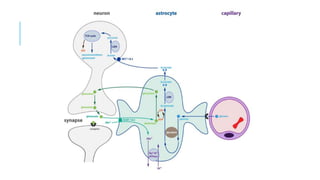
The brain has an extremely high metabolic demand, utilizing 20% of total oxygen and glucose consumption despite making up only 2% of body weight. The majority of this energy is used to maintain membrane potentials through ion transport mechanisms like the sodium-potassium pump. The brain relies almost exclusively on glucose as an energy source, consuming around 120 grams per day. While fatty acids cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, the brain can derive up to 50% of its energy from ketone bodies during prolonged starvation after three weeks of adaptation. Neurons primarily use lactate and pyruvate produced by astrocytes as an energy source rather than glucose. Astrocytes also play a key role in recycling the neurotransmitter glutamate and producing