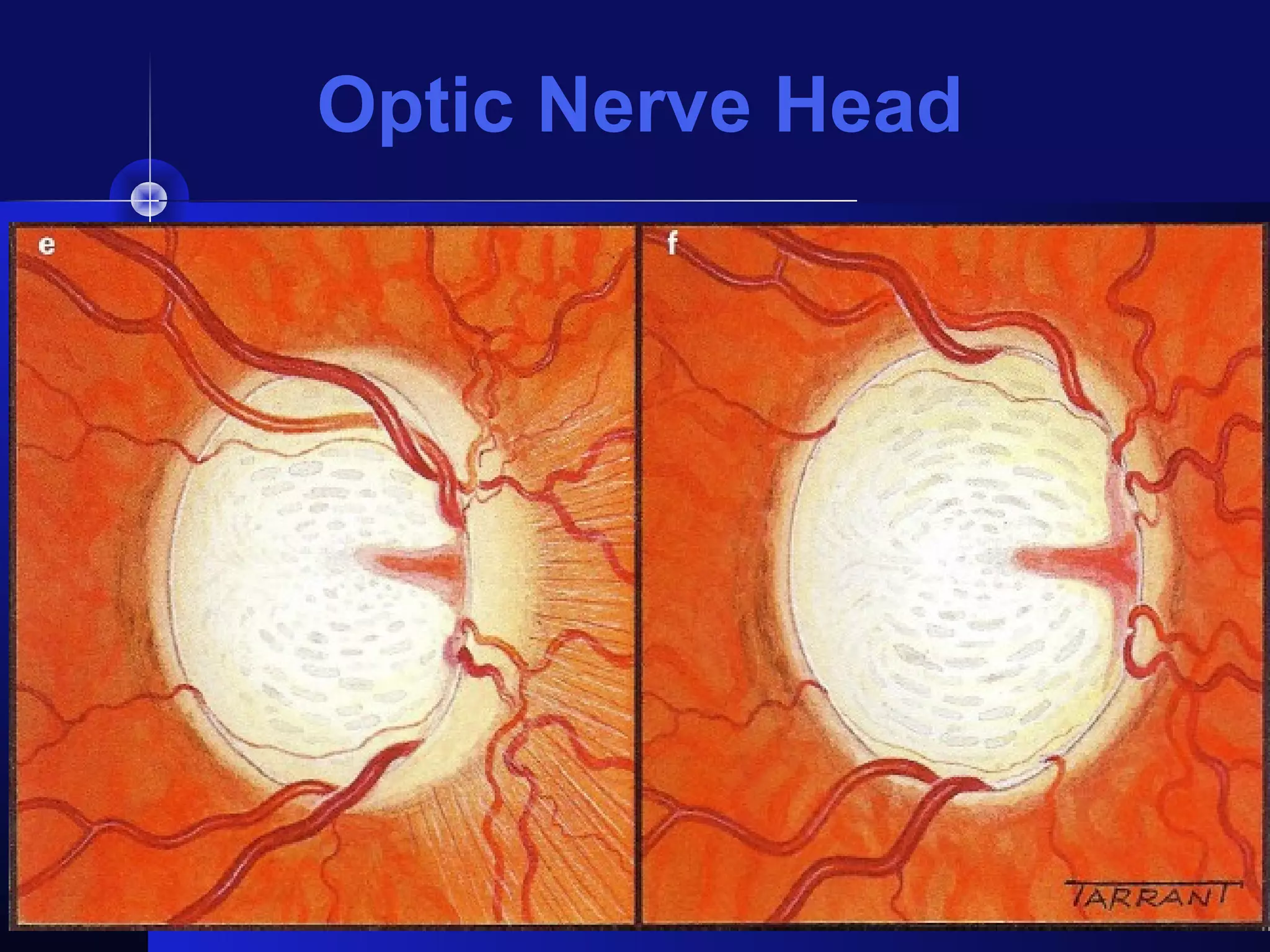
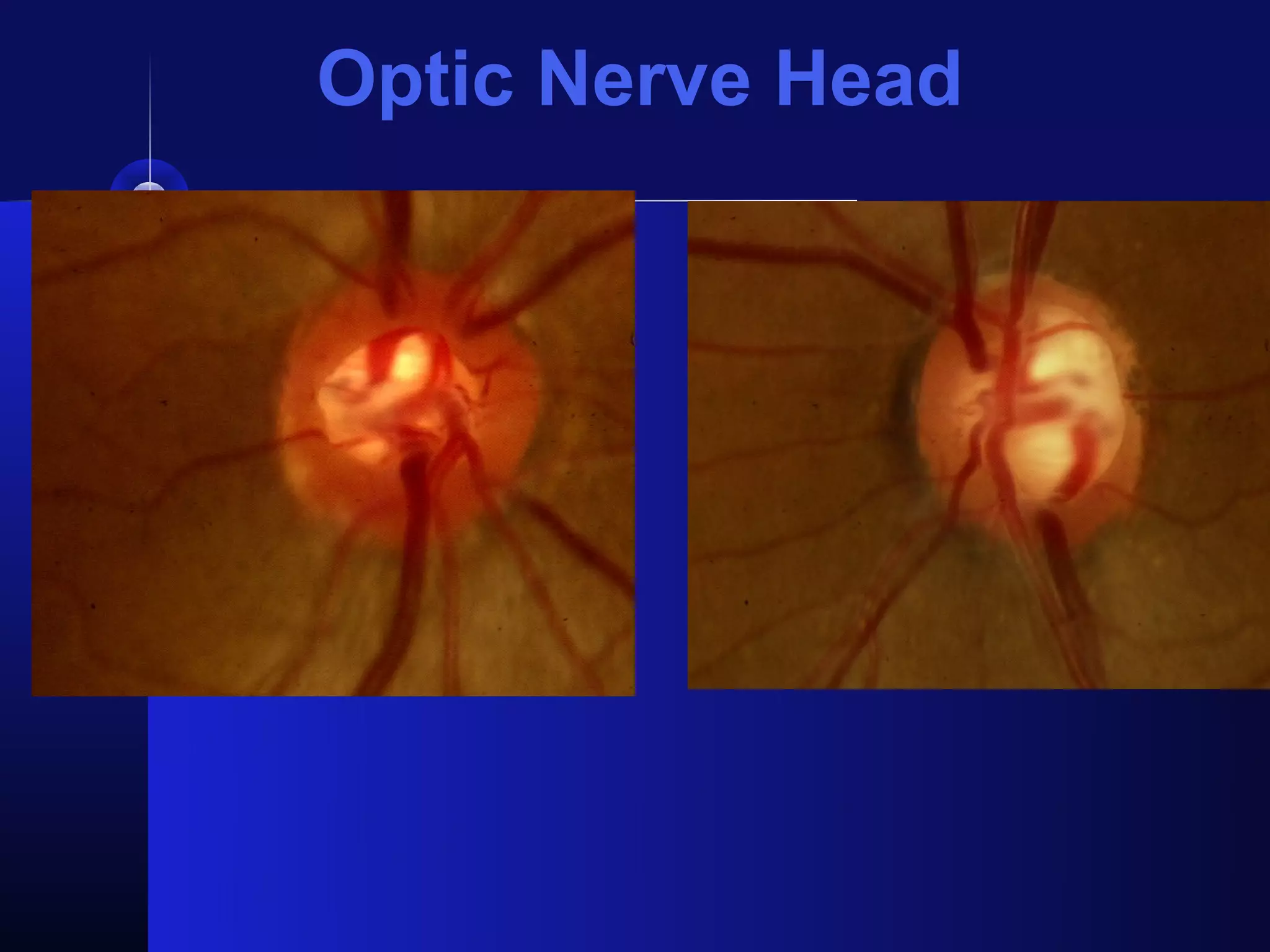
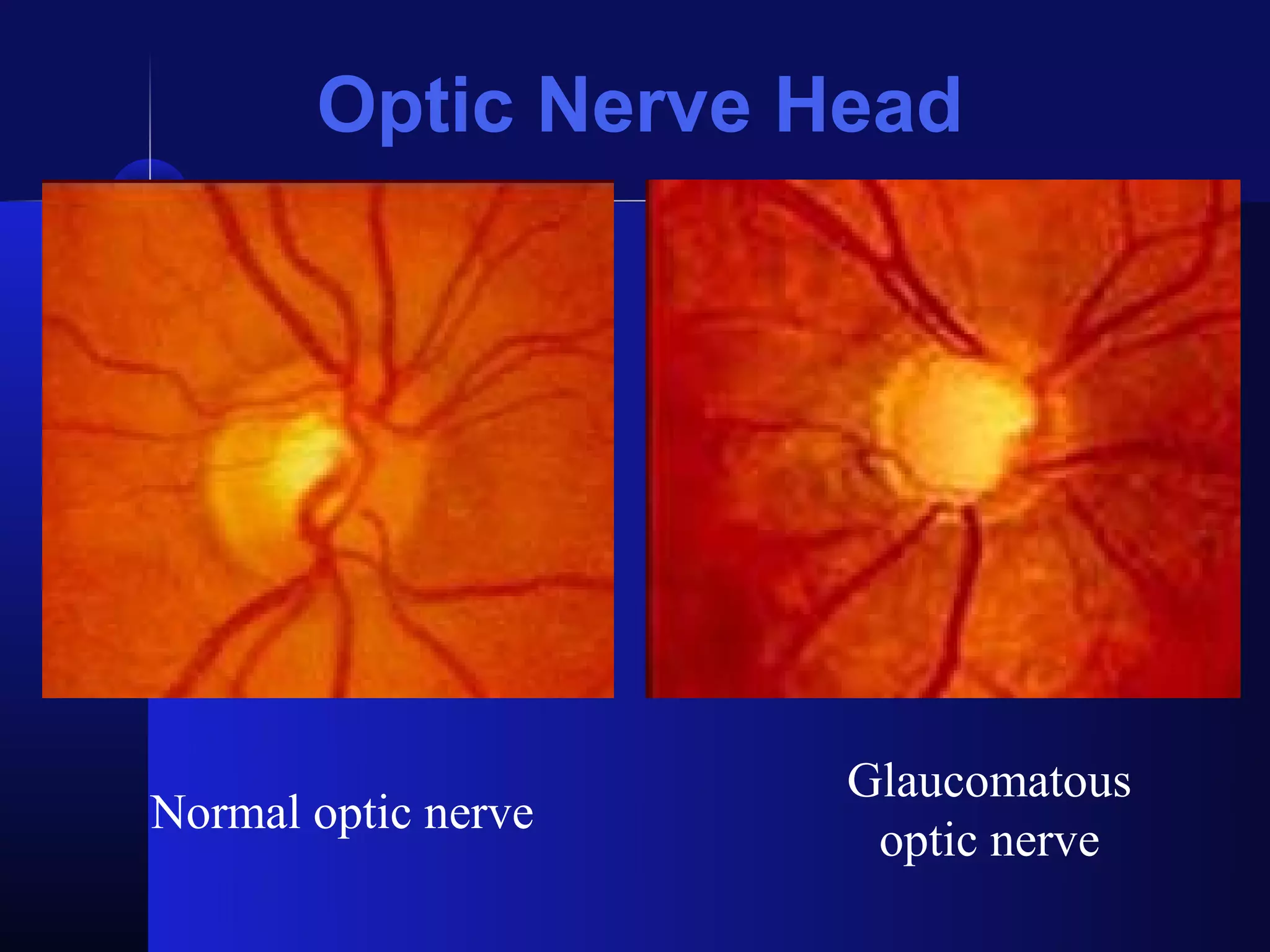
