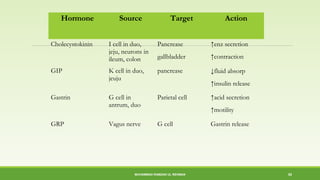
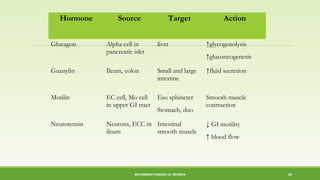
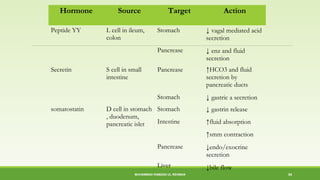
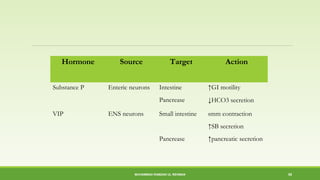
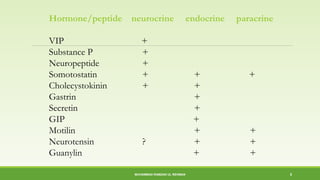
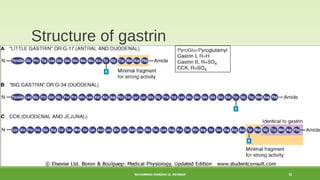
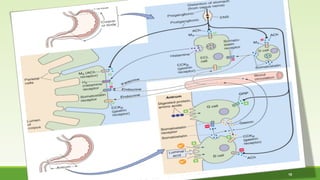
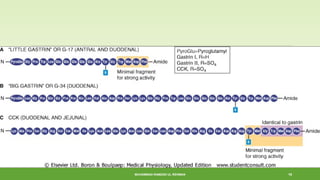
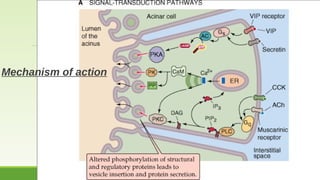
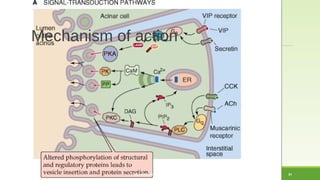
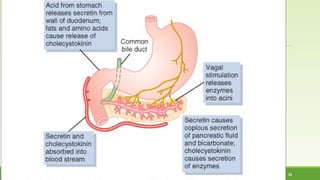
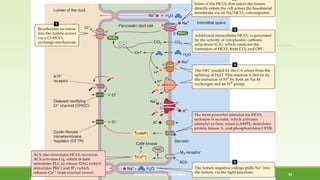
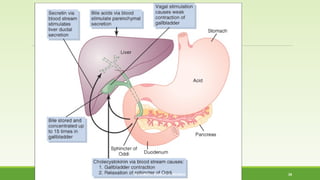
This document discusses gastrointestinal hormones and their regulation of gastrointestinal function. It describes various hormones like gastrin, cholecystokinin, secretin, gastric inhibitory peptide, and somatostatin. It explains where these hormones are produced, their targets, and main actions. Different hormones regulate processes like gastric acid secretion, pancreatic enzyme secretion, gallbladder contraction, and gastrointestinal motility. The document also discusses the regulation of hormone secretion and different pathways of action like endocrine, paracrine, autocrine, neurocrine, and juxtacrine signaling.






























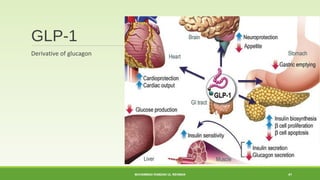
![Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1)
30 amino-acid polypeptide
Incretin hormone : intestinal hormone secreted in response to nutrient ingestion which
potentiate glucose-induced insulin release
Produced by L cell in ileum and colon, pancreatic alpha cell, neurons in hypothalamus, pituitary
gland
2 bioactive forms : GLP-1[7-36] amide , GLP-1[7-37] both forms are equipotent, same t1/2
MUHAMMAD RAMZAN UL REHMAN 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/min-metabolism-140901135656-phpapp02/85/GIT-Hormones-40-320.jpg)