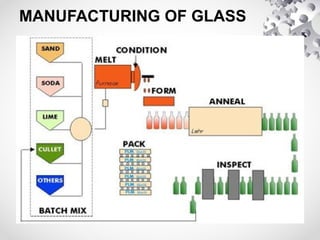
Glass is manufactured through a two-step process of batch mixing and melting ingredients at high temperatures, then shaped for various applications. The document discusses types of glass like float glass, which is made through a float process on molten tin; rolled glass, which is poured onto rollers; and toughened glass, which undergoes uneven heating to form protective layers. Laminated glass consists of two glass sheets bonded with a plastic film, making it shatterproof for safety. Glass properties and uses are also outlined.