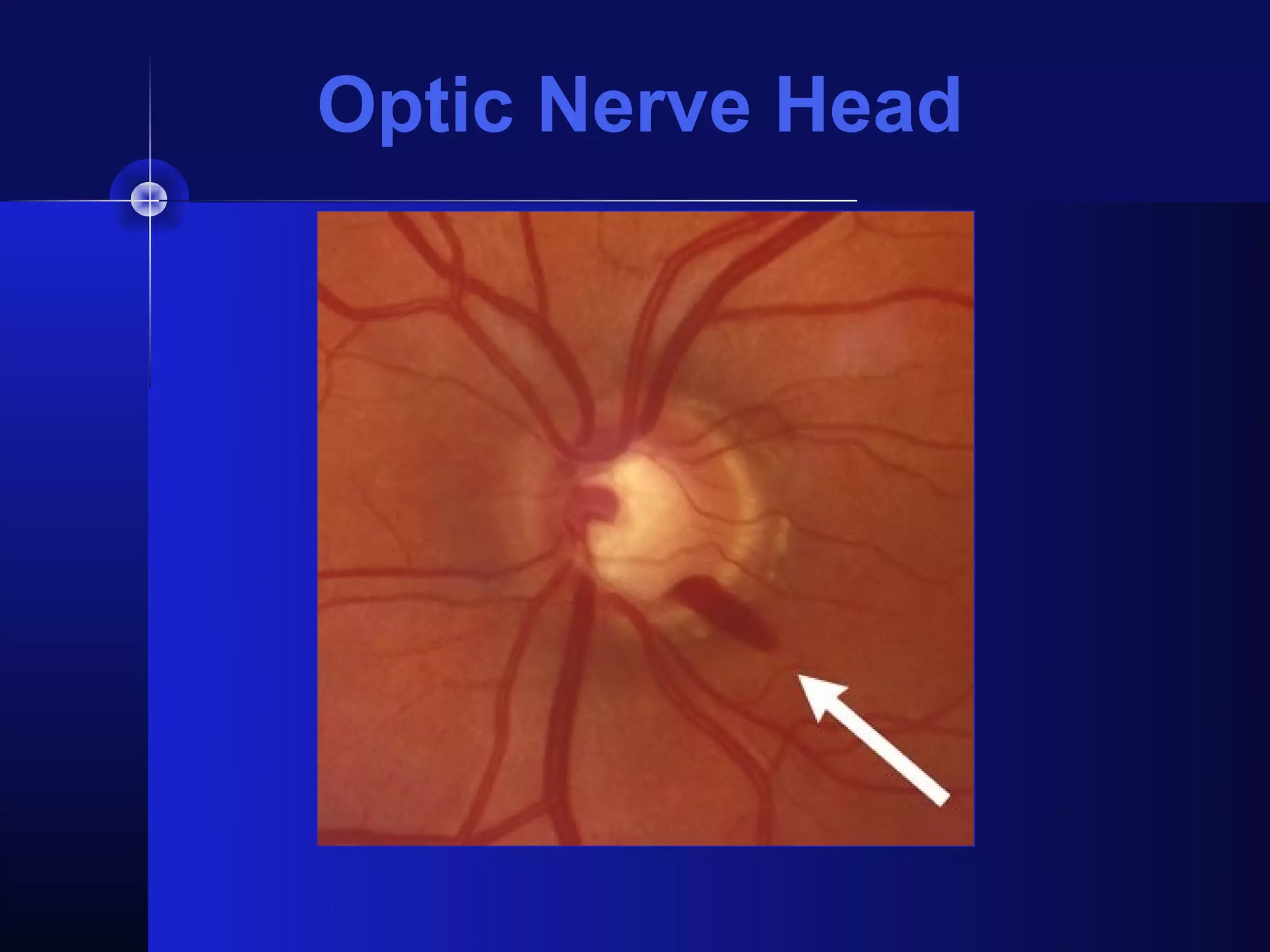
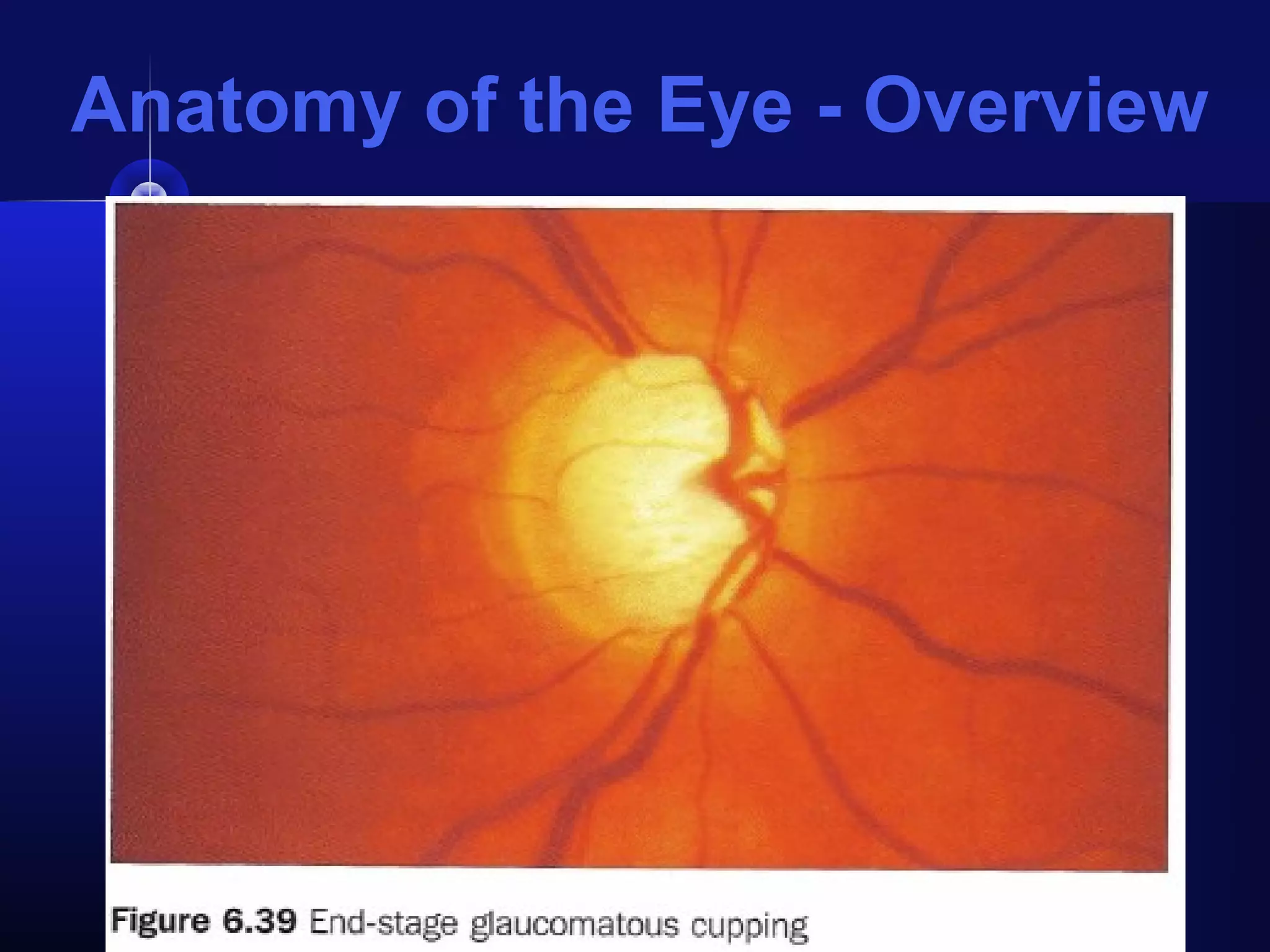
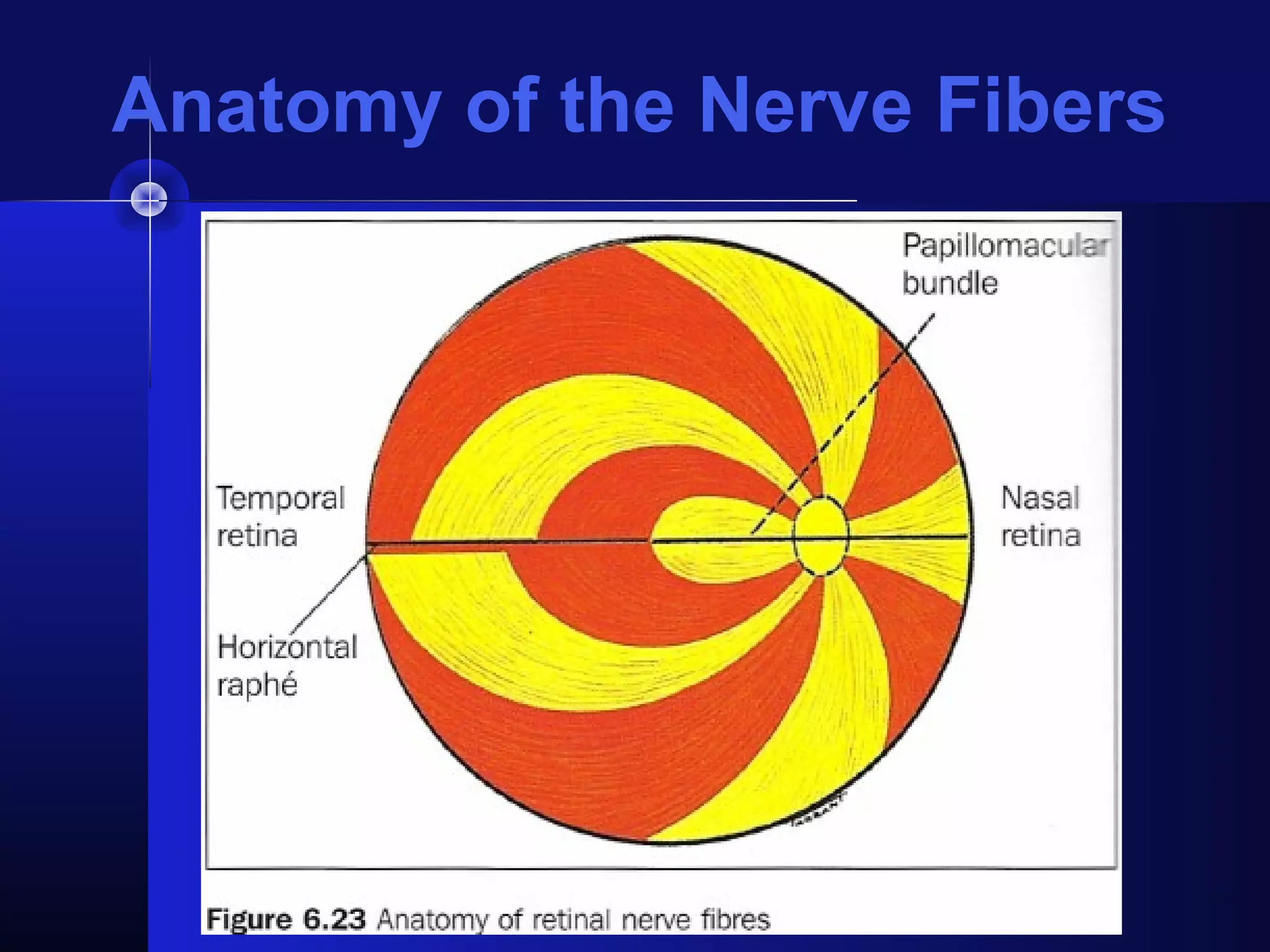
Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness worldwide. It involves damage to the optic nerve due to increased intraocular pressure. While pressure within the eye normally ranges from 11-21 mmHg, pressures above 21 are considered high risk for glaucoma. Damage occurs when pressure is not adequately relieved by drainage from the eye. Early detection through screening and treatment can prevent vision loss, but many patients are asymptomatic in early stages when peripheral vision is lost.